Use el símbolo del sistema como un profesional: todo sobre el símbolo del sistema
Publicado: 2019-05-21Con el lanzamiento de Windows 10, Microsoft ha eliminado lentamente la línea de comandos de la interfaz de Windows. La razón detrás de esto fue que la línea de comandos era una herramienta anticuada e innecesaria de una era de entrada basada en texto. Sin embargo, muchos comandos siguen siendo útiles y Windows 10 incluso agregó nuevas funciones al mundo de la línea de comandos. Ahora el símbolo del sistema se rediseñó para PowerShell, una aplicación que se puede usar igual que el símbolo del sistema. Es una aplicación colorida que reemplazará el símbolo del sistema, aunque todavía puede usar el símbolo del sistema a partir de ahora. Estos trucos del símbolo del sistema son realmente útiles para los administradores de computadoras y les dan acceso para realizar varias tareas de manera profesional.
Cómo abrir el símbolo del sistema
Presione Win + R -> escriba 'cmd' -> presione 'Enter'
En la barra de búsqueda, escriba 'cmd' y presione 'Enter'.
Si desea abrir el símbolo del sistema como administrador, en la barra de búsqueda, escriba 'cmd' y tan pronto como muestre 'Aplicación de comando', haga clic derecho sobre él y haga clic en 'Ejecutar como administrador'.
Lea también: Todo sobre los atajos de teclado de Windows 10
Cómo encontrar todos los comandos en el símbolo del sistema
Para encontrar comandos relevantes y su sintaxis en el símbolo del sistema, podemos escribir 'cmd /?' o escriba un comando seguido de '/?' por ejemplo 'ipconfig /?' abre lista de opciones y sintaxis con sus acciones. Este intérprete de comandos nos resulta útil para aprender nuevos comandos en el símbolo del sistema.
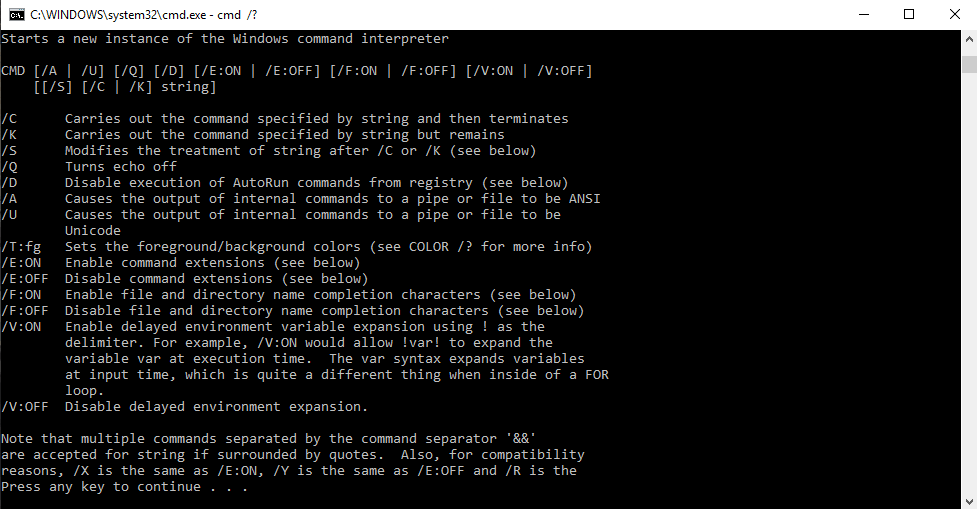
Usando la sintaxis
cmd [/c|/k] [/s] [/q] [/d] [/a|/u] [/t:{<B><F>|<F>}] [/e:{on|off}] [/f:{on|off}] [/v:{on|off}] [<String>]
Parámetros
| Parámetro | Descripción |
| /C | Ejecuta el comando especificado por String y luego se detiene. |
| /k | Ejecuta el comando especificado por String y continúa. |
| /s | Modifica el tratamiento de String después de /c o /k. |
| /q | Apaga el eco. |
| /D | Deshabilita la ejecución de comandos AutoRun. |
| /a | Da formato a la salida del comando interno a una tubería o un archivo como el Instituto Nacional Estadounidense de Estándares (ANSI). |
| /u | Formatea la salida del comando interno a una canalización o un archivo como Unicode. |
| /t:{<B><F>|<F>} | Establece los colores de fondo (B) y primer plano (F). |
| /Eón | Habilita las extensiones de comando. |
| /e:apagado | Deshabilita las extensiones de comandos. |
| /f:en | Habilita la finalización de nombres de archivos y directorios. |
| /f:apagado | Inhabilita la finalización de nombres de archivos y directorios. |
| /v:en | Habilita la expansión variable de entorno retrasada. |
| /v:apagado | Deshabilita la expansión variable de entorno retrasada. |
| <Cadena> | Especifica el comando que desea ejecutar. |
| /? | Muestra ayuda en el símbolo del sistema. |
La siguiente tabla enumera los dígitos hexadecimales válidos que puede usar como valores para <B> y <F>
| Valor | Color |
| 0 | Negro |
| 1 | Azul |
| 2 | Verde |
| 3 | Agua |
| 4 | rojo |
| 5 | Púrpura |
| 6 | Amarillo |
| 7 | blanco |
| 8 | gris |
| 9 | Azul claro |
| a | Verde claro |
| B | Agua clara |
| C | Luz roja |
| D | Púrpura claro |
| mi | Amarillo claro |
| F | Blanco brillante |
Aquí hay una lista completa de los comandos del símbolo del sistema. También puede descargar todos los comandos con su sintaxis desde el enlace al final de este artículo.
| Mando | Descripción |
| Adjuntar | Los programas pueden usar el comando agregar para abrir archivos en otro directorio como si estuvieran ubicados en el directorio actual. El comando agregar está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando agregar no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| arp | El comando arp se usa para mostrar o cambiar entradas en el caché ARP. El comando arp está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. |
| asociado | El comando assoc se usa para mostrar o cambiar el tipo de archivo asociado con una extensión de archivo en particular. El comando assoc está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| En | El comando at se usa para programar comandos y otros programas para que se ejecuten en una fecha y hora específicas. El comando at está disponible en Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. A partir de Windows 8, la programación de tareas de la línea de comandos debe completarse con el comando schtasks. |
| Atmadm | El comando atmadm se usa para mostrar información relacionada con las conexiones del modo de transferencia asíncrono (ATM) en el sistema. El comando atmadm está disponible en Windows XP. La compatibilidad con ATM se eliminó a partir de Windows Vista, lo que hizo innecesario el comando atmadm. |
| atributo | El comando attrib se usa para cambiar los atributos de un solo archivo o directorio. El comando attrib está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Auditpol | El comando auditpol se usa para mostrar o cambiar políticas de auditoría. El comando auditpol está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| Bcdboot | El comando bcdboot se usa para copiar archivos de arranque en la partición del sistema y para crear un nuevo almacén BCD del sistema. El comando bcdboot está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Bcdedit | El comando bcdedit se utiliza para ver o realizar cambios en los datos de configuración de arranque. El comando bcdedit está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. El comando bcdedit reemplazó al comando bootcfg a partir de Windows Vista. |
| Bdehdcfg | El comando bdehdcfg se usa para preparar un disco duro para el Cifrado de unidad BitLocker. El comando bdehdcfg está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Administrador de Bits | El comando bitsadmin se usa para crear, administrar y monitorear trabajos de carga y descarga. El comando bitsadmin está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. Si bien el comando bitsadmin está disponible tanto en Windows 8 como en Windows 7, se está eliminando gradualmente. En su lugar, se deben usar los cmdlets de BITS PowerShell. |
| Bootcfg | El comando bootcfg se usa para crear, modificar o ver el contenido del archivo boot.ini, un archivo oculto que se usa para identificar en qué carpeta, en qué partición y en qué disco duro se encuentra Windows. El comando bootcfg está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando bootcfg fue reemplazado por el comando bcdedit a partir de Windows Vista. Bootcfg todavía está disponible en Windows 8, 7 y Vista, pero no tiene ningún valor real ya que boot.ini no se usa en estos sistemas operativos. |
| Bootsect | El comando bootsect se usa para configurar el código de arranque maestro a uno compatible con BOOTMGR (Vista y posterior) o NTLDR (XP y anterior). El comando bootsect está disponible en Windows 8. El comando bootsect también está disponible en Windows 7 y Windows Vista, pero solo desde el Símbolo del sistema disponible en Opciones de recuperación del sistema. |
| Romper | El comando break establece o borra la comprobación extendida de CTRL + C en los sistemas DOS. El comando de interrupción está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. El comando de interrupción está disponible en Windows XP y versiones posteriores de Windows para brindar compatibilidad con los archivos de MS-DOS, pero no tiene ningún efecto en Windows. |
| Cacls | El comando cacls se usa para mostrar o cambiar las listas de control de acceso de archivos. El comando cacls está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando cacls se está reemplazando gradualmente por el comando icacls, que debe usarse en todas las versiones de Windows posteriores a Windows XP. |
| Llamar | El comando de llamada se utiliza para ejecutar un script o programa por lotes desde otro script o programa por lotes. El comando de llamada está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. El comando de llamada no tiene ningún efecto fuera de un script o un archivo por lotes. En otras palabras, ejecutar el comando de llamada en el símbolo del sistema o en el indicador de MS-DOS no hará nada. |
| CD | El comando cd es la versión abreviada del comando chdir. El comando cd está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Certreq | El comando certreq se utiliza para realizar varias funciones de certificado de entidad emisora de certificados (CA). El comando certreq está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| Certutil | El comando certutil se usa para volcar y mostrar información de configuración de la autoridad de certificación (CA) además de otras funciones de la CA. El comando certutil está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| Cambio | El comando de cambio cambia varias configuraciones del servidor de terminal, como modos de instalación, asignaciones de puertos COM e inicios de sesión. El comando de cambio está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| chcp | El comando chcp muestra o configura el número de página de códigos activo. El comando chcp está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Chdir | El comando chdir se usa para mostrar la letra de la unidad y la carpeta en la que se encuentra actualmente. Chdir también se puede usar para cambiar la unidad y/o el directorio en el que desea trabajar. El comando chdir está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, como así como en MS-DOS. |
| Checknetaislamiento | El comando checknetisolation se usa para probar aplicaciones que requieren capacidades de red. El comando checknetisolation está disponible en Windows 8. |
| Chglogon | El comando chglogon habilita, deshabilita o agota los inicios de sesión del servidor de terminales. El comando chglogon está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. Ejecutar el comando chglogon es lo mismo que ejecutar el cambio de inicio de sesión. |
| Cambiar puerto | El comando chgport se puede usar para mostrar o cambiar las asignaciones de puertos COM para compatibilidad con DOS. El comando chgport está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. Ejecutar el comando chgport es lo mismo que ejecutar cambiar puerto. |
| Chgusr | El comando chgusr se usa para cambiar el modo de instalación del servidor de terminales. El comando chgusr está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. Ejecutar el comando chgusr es lo mismo que ejecutar el cambio de usuario. |
| Chkdsk | El comando chkdsk, a menudo denominado verificar disco, se usa para identificar y corregir ciertos errores del disco duro. El comando chkdsk está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| chkntfs | El comando chkntfs se usa para configurar o mostrar la verificación de la unidad de disco durante el proceso de arranque de Windows. El comando chkntfs está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Elección | El comando de elección se usa dentro de un script o programa por lotes para proporcionar una lista de opciones y devolver el valor de esa elección al programa. El comando de elección está disponible en MS-DOS y todas las versiones de Windows excepto Windows XP. Use el comando set con el modificador /p en lugar del comando de elección en archivos por lotes y secuencias de comandos que planea usar en Windows XP. |
| Cifrar | El comando de cifrado muestra o cambia el estado de cifrado de archivos y carpetas en particiones NTFS. El comando de cifrado está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Acortar | El comando de clip se usa para redirigir la salida de cualquier comando al portapapeles en Windows. El comando de clip está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| cls | El comando cls borra la pantalla de todos los comandos ingresados previamente y otro texto. El comando cls está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Comando | El comando cmd inicia una nueva instancia del intérprete de comandos cmd.exe. El comando cmd está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| tecla de comando | El comando cmdkey se utiliza para mostrar, crear y eliminar nombres de usuario y contraseñas almacenados. El comando cmdkey está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| cmstp | El comando cmstp instala o desinstala un perfil de servicio de Connection Manager. El comando cmstp está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Color | El comando de color se usa para cambiar los colores del texto y el fondo dentro de la ventana del símbolo del sistema. El comando de color está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Mando | El comando 'comando' inicia una nueva instancia del intérprete de comandos command.com. El comando 'comando' está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando 'comando' no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| compensación | El comando comp se usa para comparar el contenido de dos archivos o conjuntos de archivos. El comando comp está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Compacto | El comando compacto se usa para mostrar o cambiar el estado de compresión de archivos y directorios en particiones NTFS. El comando compacto está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Convertir | El comando de conversión se utiliza para convertir volúmenes con formato FAT o FAT32 al formato NTFS. El comando convertir está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Dupdo | El comando de copia hace simplemente eso: copia uno o más archivos de una ubicación a otra. El comando copiar está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. El comando xcopy se considera una versión más "poderosa" del comando de copia. |
| Cscript | El comando cscript se usa para ejecutar scripts a través de Microsoft Script Host. El comando cscript está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. El comando cscript se usa más comúnmente para administrar impresoras desde la línea de comandos usando scripts como prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmgr.vbs y otros. |
| ciudad | El comando ctty se utiliza para cambiar los dispositivos de entrada y salida predeterminados del sistema. El comando ctty está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. Las funciones proporcionadas por el comando ctty ya no eran necesarias a partir de Windows XP porque el intérprete de command.com (MS-DOS) ya no es el intérprete de línea de comandos predeterminado. |
| Fecha | El comando de fecha se utiliza para mostrar o cambiar la fecha actual. El comando de fecha está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| espaciodbl | El comando dblspace se usa para crear o configurar unidades comprimidas DoubleSpace. El comando dblspace está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. DriveSpace, ejecutado con el comando drvspace, es una versión actualizada de DoubleSpace. Windows maneja de forma nativa la compresión a partir de Windows XP. |
| Depurar | El comando debug inicia Debug, una aplicación de línea de comandos utilizada para probar y editar programas. El comando de depuración está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando de depuración no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| Desfragmentar | El comando defrag se utiliza para desfragmentar una unidad que especifique. El comando defrag es la versión de línea de comandos del Desfragmentador de disco de Microsoft. El comando de desfragmentación está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Supr | El comando del se usa para eliminar uno o más archivos. El comando del está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. El comando del es el mismo que el comando erase. |
| Deltree | El comando deltree se usa para eliminar un directorio y todos los archivos y subdirectorios dentro de él. El comando deltree está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. A partir de Windows XP, una carpeta y sus archivos y subcarpetas se pueden eliminar mediante la función /s del comando rmdir. Deltree ya no era necesario con esta nueva capacidad de rmdir, por lo que se eliminó el comando. |
| Diantz | El comando diantz se utiliza para comprimir sin pérdidas uno o más archivos. El comando diantz a veces se llama ebanista. El comando diantz está disponible en Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando diantz es el mismo que el comando makecab. |
| Dirección | El comando dir se usa para mostrar una lista de archivos y carpetas contenidos dentro de la carpeta en la que está trabajando actualmente. El comando dir también muestra otra información importante como el número de serie del disco duro, la cantidad total de archivos enumerados, su tamaño combinado, la cantidad total de espacio libre que queda en el disco, y más. El comando dir está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| discocomp | El comando diskcomp se usa para comparar el contenido de dos disquetes. El comando diskcomp está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Copia de disco | El comando diskcopy se usa para copiar todo el contenido de un disquete a otro. El comando diskcopy está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Parte de disco | El comando diskpart se usa para crear, administrar y eliminar particiones del disco duro. El comando diskpart está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando diskpart reemplazó al comando fdisk a partir de Windows XP. |
| Dispersión | El comando diskperf se usa para administrar los contadores de rendimiento del disco de forma remota. El comando diskperf está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Desarmado | El comando diskraid inicia la herramienta DiskRAID que se utiliza para administrar y configurar matrices RAID. El comando diskraid está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| desmontar | El comando dism inicia la herramienta de administración y mantenimiento de imágenes de implementación (DISM). La herramienta DISM se usa para administrar funciones en imágenes de Windows. El comando dism está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Dispdiag | El comando dispdiag se utiliza para generar un registro de información sobre el sistema de visualización. El comando dispdiag está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| unirse | El comando djoin se usa para crear una nueva cuenta de computadora en un dominio. El comando djoin está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| doskey | El comando doskey se usa para editar líneas de comando, crear macros y recuperar comandos ingresados previamente. El comando doskey está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Dos concha | El comando dosshell inicia DOS Shell, una herramienta gráfica de administración de archivos para MS-DOS. El comando dosshell está disponible en Windows 95 (en modo MS-DOS) y también en MS-DOS versión 6.0 y versiones posteriores de MS-DOS que se actualizaron de versiones anteriores que contenían el comando dosshell. Un administrador de archivos gráficos, el Explorador de Windows, se convirtió en una parte integrada del sistema operativo a partir de Windows 95. |
| Dosx | El comando dosx se usa para iniciar la interfaz de modo protegido de DOS (DPMI), un modo especial diseñado para brindar a las aplicaciones de MS-DOS acceso a más de los 640 KB normalmente permitidos. El comando dosx está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando dosx no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. El comando dosx y DPMI solo están disponibles en Windows para admitir programas antiguos de MS-DOS. |
| Driverquery | El comando driverquery se usa para mostrar una lista de todos los controladores instalados. El comando driverquery está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Drvespacio | El comando drvspace se usa para crear o configurar unidades comprimidas de DriveSpace. El comando drvspace está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. DriveSpace es una versión actualizada de DoubleSpace, que se ejecuta con el comando dblspace. Windows maneja de forma nativa la compresión a partir de Windows XP. |
| Eco | El comando echo se usa para mostrar mensajes, más comúnmente desde scripts o archivos por lotes. El comando echo también se puede utilizar para activar o desactivar la función de eco. El comando echo está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Editar | El comando de edición inicia la herramienta Editor de MS-DOS que se utiliza para crear y modificar archivos de texto. El comando de edición está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando de edición no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| Edlin | El comando edlin inicia la herramienta Edlin que se utiliza para crear y modificar archivos de texto desde la línea de comandos. El comando edlin está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits, pero no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. En MS-DOS, el comando edlin solo está disponible hasta MS-DOS 5.0, por lo que, a menos que su versión posterior de MS-DOS haya sido actualizada de 5.0 o anterior, no verá el comando edlin. |
| Emm386 | El comando emm386 se usa para dar acceso a MS-DOS a más de 640 KB de memoria. El comando emm386 está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. El mismo Windows tiene acceso a la memoria extendida y expandida a partir de Windows 95. |
| Endlocal | El comando endlocal se usa para finalizar la localización de cambios en el entorno dentro de un archivo por lotes o script. El comando endlocal está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Borrar | El comando de borrado se utiliza para eliminar uno o más archivos. El comando de borrado está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. El comando erase es el mismo que el comando del. |
| Esentutl | El comando esentutl se usa para administrar las bases de datos del motor de almacenamiento extensible. El comando esentutl está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Crear evento | El comando eventcreate se usa para crear un evento personalizado en un registro de eventos. El comando eventcreate está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Activadores de eventos | El comando eventtriggers se utiliza para configurar y mostrar activadores de eventos. El comando eventtriggers está disponible en Windows XP. A partir de Windows Vista, los desencadenadores de eventos se crean mediante la función Adjuntar tarea a este evento en el Visor de eventos, lo que hace innecesario el comando eventtriggers. |
| exe2bin | El comando exe2bin se utiliza para convertir un archivo del tipo de archivo EXE (archivo ejecutable) en un archivo binario. El comando exe2bin está disponible en versiones de 32 bits de Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando exe2bin no está disponible en ninguna versión de Windows de 64 bits. |
| Salida | El comando de salida se usa para finalizar la sesión cmd.exe (Windows) o command.com (MS-DOS) en la que está trabajando actualmente. El comando de salida está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. . |
| Expandir | El comando expandir se usa para extraer los archivos y carpetas contenidos en los archivos de Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). El comando expandir está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows. El comando expandir no está disponible en la versión de 64 bits de Windows XP. |
| Extrac32 | El comando extract32 se usa para extraer los archivos y carpetas contenidos en los archivos de Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). El comando extract32 está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. El comando extract32 es en realidad un programa de extracción CAB para uso de Internet Explorer, pero se puede usar para extraer cualquier archivo de Microsoft Cabinet. Use el comando expandir en lugar del comando extract32 si es posible. |
| Extraer | El comando de extracción se utiliza para extraer los archivos y carpetas contenidos en los archivos de Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). El comando de extracción está disponible en Windows 98 y 95. El comando de extracción fue reemplazado por el comando de expansión a partir de Windows XP. |
| ayuda rapida | El comando fasthelp proporciona información más detallada sobre cualquiera de los otros comandos de MS-DOS. El comando fasthelp solo está disponible en MS-DOS. El comando de ayuda reemplazó al comando fasthelp a partir de Windows 95. |
| Apertura rápida | El comando fastopen se usa para agregar la ubicación del disco duro de un programa a una lista especial almacenada en la memoria, lo que puede mejorar el tiempo de ejecución del programa al eliminar la necesidad de que MS-DOS ubique la aplicación en el disco. El comando fastopen está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando fastopen no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. Fastopen solo está disponible en Windows 8, 7, Vista y XP para admitir archivos de MS-DOS más antiguos. |
| FC | El comando fc se usa para comparar dos archivos individuales o conjuntos y luego mostrar las diferencias entre ellos. El comando fc está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| fdisco | El comando fdisk se usa para crear, administrar y eliminar particiones del disco duro. El comando fdisk está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. El comando fdisk fue reemplazado por el comando diskpart a partir de Windows XP. La administración de particiones también está disponible desde Administración de discos en Windows 8, 7, Vista y XP. |
| Encontrar | El comando de búsqueda se utiliza para buscar una cadena de texto específica en uno o más archivos. El comando de búsqueda está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Buscar | El comando findstr se usa para encontrar patrones de cadenas de texto en uno o más archivos. El comando findstr está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Dedo | El comando finger se usa para devolver información sobre uno o más usuarios en una computadora remota que ejecuta el servicio Finger. El comando dedo está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Fltmc | El comando fltmc se usa para cargar, descargar, enumerar y administrar los controladores de filtro. El comando fltmc está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Fondue | El comando fondue, abreviatura de Features on Demand User Experience Tool, se usa para instalar cualquiera de las varias funciones opcionales de Windows desde la línea de comandos. El comando fondue está disponible en Windows 8. Las características opcionales de Windows también se pueden instalar desde el subprograma Programas y características en el Panel de control. |
| Para | El comando for se usa para ejecutar un comando específico para cada archivo en un conjunto de archivos. El comando for se usa con mayor frecuencia dentro de un archivo por lotes o script. El comando for está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Forzados | El comando forcedos se usa para iniciar el programa especificado en el subsistema MS-DOS. El comando forcedos solo está disponible en versiones de 32 bits de Windows XP. El comando forcedos solo se usa para programas MS-DOS que Windows XP no reconoce como tales. |
| Para archivos | El comando forfiles selecciona uno o más archivos para ejecutar un comando específico. El comando forfiles se usa con mayor frecuencia dentro de un archivo por lotes o script. El comando forfiles está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| Formato | El comando de formato se utiliza para formatear una unidad en el sistema de archivos que especifique. El comando de formato está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. El formateo de unidades también está disponible desde Administración de discos en Windows 8, 7, Vista y XP. |
| fútil | El comando fsutil se usa para realizar varias tareas del sistema de archivos FAT y NTFS, como administrar puntos de análisis y archivos dispersos, desmontar un volumen y extender un volumen. El comando fsutil está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| ftp | El comando ftp se puede usar para transferir archivos hacia y desde otra computadora. La computadora remota debe estar operando como un servidor FTP. El comando ftp está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. |
| tipo | El comando ftype se usa para definir un programa predeterminado para abrir un tipo de archivo específico. El comando ftype está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Obtenermac | El comando getmac se usa para mostrar la dirección de control de acceso a medios (MAC) de todos los controladores de red en un sistema. El comando getmac está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Ir | El comando goto se usa en un archivo de script o por lotes para dirigir el proceso del comando a una línea etiquetada en el script. El comando goto está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| resultado | El comando gpresult se usa para mostrar la configuración de la directiva de grupo. El comando gpresult está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| actualización | El comando gpupdate se usa para actualizar la configuración de la directiva de grupo. El comando gpupdate está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Injertable | El comando draftabl se utiliza para habilitar la capacidad de Windows para mostrar un juego de caracteres extendido en modo gráfico. El comando draftabl está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows y en MS-DOS hasta la versión 5.0. El comando draftabl no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| Gráficos | El comando de gráficos se utiliza para cargar un programa que puede imprimir gráficos. El comando de gráficos está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando de gráficos no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| Ayudar | El comando de ayuda proporciona información más detallada sobre cualquiera de los otros comandos del símbolo del sistema o de MS-DOS. El comando de ayuda está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| nombre de host | El comando hostname muestra el nombre del host actual. El comando de nombre de host está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| hwrcomp | El comando hwrcomp se usa para compilar diccionarios personalizados para el reconocimiento de escritura a mano. El comando hwrcomp está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Hwrreg | El comando hwrreg se usa para instalar un diccionario personalizado previamente compilado para el reconocimiento de escritura a mano. El comando hwrreg está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Icacls | El comando icacls se usa para mostrar o cambiar las listas de control de acceso de archivos. El comando icacls está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. El comando icacls es una versión actualizada del comando cacls. |
| Si | El comando if se usa para realizar funciones condicionales en un archivo por lotes. El comando if está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Interconexión | El comando interlnk se usa para conectar dos computadoras a través de una conexión serial o paralela para compartir archivos e impresoras. El comando interlnk solo está disponible en MS-DOS. La capacidad de conectar directamente dos computadoras está a cargo de las funciones de red en todas las versiones de Windows. |
| Intersvr | El comando intersvr se usa para iniciar el servidor Interlnk y para copiar archivos Interlnk de una computadora a otra. El comando intersvr solo está disponible en MS-DOS. La capacidad de conectar directamente dos computadoras está a cargo de las funciones de red en todas las versiones de Windows. |
| ipconfig | El comando ipconfig se usa para mostrar información IP detallada para cada adaptador de red que utiliza TCP/IP. El comando ipconfig también se puede usar para liberar y renovar direcciones IP en sistemas configurados para recibirlas a través de un servidor DHCP. El comando ipconfig está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. |
| rutaipx | El comando ipxroute se usa para mostrar y cambiar información sobre las tablas de enrutamiento IPX. El comando ipxroute está disponible en Windows XP. Microsoft eliminó su cliente NetWare nativo a partir de Windows Vista, y también eliminó el comando ipxroute asociado. |
| Irftp | El comando irftp se utiliza para transmitir archivos a través de un enlace infrarrojo. El comando irftp está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| iscsicli | El comando iscsicli inicia Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, que se usa para administrar iSCSI. El comando iscsicli está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| kb16 | El comando kb16 se usa para admitir archivos de MS-DOS que necesitan configurar un teclado para un idioma específico. El comando kb16 está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando kb16 no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. El comando kb16 reemplazó al comando keyb a partir de Windows XP, pero solo existe para admitir archivos antiguos de MS-DOS. |
| teclado | El comando keyb se usa para configurar un teclado para un idioma específico. El comando keyb está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. Consulte el comando kb16 para obtener un comando equivalente en versiones posteriores de Windows. La configuración del idioma del teclado está a cargo de los subprogramas del Panel de control de Región e idioma u Opciones regionales y de idioma (dependiendo de la versión de Windows) en Windows a partir de Windows XP. |
| lista | El comando klist se usa para enumerar los vales de servicio de Kerberos. El comando klist también se puede usar para purgar los tickets de Kerberos. El comando klist está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Kconfiguración | El comando ksetup se usa para configurar conexiones a un servidor Kerberos. El comando ksetup está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. |
| Ktmutil | El comando ktmutil inicia la utilidad Kernel Transaction Manager. El comando ktmutil está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7 y Windows Vista. |
| Etiqueta | El comando de etiqueta se utiliza para administrar la etiqueta de volumen de un disco. El comando de etiqueta está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| izq. | El comando lh es la versión abreviada del comando loadhigh. El comando lh está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Diagnóstico de licencias | El comando licensediag es una herramienta que se utiliza para generar un registro basado en texto y otros archivos de datos que contienen la activación del producto y otra información de licencias de Windows. El comando licensediag está disponible en Windows 8. |
| Fijar carga | El comando loadfix se usa para cargar el programa especificado en los primeros 64 K de memoria y luego ejecuta el programa. El comando loadfix está disponible en MS-DOS, así como en todas las versiones de Windows de 32 bits. El comando loadfix no está disponible en las versiones de Windows de 64 bits. |
| Carga alta | El comando loadhigh se usa para cargar un programa en la memoria alta y generalmente se usa desde el archivo autoexec.bat. El comando loadhigh está disponible en Windows 98 y 95, así como en MS-DOS. El uso de la memoria se maneja automáticamente a partir de Windows XP. |
| Cerrar con llave | El comando de bloqueo se utiliza para bloquear una unidad, lo que permite el acceso directo al disco para un programa. El comando de bloqueo solo está disponible en Windows 98 y 95. El bloqueo de unidades ya no está disponible a partir de Windows XP. |
| Lodctr | El comando lodctr se usa para actualizar los valores del registro relacionados con los contadores de rendimiento. El comando lodctr está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. |
| maderero | El comando logman se usa para crear y administrar registros de sesión y rendimiento de seguimiento de eventos. El comando logman también admite muchas funciones del Monitor de rendimiento. El comando logman está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Desconectarse | El comando de cierre de sesión se utiliza para terminar una sesión. El comando de cierre de sesión está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. |
| Lpq | El comando lpq muestra el estado de una cola de impresión en una computadora que ejecuta Line Printer Daemon (LPD). El comando lpq está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. El comando lpq no está disponible de forma predeterminada en Windows 8, 7 o Vista, pero se puede habilitar activando las funciones Servicio de impresión LPD y Supervisión de puerto LPR desde Programas y funciones en el Panel de control. |
| lpr | El comando lpr se usa para enviar un archivo a una computadora que ejecuta Line Printer Daemon (LPD). El comando lpr está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows. El comando lpr no está disponible de forma predeterminada en Windows 8, 7 o Vista, pero se puede habilitar activando las funciones Servicio de impresión LPD y Supervisión de puertos LPR desde Programas y funciones en el Panel de control. |
| Makecab | El comando makecab se usa para comprimir sin pérdidas uno o más archivos. El comando makecab a veces se llama Cabinet Maker. El comando makecab está disponible en Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista y Windows XP. El comando makecab es el mismo que el comando diantz, un comando que se eliminó después de Windows 7. |
| Administrar-bde | El comando manage-bde se usa para configurar el Cifrado de unidad BitLocker desde la línea de comandos. El comando manage-bde está disponible en Windows 8 y Windows 7. Existe un script con el nombre de manage-bde.wsf en Windows Vista y se puede usar con el comando cscript para realizar tareas de BitLocker desde la línea de comandos en ese sistema operativo. |
| Maryland | El comando md es la versión abreviada del comando mkdir. El comando md está disponible en todas las versiones de Windows, así como en MS-DOS. |
| Memoria | The mem command shows information about used and free memory areas and programs that are currently loaded into memory in the MS-DOS subsystem. The mem command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The mem command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Memmaker | The memmaker command is used to start MemMaker, a memory optimization tool. The memaker command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is automatically optimized beginning in Windows XP. |
| Mkdir | The mkdir command is used to create a new folder. The mkdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mklink | The mklink command is used to create a symbolic link. The mklink command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Modo | The mode command is used to configure system devices, most often COM and LPT ports. The mode command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mofcomp | The mofcomp command properly displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file. The mofcomp command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Más | The more command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The more command can also be used to paginate the results of any other Command Prompt or MS-DOS command. The more command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Montar | The mount command is used to mount Network File System (NFS) network shares. The mount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The mount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The mount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Mountvol | The mountvol command is used to display, create, or remove volume mount points. The mountvol command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Muevete | The move command is used to move one or files from one folder to another. The move command is also used to rename directories. The move command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mrinfo | The mrinfo command is used to provide information about a router's interfaces and neighbors. The mrinfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msav | The msav command starts Microsoft Antivirus. The msav command is only available in MS-DOS. Microsoft Antivirus was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Msbackup | The msbackup command starts Microsoft Backup, a tool used to back up and restore one or more files. The msbackup command is only available in MS-DOS. The msbackup command was replaced with Microsoft Backup beginning in Windows 95 and then Backup and Restore in later versions of Windows. |
| Mscdex | The mscdex command is used to provide CD-ROM access to MS-DOS. The mscdex command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows provides access to CD-ROM drives for the MS-DOS subsystem beginning in Windows XP, so the mscdex command is unnecessary in this and later operating systems. |
| Msd | The msd command starts Microsoft Diagnostics, a tool used to display information about your computer. The msd command is only available in MS-DOS. The msd command was replaced with System Information beginning in Windows 95. |
| Msg | The msg command is used to send a message to a user. The msg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msiexec | The msiexec command is used to start Windows Installer, a tool used to install and configure software. The msiexec command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Muiunattend | The muiunattend command starts the Multilanguage User Interface unattended setup process. The muiunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Nbtstat | The nbtstat command is used to show TCP/IP information and other statistical information about a remote computer. The nbtstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Red | The net command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net1 | The net1 command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net1 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The net command should be used instead of the net1 command. The net1 command was made available in Windows NT and Windows 2000 as a temporary fix for a Y2K issue that the net command had, which was corrected before the release of Windows XP. The net1 command remains in later versions of Windows only for compatibility with older programs and scripts that utilized the command. |
| Netcfg | The netcfg command is used to install the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), a lightweight version of Windows used to deploy workstations. The netcfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Netsh | The netsh command is used to start Network Shell, a command-line utility used to manage the network configuration of the local, or a remote, computer. The netsh command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Netstat | The netstat command is most commonly used to display all open network connections and listening ports. The netstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Nfsadmin | The nfsadmin command is used to manage Server for NFS or Client for NFS from the command line. The nfsadmin command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The nfsadmin command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The nfsadmin command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Nlsfunc | The nlsfunc command is used to load information specific to a particular country or region. The nlsfunc command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The nlsfunc command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Nlsfunc is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Nltest | The nltest command is used to test secure channels between Windows computers in a domain and between domain controllers that are trusting other domains. The nltest command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Nslookup | The nslookup is most commonly used to display the hostname of an entered IP address. The nslookup command queries your configured DNS server to discover the IP address. The nslookup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ntbackup | The ntbackup command is used to perform various backup functions from the Command Prompt or from within a batch or script file. The ntbackup command is available in Windows XP. The ntbackup command was replaced with the wbadmin beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Ntsd | The ntsd command is used to perform certain command line debugging tasks. The ntsd command is available in Windows XP. The ntsd command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the addition of dump file support in Task Manager. |
| Ocsetup | The ocsetup command starts the Windows Optional Component Setup tool, used to install additional Windows features. The ocsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Beginning in Windows 8, Microsoft is depreciating the ocsetup command in favor of the dism command. |
| Openfiles | The openfiles command is used to display and disconnect open files and folders on a system. The openfiles command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Path | The path command is used to display or set a specific path available to executable files. The path command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pathping | The pathping command functions much like the tracert command but will also report information about network latency and loss at each hop. The pathping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pausa | The pause command is used within a batch or script file to pause the processing of the file. When the pause command is used, a “Press any key to continue…” message displays in the command window. The pause command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pentnt | The pentnt command is used to detect floating point division errors in the Intel Pentium chip. The pentnt command is also used to enable floating point emulation and disable floating point hardware. The pentnt command is available in Windows XP. The pentnt command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the lack of Intel Pentium CPU use at the time of this operating system release. |
| Silbido | The ping command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity. The ping command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Pkgmgr | The pkgmgr command is used to start the Windows Package Manager from the Command Prompt. Package Manager installs, uninstalls, configures, and updates features and packages for Windows. The pkgmgr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnpunattend | The pnpunattend command is used to automate the installation of hardware device drivers. The pnpunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnputil | The pnputil command is used to start the Microsoft PnP Utility, a tool used to install a Plug and Play device from the command line. The pnputil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Popd | The popd command is used to change the current directory to the one most recently stored by the pushd command. The popd command is most often utilized from within a batch or script file. The popd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Energía | The power command is used to reduce the power consumed by a computer by monitoring software and hardware devices. The power command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The power command was replaced by operating system integrated power management functions beginning in Windows XP. |
| Powercfg | The powercfg command is used to manage the Windows power management settings from the command line. The powercfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Impresión | The print command is used to print a specified text file to a specified printing device. The print command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Prompt | The prompt command is used to customize the appearance of the prompt text in Command Prompt or MS-DOS. The prompt command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pushd | The pushd command is used to store a directory for use, most commonly from within a batch or script program. The pushd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pwlauncher | The pwlauncher command is used to enable, disable, or show the status of your Windows To Go startup options. The pwlauncher command is available in Windows 8. |
| Qappsrv | The qappsrv command is used to display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers available on the network. The qappsrv command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Qbasic | The qbasic command starts QBasic, the MS-DOS based programming environment for the BASIC programming language. The qbasic command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The qbasic command is not installed by default with Windows 98 or 95 but is available from the installation disc or disks. |
| Qprocess | The qprocess command is used to display information about running processes. The qprocess command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Consulta | The query command is used to display the status of a specified service. The query command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Quser | The quser command is used to display information about users currently logged on to the system. The quser command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Qwinsta | The qwinsta command is used to display information about open Remote Desktop Sessions. The qwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasautou | The rasautou command is used to manage Remote Access Dialer AutoDial addresses. The rasautou command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasdial | The rasdial command is used to start or end a network connection for a Microsoft client. The rasdial command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rcp | The rcp command is used to copy files between a Windows computer and a system running the rshd daemon. The rcp command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rcp command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rcp command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rd | The rd command is the shorthand version of the rmdir command. The rd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rdpsign | The rdpsign command is used to sign a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) file. The rdpsign command is available in Windows 7. |
| Reagentc | The reagentc command is used to configure the Windows Recovery Environment (RE). The reagentc command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Recimg | The recimg command is used to create a custom refresh image. The recimg command is available in Windows 8. |
| Recuperar | The recover command is used to recover readable data from a bad or defective disk. The recover command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| registro | The reg command is used to manage the Windows Registry from the command line. The reg command can perform common registry functions like adding registry keys, exporting the registry, etc. The reg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Regini | The regini command is used to set or change registry permissions and registry values from the command line. The regini command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Register-cimprovider | The register-cimprovider command is used to register a Common Information Model (CIM) Provider in Windows. The register-cimprovider command is available in Windows 8. |
| Regsvr32 | The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file as a command component in the Windows Registry. The regsvr32 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Relog | The relog command is used to create new performance logs from data in existing performance logs. The relog command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Movimiento rápido del ojo | The rem command is used to record comments or remarks in a batch or script file. The rem command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Ren | The ren command is the shorthand version of the rename command. The ren command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rebautizar | The rename command is used to change the name of the individual file that you specify. The rename command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Repair-bde | The repair-bde command is used to repair or decrypt a damaged drive that's been encrypted using BitLocker. The repair-bde command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Reemplazar | The replace command is used to replace one or more files with one or more other files. The replace command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Reiniciar | The reset command, executed as reset session, is used to reset the session subsystem software and hardware to known initial values. The reset command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Restaurar | The restore command is used to restore files that were backed up using the backup command. The restore command is only available in MS-DOS. The backup command was only available up to MS-DOS 5.00 but the restore command was included by default with later versions of MS-DOS to provide a way to restore files that were backed up in previous versions of MS-DOS. |
| Rexec | The rexec command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rexec daemon. The rexec command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here. The rexec command is not available in Windows 7 but can be executed in Windows XP via Windows XP Mode if need be. |
| Rmdir | The rmdir command is used to delete an existing or completely empty folder. The rmdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Robocopy | The robocopy command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. This command is also called Robust File Copy. The robocopy command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The robocopy command is superior to both the copy command and the xcopy command because robocopy supports many more options. |
| Ruta | The route command is used to manipulate network routing tables. The route command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Rpcinfo | The rpcinfo command makes a remote procedure call (RPC) to an RPC server and reports what it finds. The rpcinfo command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The rpcinfo command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The rpcinfo command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rpcping | The rpcping command is used to ping a server using RPC. The rpcping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Rsh | The rsh command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rsh daemon. The rsh command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rsh command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rsm | The rsm command is used to manage media resources using Removable Storage. The rsm command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsm command was optional in Windows Vista and then removed in Windows 7 due to Removable Storage Manager being removed from the operating system. Search for the rsm command in the C:\Windows\winsxs folder in Windows Vista if you're having trouble executing the command. |
| Runas | The runas command is used to execute a program using another user's credentials. The runas command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rwinsta | The rwinsta command is the shorthand version of the reset session command. The rwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Sc | The sc command is used to configure information about services. The sc command communicates with the Service Control Manager. The sc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Scandisk | The scandisk command is used to start Microsoft ScanDisk, a disk repair program. The scandisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The scandisk command was replaced by the chkdsk command beginning in Windows XP. |
| Scanreg | The scanreg command starts Windows Registry Checker, a basic registry repair program and backup utility. The scanreg command is available in Windows 98 and Windows 95. The functions provided by the scanreg command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP due to changes in how the Windows Registry functions. |
| Schtasks | The schtasks command is used to schedule specified programs or commands to run at certain times. The schtasks command can be used to create, delete, query, change, run, and end scheduled tasks. The schtasks command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.? |
| Sdbinst | The sdbinst command is used to deploy customized SDB database files. The sdbinst command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Secedit | The secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security by comparing the current security configuration to a template. The secedit command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Colocar | The set command is used to display, enable, or disable environment variables in MS-DOS or from the Command Prompt. The set command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Setlocal | The setlocal command is used to start the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The setlocal command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Setspn | The setspn command is used to manage the Service Principal Names (SPN) for an Active Directory (AD) service account. The setspn command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Setver | The setver command is used to set the MS-DOS version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. The setver command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The setver command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Setx | The setx command is used to create or change environment variables in the user environment or the system environment. The setx command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sfc | The sfc command is used to verify and replace important Windows system files. The sfc command is also referred to as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker, depending on the operating system. The sfc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Shadow | The shadow command is used to monitor another Remote Desktop Services session. The shadow command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Cuota | The share command is used to install file locking and file sharing functions in MS-DOS. The share command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The share command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Share is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Cambio | The shift command is used to change the position of replaceable parameters in a batch or script file. The shift command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Showmount | The showmount command is used to display information about NFS mounted file systems. The showmount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The showmount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The showmount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Shutdown | The shutdown command can be used to shut down, restart, or log off the current system or a remote computer. The shutdown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Smartdrv | The smartdrv command installs and configures SMARTDrive, a disk caching utility for MS-DOS. The smartdrv command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Caching is automatic beginning in Windows XP, making the smartdrv command unnecessary. |
| Clasificar | The sort command is used to read data from a specified input, sort that data, and return the results of that sort to the Command Prompt screen, a file, or another output device. The sort command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Comienzo | The start command is used to open a new command line window to run a specified program or command. The start command can also be used to start an application without creating a new window. The start command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Subst | The subst command is used to associate a local path with a drive letter. The subst command is a lot like the net use command except a local path is used instead of a shared network path. The subst command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The subst command replaced the assign command beginning with MS-DOS 6.0. |
| Sxstrace | The sxstrace command is used to start the WinSxs Tracing Utility, a programming diagnostic tool. The sxstrace command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sys | The sys command is used to copy the MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk. The sys command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The sys command is used most often to create a simple bootable disk or hard drive. The necessary system files for Windows are too large to fit on a disk, so the sys command was removed beginning in Windows XP. |
| Systeminfo | The systeminfo command is used to display basic Windows configuration information for the local or a remote computer. The systeminfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Takeown | The takedown command is used to regain access to a file that that an administrator was denied access to when reassigning ownership of the file. The takeown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Taskkill | The taskkill command is used to terminate a running task. The taskkill command is the command line equivalent of ending a process in Task Manager in Windows. The taskkill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tasklist | Displays a list of applications, services, and the Process ID (PID) currently running on either a local or a remote computer. The tasklist command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tcmsetup | The tcmsetup command is used to set up or disable the Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) client. The tcmsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Telnet | The telnet command is used to communicate with remote computers that use the Telnet protocol. The telnet command is available in all versions of Windows. The telnet command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tftp | The tftp command is used to transfer files to and from a remote computer that's running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) service or daemon. The tftp command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tftp command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the TFTP Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Hora | The time command is used to show or change the current time. The time command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Se acabó el tiempo | The timeout command is typically used in a batch or script file to provide a specified timeout value during a procedure. The timeout command can also be used to ignore keypresses. The timeout command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Título | The title command is used to set the Command Prompt window title. The title command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tlntadmn | The tlntadmn command is used to administer a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. The tlntadmn command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tlntadmn command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Server Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tpmvscmgr | The tpmvscmgr command is used to create and destroy TPM virtual smart cards. The tpmvscmgr command is available in Windows 8. |
| Tracerpt | The tracerpt command is used to process event trace logs or real-time data from instrumented event trace providers. The tracerpt command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| seguimiento | The tracert command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to a specified remote computer with increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values and displays the IP address and hostname, if available, of the router interfaces between the source and destination. The tracert command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Árbol | The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path. The tree command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Tscon | The tscon command is used to attach a user session to a Remote Desktop session. The tscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsdiscon | The tsdiscon command is used to disconnect a Remote Desktop session. The tsdiscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tskill | The tskill command is used to end the specified process. The tskill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsshutdn | The tsshutdn command is used to remotely shut down or restart a terminal server. The tsshutdn command is available in Windows XP. The ability to shut down a computer remotely is also available in the more powerful shutdown command, so tsshutdn was removed beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Escribe | The type command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The type command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Typeperf | The typerperf command displays performance data in the Command Prompt window or writes the data to specified log file. The typeperf command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tzutil | The tzutil command is used to display or configure the current system's time zone. The tzutil command can also be used to enable or disable Daylight Saving Time adjustments. The tzutil command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Umount | The umount command is used to remove Network File System (NFS) mounted network shares. The umount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The umount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The umount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Undelete | The undelete command is used to undo a deletion performed with the MS-DOS delete command. The undelete command is only available in MS-DOS. The undelete command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to the availability of the Recycle Bin in Windows. Additionally, free file recovery programs are available from third-party software makers. |
| Unformat | The unformat command is used to undo the formatting on a drive performed by the MS-DOS format command. The unformat command is only available in MS-DOS. The unformat command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to file system changes. |
| desbloquear | The unlock command is used to unlock a drive, disabling direct disk access for a program. The unlock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP. |
| Unlodctr | The unlodctr command removes Explain text and Performance counter names for a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. The unlodctr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Vaultcmd | The vaultcmd command is used to create, remove, and show stored credentials. The vaultcmd command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Ver | The ver command is used to display the current Windows or MS-DOS version number. The ver command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Verificar | The verify command is used to enable or disable the ability of Command Prompt, or MS-DOS, to verify that files are written correctly to a disk. The verify command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vol. | The vol command shows the volume label and serial number of a specified disk, assuming this information exists. The vol command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vsafe | The vsafe command is used to start VSafe, a basic virus protection system for MS-DOS. The vsafe command is only available in MS-DOS. VSafe was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Vssadmin | The vssadmin command starts the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool which displays current volume shadow copy backups and all installed shadow copy writers and providers. The vssadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| W32tm | The w32tm command is used to diagnose issues with Windows Time. The w32tm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Waitfor | The waitfor command is used to send or wait for a signal on a system. The waitfor command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wbadmin | The wbadmin command is used to start and stop backup jobs, display details about a previous backup, list the items within a backup, and report on the status of a currently running backup. The wbadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The wbadmin command replaced the ntbackup command beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Wecutil | The wecutil command is used to manage subscriptions to events that are forwarded from WS-Management supported computers. The wecutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wevtutil | The wevtutil command starts the Windows Events Command Line Utility which is used to manage event logs and publishers. The wevtutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Donde | The where command is used to search for files that match a specified pattern. The where command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Whoami | The whoami command is used to retrieve user name and group information on a network. The whoami command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winmgmt | The winmgmt command starts the command line version of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. The winmgmt command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Winrm | The winrm command is used to start the command line version of Windows Remote Management, used to manage secure communications with local and remote computers using web services. The winrm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winrs | The winrs command is used to open a secure command window with a remote host. The winrs command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winsat | The winsat command starts the Windows System Assessment Tool, a program that assesses various features, attributes, and capabilities of a computer running Windows. The winsat command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wmic | The wmic command starts the Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC), a scripting interface that simplifies the use of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and systems managed via WMI. The wmic command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Wsmanhttpconfig | The wsmanhttpconfig command is used to manage aspects of the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service. The wsmanhttpconfig command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Xcopy | The xcopy command can copy one or more files or directory trees from one location to another. The xcopy command is generally considered a more “powerful” version of the copy command through the robocopy command trumps even xcopy. The xcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. A command by the name of xcopy32 existed in Windows 95 and Windows 98. To avoid a long and confusing explanation here, just know that no matter if you executed the xcopy command or the xcopy32 command, you were always executing the most updated version of the command. |
| Xwizard | The xwizard command, short for Extensible Wizard, is used to register data in Windows, often from a preconfigured XML file. The xwizard command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
The above list is a set of most essential commands of command prompt. To view or download a PDF version of complete set of windows commands, please click on the below button.

Descargar como PDF
Para obtener más consejos, trucos y actualizaciones relacionadas con la tecnología, suscríbase a Tweak Library y, si le gustan más los videos relacionados con la tecnología, mire y suscríbase a nuestro canal de YouTube . También puede comunicarse con nosotros en Facebook y Pinterest .
