Utilizați promptul de comandă ca un profesionist - Totul despre linia de comandă
Publicat: 2019-05-21Odată cu lansarea Windows 10, Microsoft a împins încet linia de comandă din interfața Windows. Motivul din spatele acestui lucru a fost că linia de comandă era un instrument învechit și cel mai inutil dintr-o eră a introducerii pe bază de text. Cu toate acestea, multe comenzi sunt încă utile, iar Windows 10 chiar a adăugat noi funcții în lumea liniei de comandă. Acum promptul de comandă este reproiectat la PowerShell, o aplicație care poate fi utilizată la fel ca și promptul de comandă. Este o aplicație plină de culoare care înlocuiește promptul de comandă, deși încă puteți utiliza promptul de comandă de acum. Aceste trucuri cu promptul de comandă sunt cu adevărat utile pentru administratorii de computere și le oferă acces profesional pentru a îndeplini mai multe sarcini.
Cum să deschideți promptul de comandă
Apăsați Win + R -> tastați „cmd” -> apăsați „Enter”
În bara de căutare, tastați „cmd”, apăsați „Enter”.
Dacă doriți să deschideți promptul de comandă ca administrator, în bara de căutare, tastați „cmd” și de îndată ce apare „Command Application”, faceți clic dreapta pe ea și faceți clic pe „Run as administrator”.
Citește și: Totul despre comenzile rapide de la tastatură Windows 10
Cum să găsiți toate comenzile pe promptul de comandă
Pentru a găsi comenzi relevante și sintaxa acestora în promptul de comandă, putem tasta „cmd/?” sau tastați o comandă urmată de „/?” de exemplu 'ipconfig /?' deschide lista de opțiuni și sintaxa cu acțiunile acestora. Acest interpret de comenzi ne este util pentru a învăța comenzi noi la promptul de comandă.
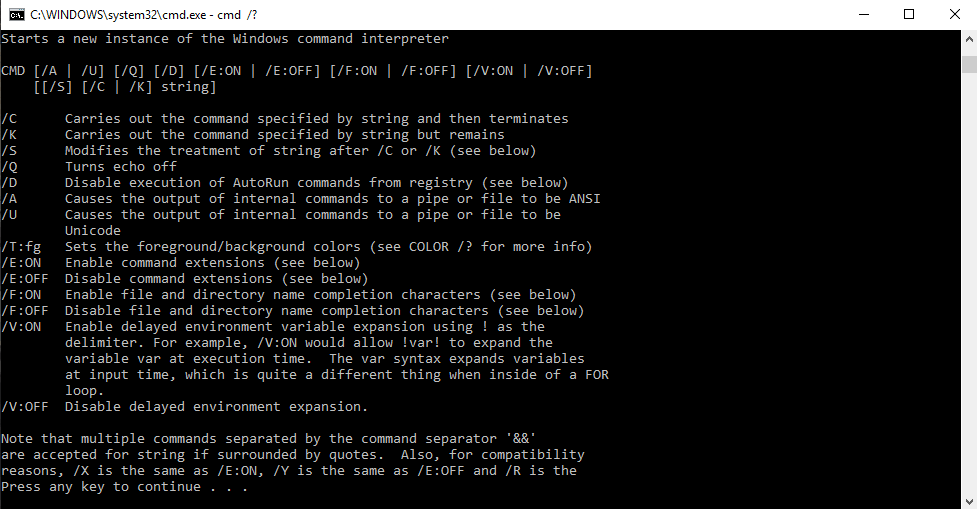
Folosind Sintaxa
cmd [/c|/k] [/s] [/q] [/d] [/a|/u] [/t:{<B><F>|<F>}] [/e:{on|off}] [/f:{on|off}] [/v:{on|off}] [<String>]
Parametrii
| Parametru | Descriere |
| /c | Efectuează comanda specificată de String și apoi se oprește. |
| /k | Efectuează comanda specificată de String și continuă. |
| /s | Modifică tratamentul String după /c sau /k. |
| /q | Oprește ecoul. |
| /d | Dezactivează executarea comenzilor AutoRun. |
| /A | Formatează ieșirea comenzii interne într-o conductă sau într-un fișier ca Institutul Național American de Standarde (ANSI). |
| /u | Formatează ieșirea comenzii interne într-o conductă sau într-un fișier ca Unicode. |
| /t:{<B><F>|<F>} | Setează culorile de fundal (B) și prim-plan (F). |
| /e:on | Activează extensiile de comandă. |
| /e:off | Dezactivează extensiile de comenzi. |
| /f:on | Activează completarea numelui de fișier și director. |
| /f:off | Dezactivează completarea numelui fișierului și directorului. |
| /v:on | Permite extinderea variabilelor de mediu întârziate. |
| /v:off | Dezactivează extinderea variabilelor de mediu întârziate. |
| <Șir> | Specifică comanda pe care doriți să o efectuați. |
| /? | Afișează ajutor la promptul de comandă. |
Următorul tabel listează cifre hexazecimale valide pe care le puteți utiliza ca valori pentru <B> și <F>
| Valoare | Culoare |
| 0 | Negru |
| 1 | Albastru |
| 2 | Verde |
| 3 | Aqua |
| 4 | roșu |
| 5 | Violet |
| 6 | Galben |
| 7 | alb |
| 8 | gri |
| 9 | Albastru deschis |
| A | Verde deschis |
| b | Acva ușor |
| c | Lumina rosie |
| d | violet deschis |
| e | Lumină galbenă |
| f | Alb strălucitor |
Iată o listă completă de comenzi din promptul de comandă. De asemenea, puteți descărca toate comenzile cu sintaxa lor din linkul din partea de jos a acestui articol.
| Comanda | Descriere |
| Adăuga | Comanda append poate fi folosită de programe pentru a deschide fișiere dintr-un alt director ca și cum ar fi fost localizate în directorul curent. Comanda append este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile pe 32 de biți de Windows. Comanda append nu este disponibilă în versiunile Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Arp | Comanda arp este folosită pentru a afișa sau modifica intrările din memoria cache ARP. Comanda arp este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. |
| conf. univ | Comanda assoc este utilizată pentru a afișa sau modifica tipul de fișier asociat cu o anumită extensie de fișier. Comanda asoc este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| La | Comanda at este folosită pentru a programa comenzi și alte programe să ruleze la o anumită dată și oră. At command este disponibil în Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Începând cu Windows 8, programarea sarcinilor în linia de comandă ar trebui să fie finalizată cu comanda schtasks. |
| Atmadm | Comanda atmadm este utilizată pentru a afișa informații legate de conexiunile în modul de transfer asincron (ATM) pe sistem. Comanda atmadm este disponibilă în Windows XP. Suportul pentru ATM a fost eliminat începând cu Windows Vista, făcând inutilă comanda atmadm. |
| Atrib | Comanda attrib este folosită pentru a modifica atributele unui singur fișier sau unui director. Comanda attrib este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Auditpol | Comanda auditpol este utilizată pentru a afișa sau modifica politicile de audit. Comanda auditpol este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Bcdboot | Comanda bcdboot este folosită pentru a copia fișierele de boot în partiția de sistem și pentru a crea un nou magazin BCD de sistem. Comanda bcdboot este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Bcdedit | Comanda bcdedit este utilizată pentru a vizualiza sau a face modificări la datele de configurare a pornirii. Comanda bcdedit este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. Comanda bcdedit a înlocuit comanda bootcfg începând cu Windows Vista. |
| Bdehdcfg | Comanda bdehdcfg este utilizată pentru a pregăti un hard disk pentru BitLocker Drive Encryption. Comanda bdehdcfg este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Bitsadmin | Comanda bitsadmin este utilizată pentru a crea, gestiona și monitoriza joburile de descărcare și încărcare. Comanda bitsadmin este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. Deși comanda bitsadmin este disponibilă atât în Windows 8, cât și în Windows 7, aceasta este în curs de eliminare. În schimb, ar trebui folosite cmdleturile BITS PowerShell. |
| Bootcfg | Comanda bootcfg este utilizată pentru a construi, modifica sau vizualiza conținutul fișierului boot.ini, un fișier ascuns care este folosit pentru a identifica în ce folder, pe ce partiție și pe ce hard disk se află Windows. Comanda bootcfg este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda bootcfg a fost înlocuită cu comanda bcdedit începând cu Windows Vista. Bootcfg este încă disponibil în Windows 8, 7 și Vista, dar nu are valoare reală, deoarece boot.ini nu este utilizat în aceste sisteme de operare. |
| Bootsect | Comanda bootsect este utilizată pentru a configura codul de pornire principal la unul compatibil cu BOOTMGR (Vista și versiuni ulterioare) sau NTLDR (XP și versiuni anterioare). Comanda bootsect este disponibilă în Windows 8. Comanda bootsect este disponibilă și în Windows 7 și Windows Vista, dar numai din promptul de comandă disponibil în Opțiuni de recuperare a sistemului. |
| Pauză | Comanda break setează sau șterge verificarea extinsă CTRL + C pe sistemele DOS. Comanda break este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. Comanda break este disponibilă în Windows XP și versiunile ulterioare de Windows pentru a oferi compatibilitate cu fișierele MS-DOS, dar nu are niciun efect în Windows în sine. |
| Cacls | Comanda cacls este folosită pentru a afișa sau modifica listele de control de acces ale fișierelor. Comanda cacls este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda cacls este eliminată treptat în favoarea comenzii icacls, care ar trebui utilizată în schimb în toate versiunile de Windows după Windows XP. |
| Apel | Comanda de apel este utilizată pentru a rula un script sau un program lot din interiorul unui alt script sau program lot. Comanda de apel este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. Comanda de apel nu are efect în afara unui script sau a unui fișier batch. Cu alte cuvinte, rularea comenzii de apel la promptul de comandă sau la promptul MS-DOS nu va face nimic. |
| CD | Comanda cd este versiunea scurtă a comenzii chdir. Comanda cd este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Certreq | Comanda certreq este utilizată pentru a efectua diverse funcții de certificate ale autorității de certificare (CA). Comanda certreq este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Certitil | Comanda certutil este utilizată pentru a descărca și afișa informațiile de configurare a autorității de certificare (CA), în plus față de alte funcții CA. Comanda certutil este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Schimbare | Comanda de modificare modifică diferite setări ale serverului terminal, cum ar fi modurile de instalare, mapările portului COM și conectările. Comanda de modificare este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Chcp | Comanda chcp afișează sau configurează numărul activ al paginii de coduri. Comanda chcp este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Chdir | Comanda chdir este folosită pentru a afișa litera unității și folderul în care vă aflați în prezent. Chdir poate fi, de asemenea, utilizat pentru a schimba unitatea și/sau directorul în care doriți să lucrați. Comanda chdir este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, ca precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Checknetizolare | Comanda checknetisolation este folosită pentru a testa aplicațiile care necesită capabilități de rețea. Comanda checknetisolation este disponibilă în Windows 8. |
| Chglogon | Comanda chglogon activează, dezactivează sau drenează conectările la sesiunea serverului terminal. Comanda chglogon este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. Executarea comenzii chglogon este la fel cu executarea modificării logarii. |
| Chgport | Comanda chgport poate fi utilizată pentru a afișa sau modifica mapările portului COM pentru compatibilitatea cu DOS. Comanda chgport este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. Executarea comenzii chgport este aceeași cu executarea modificării portului. |
| Chgusr | Comanda chgusr este folosită pentru a schimba modul de instalare pentru serverul terminal. Comanda chgusr este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. Executarea comenzii chgusr este aceeași cu executarea modificării utilizatorului. |
| Chkdsk | Comanda chkdsk, denumită adesea check disk, este utilizată pentru a identifica și corecta anumite erori de hard disk. Comanda chkdsk este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Chkntfs | Comanda chkntfs este utilizată pentru a configura sau afișa verificarea unității de disc în timpul procesului de pornire Windows. Comanda chkntfs este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Alegere | Comanda choice este utilizată în cadrul unui script sau program lot pentru a furniza o listă de opțiuni și pentru a returna valoarea acelei alegeri programului. Comanda de alegere este disponibilă în MS-DOS și în toate versiunile de Windows, cu excepția Windows XP. Utilizați comanda set cu comutatorul /p în locul comenzii choice în fișierele batch și scripturile pe care intenționați să le utilizați în Windows XP. |
| Cifru | Comanda de criptare arată sau modifică starea de criptare a fișierelor și folderelor de pe partițiile NTFS. Comanda de cifrare este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Clamă | Comanda clip este folosită pentru a redirecționa ieșirea de la orice comandă în clipboard în Windows. Comanda clip este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Cls | Comanda cls șterge ecranul de toate comenzile introduse anterior și de alt text. Comanda cls este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Cmd | Comanda cmd pornește o nouă instanță a interpretorului de comenzi cmd.exe. Comanda cmd este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Cmdkey | Comanda cmdkey este utilizată pentru a afișa, crea și elimina numele de utilizator și parolele stocate. Comanda cmdkey este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Cmstp | Comanda cmstp instalează sau dezinstalează un profil de serviciu Connection Manager. Comanda cmstp este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Culoare | Comanda de culoare este utilizată pentru a schimba culorile textului și fundalului în fereastra Prompt de comandă. Comanda de culoare este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Comanda | Comanda „comandă” pornește o nouă instanță a interpretorului de comandă command.com. Comanda „comandă” este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile Windows pe 32 de biți. Comanda „comandă” nu este disponibilă în versiunile Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Comp | Comanda comp este folosită pentru a compara conținutul a două fișiere sau seturi de fișiere. Comanda comp este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Compact | Comanda compactă este utilizată pentru a afișa sau modifica starea de compresie a fișierelor și directoarelor pe partițiile NTFS. Comanda compactă este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Convertit | Comanda convert este folosită pentru a converti volumele formatate FAT sau FAT32 în formatul NTFS. Comanda convert este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Copie | Comanda de copiere face pur și simplu asta - copiază unul sau mai multe fișiere dintr-o locație în alta. Comanda de copiere este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. Comanda xcopy este considerată a fi o versiune mai „puternică” a comenzii copy. |
| Cscript | Comanda cscript este folosită pentru a executa scripturi prin Microsoft Script Host. Comanda cscript este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. Comanda cscript este folosită cel mai popular pentru a gestiona imprimante din linia de comandă folosind scripturi precum prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmngr.vbs și altele. |
| Ctty | Comanda ctty este utilizată pentru a modifica dispozitivele implicite de intrare și ieșire pentru sistem. Comanda ctty este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. Funcțiile furnizate de comanda ctty nu mai erau necesare începând cu Windows XP, deoarece interpretul command.com (MS-DOS) nu mai este interpretul implicit de linie de comandă. |
| Data | Comanda data este utilizată pentru a afișa sau modifica data curentă. Comanda data este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Dblspace | Comanda dblspace este utilizată pentru a crea sau configura unități comprimate DoubleSpace. Comanda dblspace este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. DriveSpace, executat folosind comanda drvspace, este o versiune actualizată a DoubleSpace. Windows gestionează în mod nativ compresia începând cu Windows XP. |
| Depanați | Comanda debug pornește Debug, o aplicație de linie de comandă folosită pentru a testa și edita programe. Comanda de depanare este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile Windows pe 32 de biți. Comanda de depanare nu este disponibilă în versiunile de Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Defrag | Comanda defragmentare este utilizată pentru a defragmenta o unitate pe care o specificați. Comanda defrag este versiunea de linie de comandă a Disk Defragmenter de la Microsoft. Comanda defragmentare este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Del | Comanda del este folosită pentru a șterge unul sau mai multe fișiere. Comanda del este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. Comanda del este aceeași cu comanda de ștergere. |
| Deltree | Comanda deltree este folosită pentru a șterge un director și toate fișierele și subdirectoarele din acesta. Comanda deltree este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. Începând cu Windows XP, un folder și fișierele și subfolderele sale pot fi eliminate folosind funcția /s a comenzii rmdir. Deltree nu mai era necesar cu această nouă capacitate rmdir, așa că comanda a fost eliminată. |
| Diantz | Comanda diantz este folosită pentru a comprima fără pierderi unul sau mai multe fișiere. Comanda diantz este uneori numită Cabinet Maker. Comanda diantz este disponibilă în Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda diantz este aceeași cu comanda makecab. |
| Dir | Comanda dir este folosită pentru a afișa o listă de fișiere și foldere conținute în folderul în care lucrați în prezent. Comanda dir afișează și alte informații importante, cum ar fi numărul de serie al hard diskului, numărul total de fișiere listate, dimensiunea lor combinată, cantitatea totală de spațiu liber rămas pe unitate și multe altele. Comanda dir este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Diskcomp | Comanda diskcomp este folosită pentru a compara conținutul a două dischete. Comanda diskcomp este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Copiere pe disc | Comanda diskcopy este folosită pentru a copia întregul conținut al unei dischete pe alta. Comanda diskcopy este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Diskpart | Comanda diskpart este utilizată pentru a crea, gestiona și șterge partițiile hard disk. Comanda diskpart este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda diskpart a înlocuit comanda fdisk începând cu Windows XP. |
| Diskperf | Comanda diskperf este utilizată pentru a gestiona de la distanță contoarele de performanță a discului. Comanda diskperf este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Diskraid | Comanda diskraid pornește instrumentul DiskRAID care este utilizat pentru a gestiona și configura matricele RAID. Comanda diskraid este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Dism | Comanda dism pornește instrumentul Deployment Image Service and Management (DISM). Instrumentul DISM este utilizat pentru a gestiona funcțiile din imaginile Windows. Comanda dism este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Dispdiag | Comanda dispdiag este folosită pentru a scoate un jurnal de informații despre sistemul de afișare. Comanda dispdiag este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Djoin | Comanda djoin este folosită pentru a crea un nou cont de computer într-un domeniu. Comanda djoin este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Doskey | Comanda doskey este folosită pentru a edita linii de comandă, pentru a crea macrocomenzi și pentru a reapela comenzile introduse anterior. Comanda doskey este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Dosshell | Comanda dosshell pornește DOS Shell, un instrument grafic de gestionare a fișierelor pentru MS-DOS. Comanda dosshell este disponibilă în Windows 95 (în modul MS-DOS) și, de asemenea, în MS-DOS versiunea 6.0 și versiunile ulterioare MS-DOS care au fost actualizate de la versiunile anterioare care conțineau comanda dosshell. Un manager de fișiere grafic, Windows Explorer, a devenit o parte integrată a sistemului de operare începând cu Windows 95. |
| Dosx | Comanda dosx este folosită pentru a porni DOS Protected Mode Interface (DPMI), un mod special conceput pentru a oferi aplicațiilor MS-DOS acces la mai mult decât cei 640 KB permis în mod normal. Comanda dosx este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda dosx nu este disponibilă în versiunile pe 64 de biți de Windows. Comanda dosx și DPMI sunt disponibile numai în Windows pentru a accepta programe MS-DOS mai vechi. |
| Driverquery | Comanda driverquery este folosită pentru a afișa o listă a tuturor driverelor instalate. Comanda driverquery este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Drvspace | Comanda drvspace este utilizată pentru a crea sau configura unități comprimate DriveSpace. Comanda drvspace este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. DriveSpace este o versiune actualizată a DoubleSpace, executată folosind comanda dblspace. Windows gestionează în mod nativ compresia începând cu Windows XP. |
| Ecou | Comanda echo este folosită pentru a afișa mesaje, cel mai frecvent din fișierele script sau batch. Comanda ecou poate fi folosită și pentru a activa sau dezactiva funcția de ecou. Comanda echo este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Editați | × | Comanda de editare pornește instrumentul MS-DOS Editor care este folosit pentru a crea și modifica fișiere text. Comanda de editare este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile Windows pe 32 de biți. Comanda de editare nu este disponibilă în versiunile Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Edlin | Comanda edlin pornește instrumentul Edlin care este folosit pentru a crea și modifica fișiere text din linia de comandă. Comanda edlin este disponibilă în toate versiunile Windows pe 32 de biți, dar nu este disponibilă în versiunile Windows pe 64 de biți. În MS-DOS, comanda edlin este disponibilă numai până la MS-DOS 5.0, așa că, cu excepția cazului în care versiunea ulterioară a MS-DOS a fost actualizată de la 5.0 sau anterioară, nu veți vedea comanda edlin. |
| Emm386 | Comanda emm386 este folosită pentru a oferi acces MS-DOS la mai mult de 640 KB de memorie. Comanda emm386 este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. Windows însuși are acces la memoria extinsă și extinsă începând cu Windows 95. |
| Endlocal | Comanda endlocal este utilizată pentru a termina localizarea modificărilor de mediu în interiorul unui fișier lot sau script. Comanda endlocal este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Şterge | Comanda de ștergere este utilizată pentru a șterge unul sau mai multe fișiere. Comanda de ștergere este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. Comanda de ștergere este aceeași cu comanda del. |
| Esentutl | Comanda esentutl este utilizată pentru a gestiona bazele de date Extensible Storage Engine. Comanda esentutl este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Eventcreate | Comanda eventcreate este folosită pentru a crea un eveniment personalizat într-un jurnal de evenimente. Comanda eventcreate este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Declanșatoare de evenimente | Comanda eventtriggers este utilizată pentru a configura și afișa declanșatoarele de evenimente. Comanda eventtriggers este disponibilă în Windows XP. Începând cu Windows Vista, declanșatoarele de evenimente sunt create folosind funcția Atașare sarcină la acest eveniment din Vizualizatorul de evenimente, făcând ca comanda eventtriggers să nu fie necesară. |
| Exe2bin | Comanda exe2bin este utilizată pentru a converti un fișier de tip EXE (fișier executabil) într-un fișier binar. Comanda exe2bin este disponibilă în versiunile pe 32 de biți ale Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda exe2bin nu este disponibilă în nicio versiune de Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Ieșire | Comanda de ieșire este utilizată pentru a încheia sesiunea cmd.exe (Windows) sau command.com (MS-DOS) în care lucrați în prezent. Comanda de ieșire este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS . |
| Extinde | Comanda de extindere este utilizată pentru a extrage fișierele și folderele conținute în fișierele Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Comanda de extindere este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile de Windows. Comanda de extindere nu este disponibilă în versiunea pe 64 de biți a Windows XP. |
| Extras32 | Comanda extrac32 este utilizată pentru a extrage fișierele și folderele conținute în fișierele Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Comanda extrac32 este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. Comanda extrac32 este de fapt un program de extracție CAB pentru utilizarea de către Internet Explorer, dar poate fi folosită pentru a extrage orice fișier Microsoft Cabinet. Folosiți comanda expand în loc de comanda extrac32 dacă este posibil. |
| Extrage | Comanda de extragere este utilizată pentru a extrage fișierele și folderele conținute în fișierele Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Comanda de extragere este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95. Comanda de extragere a fost înlocuită cu comanda de extindere începând cu Windows XP. |
| Ajutor rapid | Comanda fasthelp oferă informații mai detaliate despre oricare dintre celelalte comenzi MS-DOS. Comanda fasthelp este disponibilă numai în MS-DOS. Comanda help a înlocuit comanda fasthelp începând cu Windows 95. |
| Deschide rapid | Comanda fastopen este folosită pentru a adăuga locația hard disk-ului unui program la o listă specială stocată în memorie, îmbunătățind potențial timpul de lansare a programului prin eliminarea necesității ca MS-DOS să localizeze aplicația pe unitate. Comanda fastopen este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile pe 32 de biți de Windows. Comanda fastopen nu este disponibilă în versiunile de Windows pe 64 de biți. Fastopen este disponibil numai în Windows 8, 7, Vista și XP pentru a accepta fișiere MS-DOS mai vechi. |
| Fc | Comanda fc este folosită pentru a compara două fișiere individuale sau seturi de fișiere și apoi pentru a arăta diferențele dintre ele. Comanda fc este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Fdisk | Comanda fdisk este folosită pentru a crea, gestiona și șterge partițiile hard disk. Comanda fdisk este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. Comanda fdisk a fost înlocuită cu comanda diskpart începând cu Windows XP. Gestionarea partițiilor este disponibilă și din Gestionarea discurilor în Windows 8, 7, Vista și XP. |
| Găsi | Comanda find este folosită pentru a căuta un șir de text specificat într-unul sau mai multe fișiere. Comanda find este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Findstr | Comanda findstr este folosită pentru a găsi modele de șir de text într-unul sau mai multe fișiere. Comanda findstr este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Deget | Comanda finger este utilizată pentru a returna informații despre unul sau mai mulți utilizatori pe un computer la distanță care rulează serviciul Finger. Comanda finger este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Fltmc | Comanda fltmc este utilizată pentru a încărca, descărca, lista și gestiona în alt mod driverele de filtrare. Comanda fltmc este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Fondue | Comanda fondue, prescurtare de la Features on Demand User Experience Tool, este utilizată pentru a instala oricare dintre câteva caracteristici opționale Windows din linia de comandă. Comanda fondue este disponibilă în Windows 8. Caracteristicile opționale Windows pot fi instalate și din aplicația Programe și caracteristici din Panoul de control. |
| Pentru | Comanda for este folosită pentru a rula o comandă specificată pentru fiecare fișier dintr-un set de fișiere. Comanda for este folosită cel mai adesea într-un fișier lot sau script. Comanda for este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Forcedos | Comanda forcedos este utilizată pentru a porni programul specificat în subsistemul MS-DOS. Comanda forcedos este disponibilă numai în versiunile pe 32 de biți ale Windows XP. Comanda forcedos este utilizată numai pentru programele MS-DOS care nu sunt recunoscute ca atare de Windows XP. |
| Forfiles | Comanda forfiles selectează unul sau mai multe fișiere pentru a executa o comandă specificată. Comanda forfiles este folosită cel mai adesea într-un fișier lot sau script. Comanda forfiles este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Format | Comanda format este folosită pentru a formata o unitate în sistemul de fișiere pe care îl specificați. Comanda de format este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. Formatarea unității este disponibilă și din Gestionarea discurilor în Windows 8, 7, Vista și XP. |
| Fsutil | Comanda fsutil este utilizată pentru a efectua diverse sarcini ale sistemului de fișiere FAT și NTFS, cum ar fi gestionarea punctelor de analiză și a fișierelor rare, demontarea unui volum și extinderea unui volum. Comanda fsutil este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Ftp | Comanda ftp poate fi folosită pentru a transfera fișiere către și de la un alt computer. Computerul de la distanță trebuie să funcționeze ca server FTP. Comanda ftp este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. |
| Ftype | Comanda ftype este folosită pentru a defini un program implicit pentru a deschide un tip de fișier specificat. Comanda ftype este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Getmac | Comanda getmac este utilizată pentru a afișa adresa de control al accesului media (MAC) a tuturor controlerelor de rețea dintr-un sistem. Comanda getmac este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Mergi la | Comanda goto este utilizată într-un fișier lot sau script pentru a direcționa procesul de comandă către o linie etichetată din script. Comanda goto este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Gpresult | Comanda gpresult este utilizată pentru a afișa setările politicii de grup. Comanda gpresult este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Gpupdate | Comanda gpupdate este utilizată pentru a actualiza setările politicii de grup. Comanda gpupdate este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Graftabl | Comanda graftabl este utilizată pentru a activa capacitatea Windows de a afișa un set de caractere extins în modul grafic. Comanda graftabl este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows și în MS-DOS până la versiunea 5.0. Comanda graftabl nu este disponibilă în versiunile de Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Grafică | Comanda grafică este folosită pentru a încărca un program care poate imprima grafică. Comanda grafică este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile Windows pe 32 de biți. Comanda grafică nu este disponibilă în versiunile de Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Ajutor | Comanda de ajutor oferă informații mai detaliate despre oricare dintre celelalte comenzi Command Prompt sau MS-DOS. Comanda de ajutor este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Nume gazdă | Comanda hostname afișează numele gazdei curente. Comanda hostname este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Hwrcomp | Comanda hwrcomp este folosită pentru a compila dicționare personalizate pentru recunoașterea scrisului de mână. Comanda hwrcomp este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Hwrreg | Comanda hwrreg este utilizată pentru a instala un dicționar personalizat compilat anterior pentru recunoașterea scrisului de mână. Comanda hwrreg este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Icacls | Comanda icacls este utilizată pentru a afișa sau modifica listele de control de acces ale fișierelor. Comanda icacls este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. Comanda icacls este o versiune actualizată a comenzii cacls. |
| Dacă | Comanda if este utilizată pentru a efectua funcții condiționate într-un fișier batch. Comanda if este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Interlnk | Comanda interlnk este utilizată pentru a conecta două computere printr-o conexiune serială sau paralelă pentru a partaja fișiere și imprimante. Comanda interlnk este disponibilă numai în MS-DOS. Capacitatea de a conecta direct două computere este gestionată de funcțiile de rețea în toate versiunile de Windows. |
| Intersvr | Comanda intersvr este folosită pentru a porni serverul Interlnk și pentru a copia fișiere Interlnk de pe un computer pe altul. Comanda intersvr este disponibilă numai în MS-DOS. Capacitatea de a conecta direct două computere este gestionată de funcțiile de rețea în toate versiunile de Windows. |
| Ipconfig | Comanda ipconfig este utilizată pentru a afișa informații detaliate despre IP pentru fiecare adaptor de rețea care utilizează TCP/IP. Comanda ipconfig poate fi folosită și pentru a elibera și reînnoi adresele IP pe sistemele configurate să le primească prin intermediul unui server DHCP. Comanda ipconfig este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. |
| Ipxroute | Comanda ipxroute este folosită pentru a afișa și modifica informații despre tabelele de rutare IPX. Comanda ipxroute este disponibilă în Windows XP. Microsoft și-a eliminat clientul NetWare nativ începând cu Windows Vista, eliminând și comanda ipxroute asociată. |
| Irftp | Comanda irftp este folosită pentru a transmite fișiere printr-o legătură în infraroșu. Comanda irftp este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Iscsicli | Comanda iscsicli pornește Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, folosit pentru a gestiona iSCSI. Comanda iscsicli este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Kb16 | Comanda kb16 este utilizată pentru a suporta fișiere MS-DOS care trebuie să configureze o tastatură pentru o anumită limbă. Comanda kb16 este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda kb16 nu este disponibilă în versiunile Windows pe 64 de biți. Comanda kb16 a înlocuit comanda keyb începând cu Windows XP, dar există doar pentru a accepta fișiere MS-DOS mai vechi. |
| Keyb | Comanda keyb este folosită pentru a configura o tastatură pentru o anumită limbă. Comanda keyb este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. Consultați comanda kb16 pentru o comandă echivalentă în versiunile ulterioare de Windows. Setările de limbă a tastaturii sunt gestionate de aplicațiile Regiune și limbă sau Opțiuni regionale și de limbă (în funcție de versiunea de Windows) Panoul de control din Windows începând cu Windows XP. |
| Klist | Comanda klist este folosită pentru a lista biletele de serviciu Kerberos. Comanda klist poate fi folosită și pentru a curăța biletele Kerberos. Comanda klist este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Ksetup | Comanda ksetup este utilizată pentru a configura conexiunile la un server Kerberos. Comanda ksetup este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. |
| Ktmutil | Comanda ktmutil pornește utilitarul Kernel Transaction Manager. Comanda ktmutil este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7 și Windows Vista. |
| Eticheta | Comanda label este utilizată pentru a gestiona eticheta de volum a unui disc. Comanda label este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Lh | Comanda lh este versiunea scurtă a comenzii loadhigh. Comanda lh este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. |
| Licențierediag | Comanda licensingdiag este un instrument folosit pentru a genera un jurnal bazat pe text și alte fișiere de date care conțin activarea produsului și alte informații de licențiere Windows. Comanda licensingdiag este disponibilă în Windows 8. |
| Loadfix | Comanda loadfix este folosită pentru a încărca programul specificat în primii 64K de memorie și apoi rulează programul. Comanda loadfix este disponibilă în MS-DOS, precum și în toate versiunile de Windows pe 32 de biți. Comanda loadfix nu este disponibilă în versiunile de Windows pe 64 de biți. |
| Loadhigh | Comanda loadhigh este folosită pentru a încărca un program în memorie mare și este de obicei folosită din fișierul autoexec.bat. Comanda loadhigh este disponibilă în Windows 98 și 95, precum și în MS-DOS. Utilizarea memoriei este gestionată automat începând cu Windows XP. |
| Lacăt | Comanda de blocare este utilizată pentru a bloca o unitate, permițând accesul direct la disc pentru un program. Comanda de blocare este disponibilă numai în Windows 98 și 95. Blocarea unității nu mai este disponibilă din Windows XP. |
| Lodctr | Comanda lodctr este utilizată pentru a actualiza valorile de registry legate de contoarele de performanță. Comanda lodctr este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. |
| Logman | Comanda logman este utilizată pentru a crea și gestiona jurnalele de sesiune și performanță de urmărire a evenimentelor. Comanda logman acceptă, de asemenea, multe funcții ale Monitorului de performanță. Comanda logman este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Ieși din cont | Comanda de logoff este folosită pentru a încheia o sesiune. Comanda de deconectare este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. |
| Lpq | Comanda lpq afișează starea unei cozi de imprimare pe un computer care rulează Line Printer Daemon (LPD). Comanda lpq este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. Comanda lpq nu este disponibilă în mod implicit în Windows 8, 7 sau Vista, dar poate fi activată activând funcțiile LPD Print Service și LPR Port Monitor din Programs and Features din Control Panel. |
| Lpr | Comanda lpr este folosită pentru a trimite un fișier către un computer care rulează Line Printer Daemon (LPD). Comanda lpr este disponibilă în toate versiunile de Windows. Comanda lpr nu este disponibilă în mod implicit în Windows 8, 7 sau Vista, dar poate fi activată activând funcțiile LPD Print Service și LPR Port Monitor din Programs and Features din Control Panel. |
| Makecab | Comanda makecab este folosită pentru a comprima fără pierderi unul sau mai multe fișiere. Comanda makecab este uneori numită Cabinet Maker. Comanda makecab este disponibilă în Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista și Windows XP. Comanda makecab este aceeași cu comanda diantz, o comandă care a fost eliminată după Windows 7. |
| Manage-bde | Comanda manage-bde este utilizată pentru a configura BitLocker Drive Encryption din linia de comandă. Comanda manage-bde este disponibilă în Windows 8 și Windows 7. Un script cu numele manage-bde.wsf există în Windows Vista și poate fi utilizat cu comanda cscript pentru a efectua sarcini BitLocker din linia de comandă din sistemul de operare respectiv. |
| Md | Comanda md este versiunea scurtă a comenzii mkdir. The md command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mem | The mem command shows information about used and free memory areas and programs that are currently loaded into memory in the MS-DOS subsystem. The mem command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The mem command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Memmaker | The memmaker command is used to start MemMaker, a memory optimization tool. The memaker command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is automatically optimized beginning in Windows XP. |
| Mkdir | The mkdir command is used to create a new folder. The mkdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mklink | The mklink command is used to create a symbolic link. The mklink command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Mode | The mode command is used to configure system devices, most often COM and LPT ports. The mode command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mofcomp | The mofcomp command properly displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file. The mofcomp command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Mai mult | The more command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The more command can also be used to paginate the results of any other Command Prompt or MS-DOS command. The more command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mount | The mount command is used to mount Network File System (NFS) network shares. The mount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The mount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The mount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Mountvol | The mountvol command is used to display, create, or remove volume mount points. The mountvol command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Move | The move command is used to move one or files from one folder to another. The move command is also used to rename directories. The move command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mrinfo | The mrinfo command is used to provide information about a router's interfaces and neighbors. The mrinfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msav | The msav command starts Microsoft Antivirus. The msav command is only available in MS-DOS. Microsoft Antivirus was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Msbackup | The msbackup command starts Microsoft Backup, a tool used to back up and restore one or more files. The msbackup command is only available in MS-DOS. The msbackup command was replaced with Microsoft Backup beginning in Windows 95 and then Backup and Restore in later versions of Windows. |
| Mscdex | The mscdex command is used to provide CD-ROM access to MS-DOS. The mscdex command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows provides access to CD-ROM drives for the MS-DOS subsystem beginning in Windows XP, so the mscdex command is unnecessary in this and later operating systems. |
| Msd | The msd command starts Microsoft Diagnostics, a tool used to display information about your computer. The msd command is only available in MS-DOS. The msd command was replaced with System Information beginning in Windows 95. |
| Msg | The msg command is used to send a message to a user. The msg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msiexec | The msiexec command is used to start Windows Installer, a tool used to install and configure software. The msiexec command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Muiunattend | The muiunattend command starts the Multilanguage User Interface unattended setup process. The muiunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Nbtstat | The nbtstat command is used to show TCP/IP information and other statistical information about a remote computer. The nbtstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net | The net command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net1 | The net1 command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net1 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The net command should be used instead of the net1 command. The net1 command was made available in Windows NT and Windows 2000 as a temporary fix for a Y2K issue that the net command had, which was corrected before the release of Windows XP. The net1 command remains in later versions of Windows only for compatibility with older programs and scripts that utilized the command. |
| Netcfg | The netcfg command is used to install the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), a lightweight version of Windows used to deploy workstations. The netcfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Netsh | The netsh command is used to start Network Shell, a command-line utility used to manage the network configuration of the local, or a remote, computer. The netsh command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Netstat | The netstat command is most commonly used to display all open network connections and listening ports. The netstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Nfsadmin | The nfsadmin command is used to manage Server for NFS or Client for NFS from the command line. The nfsadmin command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The nfsadmin command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The nfsadmin command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Nlsfunc | The nlsfunc command is used to load information specific to a particular country or region. The nlsfunc command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The nlsfunc command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Nlsfunc is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Nltest | The nltest command is used to test secure channels between Windows computers in a domain and between domain controllers that are trusting other domains. The nltest command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Nslookup | The nslookup is most commonly used to display the hostname of an entered IP address. The nslookup command queries your configured DNS server to discover the IP address. The nslookup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ntbackup | The ntbackup command is used to perform various backup functions from the Command Prompt or from within a batch or script file. The ntbackup command is available in Windows XP. The ntbackup command was replaced with the wbadmin beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Ntsd | The ntsd command is used to perform certain command line debugging tasks. The ntsd command is available in Windows XP. The ntsd command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the addition of dump file support in Task Manager. |
| Ocsetup | The ocsetup command starts the Windows Optional Component Setup tool, used to install additional Windows features. The ocsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Beginning in Windows 8, Microsoft is depreciating the ocsetup command in favor of the dism command. |
| Openfiles | The openfiles command is used to display and disconnect open files and folders on a system. The openfiles command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| cale | The path command is used to display or set a specific path available to executable files. The path command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pathping | The pathping command functions much like the tracert command but will also report information about network latency and loss at each hop. The pathping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pauză | The pause command is used within a batch or script file to pause the processing of the file. When the pause command is used, a “Press any key to continue…” message displays in the command window. The pause command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pentnt | The pentnt command is used to detect floating point division errors in the Intel Pentium chip. The pentnt command is also used to enable floating point emulation and disable floating point hardware. The pentnt command is available in Windows XP. The pentnt command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the lack of Intel Pentium CPU use at the time of this operating system release. |
| Ping | The ping command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity. The ping command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Pkgmgr | The pkgmgr command is used to start the Windows Package Manager from the Command Prompt. Package Manager installs, uninstalls, configures, and updates features and packages for Windows. The pkgmgr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnpunattend | The pnpunattend command is used to automate the installation of hardware device drivers. The pnpunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnputil | The pnputil command is used to start the Microsoft PnP Utility, a tool used to install a Plug and Play device from the command line. The pnputil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Popd | The popd command is used to change the current directory to the one most recently stored by the pushd command. The popd command is most often utilized from within a batch or script file. The popd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Power | The power command is used to reduce the power consumed by a computer by monitoring software and hardware devices. The power command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The power command was replaced by operating system integrated power management functions beginning in Windows XP. |
| Powercfg | The powercfg command is used to manage the Windows power management settings from the command line. The powercfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Imprimare | The print command is used to print a specified text file to a specified printing device. The print command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Prompt | The prompt command is used to customize the appearance of the prompt text in Command Prompt or MS-DOS. The prompt command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pushd | The pushd command is used to store a directory for use, most commonly from within a batch or script program. The pushd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pwlauncher | The pwlauncher command is used to enable, disable, or show the status of your Windows To Go startup options. The pwlauncher command is available in Windows 8. |
| Qappsrv | The qappsrv command is used to display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers available on the network. The qappsrv command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Qbasic | The qbasic command starts QBasic, the MS-DOS based programming environment for the BASIC programming language. The qbasic command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The qbasic command is not installed by default with Windows 98 or 95 but is available from the installation disc or disks. |
| Qprocess | The qprocess command is used to display information about running processes. The qprocess command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Interogare | The query command is used to display the status of a specified service. The query command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Quser | The quser command is used to display information about users currently logged on to the system. The quser command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Qwinsta | The qwinsta command is used to display information about open Remote Desktop Sessions. The qwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasautou | The rasautou command is used to manage Remote Access Dialer AutoDial addresses. The rasautou command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasdial | The rasdial command is used to start or end a network connection for a Microsoft client. The rasdial command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rcp | The rcp command is used to copy files between a Windows computer and a system running the rshd daemon. The rcp command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rcp command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rcp command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rd | The rd command is the shorthand version of the rmdir command. The rd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rdpsign | The rdpsign command is used to sign a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) file. The rdpsign command is available in Windows 7. |
| Reagentc | The reagentc command is used to configure the Windows Recovery Environment (RE). The reagentc command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Recimg | The recimg command is used to create a custom refresh image. The recimg command is available in Windows 8. |
| Recover | The recover command is used to recover readable data from a bad or defective disk. The recover command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Reg | The reg command is used to manage the Windows Registry from the command line. The reg command can perform common registry functions like adding registry keys, exporting the registry, etc. The reg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Regini | The regini command is used to set or change registry permissions and registry values from the command line. The regini command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Register-cimprovider | The register-cimprovider command is used to register a Common Information Model (CIM) Provider in Windows. The register-cimprovider command is available in Windows 8. |
| Regsvr32 | The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file as a command component in the Windows Registry. The regsvr32 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Relog | The relog command is used to create new performance logs from data in existing performance logs. The relog command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rem | The rem command is used to record comments or remarks in a batch or script file. The rem command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Ren | The ren command is the shorthand version of the rename command. The ren command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rename | The rename command is used to change the name of the individual file that you specify. The rename command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Repair-bde | The repair-bde command is used to repair or decrypt a damaged drive that's been encrypted using BitLocker. The repair-bde command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Replace | The replace command is used to replace one or more files with one or more other files. The replace command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Resetați | The reset command, executed as reset session, is used to reset the session subsystem software and hardware to known initial values. The reset command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Restore | The restore command is used to restore files that were backed up using the backup command. The restore command is only available in MS-DOS. The backup command was only available up to MS-DOS 5.00 but the restore command was included by default with later versions of MS-DOS to provide a way to restore files that were backed up in previous versions of MS-DOS. |
| Rexec | The rexec command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rexec daemon. The rexec command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here. The rexec command is not available in Windows 7 but can be executed in Windows XP via Windows XP Mode if need be. |
| Rmdir | The rmdir command is used to delete an existing or completely empty folder. The rmdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Robocopy | The robocopy command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. This command is also called Robust File Copy. The robocopy command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The robocopy command is superior to both the copy command and the xcopy command because robocopy supports many more options. |
| Route | The route command is used to manipulate network routing tables. The route command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Rpcinfo | The rpcinfo command makes a remote procedure call (RPC) to an RPC server and reports what it finds. The rpcinfo command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The rpcinfo command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The rpcinfo command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rpcping | The rpcping command is used to ping a server using RPC. The rpcping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Rsh | The rsh command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rsh daemon. The rsh command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rsh command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rsm | The rsm command is used to manage media resources using Removable Storage. The rsm command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsm command was optional in Windows Vista and then removed in Windows 7 due to Removable Storage Manager being removed from the operating system. Search for the rsm command in the C:\Windows\winsxs folder in Windows Vista if you're having trouble executing the command. |
| Runas | The runas command is used to execute a program using another user's credentials. The runas command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rwinsta | The rwinsta command is the shorthand version of the reset session command. The rwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Sc | The sc command is used to configure information about services. The sc command communicates with the Service Control Manager. The sc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Scandisk | The scandisk command is used to start Microsoft ScanDisk, a disk repair program. The scandisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The scandisk command was replaced by the chkdsk command beginning in Windows XP. |
| Scanreg | The scanreg command starts Windows Registry Checker, a basic registry repair program and backup utility. The scanreg command is available in Windows 98 and Windows 95. The functions provided by the scanreg command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP due to changes in how the Windows Registry functions. |
| Schtasks | The schtasks command is used to schedule specified programs or commands to run at certain times. The schtasks command can be used to create, delete, query, change, run, and end scheduled tasks. The schtasks command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.? |
| Sdbinst | The sdbinst command is used to deploy customized SDB database files. The sdbinst command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Secedit | The secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security by comparing the current security configuration to a template. The secedit command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Set | The set command is used to display, enable, or disable environment variables in MS-DOS or from the Command Prompt. The set command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Setlocal | The setlocal command is used to start the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The setlocal command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Setspn | The setspn command is used to manage the Service Principal Names (SPN) for an Active Directory (AD) service account. The setspn command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Setver | The setver command is used to set the MS-DOS version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. The setver command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The setver command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Setx | The setx command is used to create or change environment variables in the user environment or the system environment. The setx command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sfc | The sfc command is used to verify and replace important Windows system files. The sfc command is also referred to as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker, depending on the operating system. The sfc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Shadow | The shadow command is used to monitor another Remote Desktop Services session. The shadow command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Acțiune | The share command is used to install file locking and file sharing functions in MS-DOS. The share command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The share command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Share is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Shift | The shift command is used to change the position of replaceable parameters in a batch or script file. The shift command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Showmount | The showmount command is used to display information about NFS mounted file systems. The showmount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The showmount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The showmount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Shutdown | The shutdown command can be used to shut down, restart, or log off the current system or a remote computer. The shutdown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Smartdrv | The smartdrv command installs and configures SMARTDrive, a disk caching utility for MS-DOS. The smartdrv command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Caching is automatic beginning in Windows XP, making the smartdrv command unnecessary. |
| Fel | The sort command is used to read data from a specified input, sort that data, and return the results of that sort to the Command Prompt screen, a file, or another output device. The sort command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Start | The start command is used to open a new command line window to run a specified program or command. The start command can also be used to start an application without creating a new window. The start command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Subst | The subst command is used to associate a local path with a drive letter. The subst command is a lot like the net use command except a local path is used instead of a shared network path. The subst command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The subst command replaced the assign command beginning with MS-DOS 6.0. |
| Sxstrace | The sxstrace command is used to start the WinSxs Tracing Utility, a programming diagnostic tool. The sxstrace command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sys | The sys command is used to copy the MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk. The sys command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The sys command is used most often to create a simple bootable disk or hard drive. The necessary system files for Windows are too large to fit on a disk, so the sys command was removed beginning in Windows XP. |
| Systeminfo | The systeminfo command is used to display basic Windows configuration information for the local or a remote computer. The systeminfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Takeown | The takedown command is used to regain access to a file that that an administrator was denied access to when reassigning ownership of the file. The takeown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Taskkill | The taskkill command is used to terminate a running task. The taskkill command is the command line equivalent of ending a process in Task Manager in Windows. The taskkill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tasklist | Displays a list of applications, services, and the Process ID (PID) currently running on either a local or a remote computer. The tasklist command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tcmsetup | The tcmsetup command is used to set up or disable the Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) client. The tcmsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Telnet | The telnet command is used to communicate with remote computers that use the Telnet protocol. The telnet command is available in all versions of Windows. The telnet command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tftp | The tftp command is used to transfer files to and from a remote computer that's running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) service or daemon. The tftp command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tftp command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the TFTP Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Time | The time command is used to show or change the current time. The time command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Timeout | The timeout command is typically used in a batch or script file to provide a specified timeout value during a procedure. The timeout command can also be used to ignore keypresses. The timeout command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Titlu | The title command is used to set the Command Prompt window title. The title command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tlntadmn | The tlntadmn command is used to administer a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. The tlntadmn command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tlntadmn command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Server Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tpmvscmgr | The tpmvscmgr command is used to create and destroy TPM virtual smart cards. The tpmvscmgr command is available in Windows 8. |
| Tracerpt | The tracerpt command is used to process event trace logs or real-time data from instrumented event trace providers. The tracerpt command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tracert | The tracert command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to a specified remote computer with increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values and displays the IP address and hostname, if available, of the router interfaces between the source and destination. The tracert command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Copac | The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path. The tree command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Tscon | The tscon command is used to attach a user session to a Remote Desktop session. The tscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsdiscon | The tsdiscon command is used to disconnect a Remote Desktop session. The tsdiscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tskill | The tskill command is used to end the specified process. The tskill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsshutdn | The tsshutdn command is used to remotely shut down or restart a terminal server. The tsshutdn command is available in Windows XP. The ability to shut down a computer remotely is also available in the more powerful shutdown command, so tsshutdn was removed beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Tip | The type command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The type command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Typeperf | The typerperf command displays performance data in the Command Prompt window or writes the data to specified log file. The typeperf command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tzutil | The tzutil command is used to display or configure the current system's time zone. The tzutil command can also be used to enable or disable Daylight Saving Time adjustments. The tzutil command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Umount | The umount command is used to remove Network File System (NFS) mounted network shares. The umount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The umount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The umount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Undelete | The undelete command is used to undo a deletion performed with the MS-DOS delete command. The undelete command is only available in MS-DOS. The undelete command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to the availability of the Recycle Bin in Windows. Additionally, free file recovery programs are available from third-party software makers. |
| Unformat | The unformat command is used to undo the formatting on a drive performed by the MS-DOS format command. The unformat command is only available in MS-DOS. The unformat command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to file system changes. |
| Unlock | The unlock command is used to unlock a drive, disabling direct disk access for a program. The unlock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP. |
| Unlodctr | The unlodctr command removes Explain text and Performance counter names for a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. The unlodctr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Vaultcmd | The vaultcmd command is used to create, remove, and show stored credentials. The vaultcmd command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Ver | The ver command is used to display the current Windows or MS-DOS version number. The ver command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Verify | The verify command is used to enable or disable the ability of Command Prompt, or MS-DOS, to verify that files are written correctly to a disk. The verify command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vol | The vol command shows the volume label and serial number of a specified disk, assuming this information exists. The vol command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vsafe | The vsafe command is used to start VSafe, a basic virus protection system for MS-DOS. The vsafe command is only available in MS-DOS. VSafe was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Vssadmin | The vssadmin command starts the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool which displays current volume shadow copy backups and all installed shadow copy writers and providers. The vssadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| W32tm | The w32tm command is used to diagnose issues with Windows Time. The w32tm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Waitfor | The waitfor command is used to send or wait for a signal on a system. The waitfor command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wbadmin | The wbadmin command is used to start and stop backup jobs, display details about a previous backup, list the items within a backup, and report on the status of a currently running backup. The wbadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The wbadmin command replaced the ntbackup command beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Wecutil | The wecutil command is used to manage subscriptions to events that are forwarded from WS-Management supported computers. The wecutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wevtutil | The wevtutil command starts the Windows Events Command Line Utility which is used to manage event logs and publishers. The wevtutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Unde | The where command is used to search for files that match a specified pattern. The where command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Whoami | The whoami command is used to retrieve user name and group information on a network. The whoami command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winmgmt | The winmgmt command starts the command line version of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. The winmgmt command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Winrm | The winrm command is used to start the command line version of Windows Remote Management, used to manage secure communications with local and remote computers using web services. The winrm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winrs | The winrs command is used to open a secure command window with a remote host. The winrs command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winsat | The winsat command starts the Windows System Assessment Tool, a program that assesses various features, attributes, and capabilities of a computer running Windows. The winsat command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wmic | The wmic command starts the Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC), a scripting interface that simplifies the use of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and systems managed via WMI. The wmic command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Wsmanhttpconfig | The wsmanhttpconfig command is used to manage aspects of the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service. The wsmanhttpconfig command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Xcopy | The xcopy command can copy one or more files or directory trees from one location to another. The xcopy command is generally considered a more “powerful” version of the copy command through the robocopy command trumps even xcopy. The xcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. A command by the name of xcopy32 existed in Windows 95 and Windows 98. To avoid a long and confusing explanation here, just know that no matter if you executed the xcopy command or the xcopy32 command, you were always executing the most updated version of the command. |
| Xwizard | The xwizard command, short for Extensible Wizard, is used to register data in Windows, often from a preconfigured XML file. The xwizard command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
The above list is a set of most essential commands of command prompt. To view or download a PDF version of complete set of windows commands, please click on the below button.

Descărcați ca PDF
Pentru mai multe astfel de sfaturi, trucuri și actualizări legate de tehnologie, abonați-vă la Tweak Library și, dacă vă plac mai mult videoclipurile legate de tehnologie, vizionați și abonați-vă la canalul nostru YouTube . Ne puteți contacta și pe Facebook și Pinterest .
