Usa il prompt dei comandi come un professionista - Tutto sul prompt dei comandi
Pubblicato: 2019-05-21Con il lancio di Windows 10, Microsoft ha lentamente spostato la riga di comando fuori dall'interfaccia di Windows. Il motivo era che la riga di comando era uno strumento antiquato e più non necessario dell'era dell'input testuale. Tuttavia, molti comandi sono ancora utili e Windows 10 ha persino aggiunto nuove funzionalità al mondo della riga di comando. Ora il prompt dei comandi è stato riprogettato in PowerShell, un'app che può essere utilizzata come il prompt dei comandi. È un'app colorata che sostituirà il prompt dei comandi anche se al momento puoi ancora utilizzare il prompt dei comandi. Questi trucchi del prompt dei comandi sono davvero utili per gli amministratori di computer e danno loro accesso per svolgere professionalmente diverse attività.
Come aprire il prompt dei comandi
Premi Win + R -> digita "cmd" -> premi "Invio"
Nella barra di ricerca, digita "cmd" premi "Invio".
Se desideri aprire il prompt dei comandi come amministratore, nella barra di ricerca, digita "cmd" e non appena viene visualizzato "Applicazione di comando", fai clic con il pulsante destro del mouse su di esso e fai clic su "Esegui come amministratore".
Leggi anche: Tutto sulle scorciatoie da tastiera di Windows 10
Come trovare tutti i comandi sul prompt dei comandi
Per trovare i comandi rilevanti e la loro sintassi nel prompt dei comandi, possiamo digitare 'cmd /?' oppure digita un comando seguito da '/?' ad esempio 'ipconfig /?' apre l'elenco di opzioni e la sintassi con le relative azioni. Questo interprete di comandi è utile per apprendere nuovi comandi al prompt dei comandi.
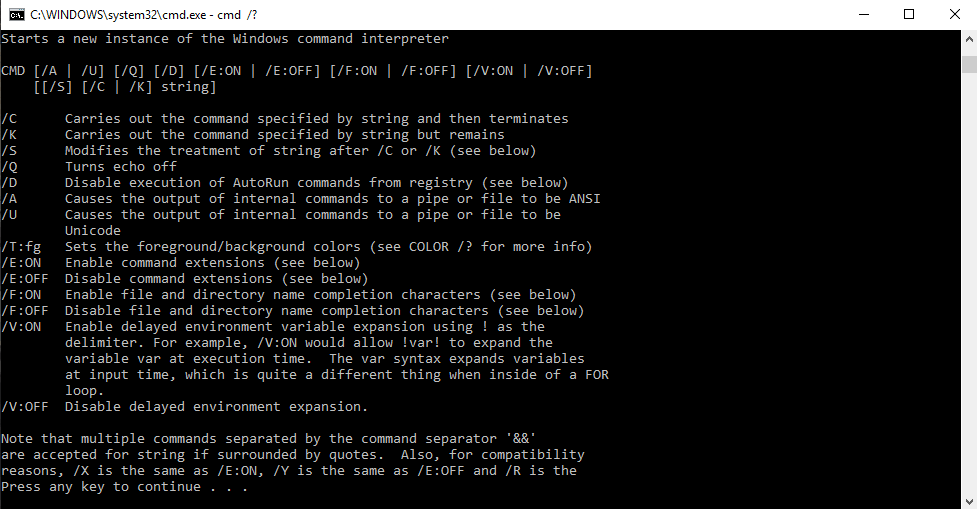
Usando la sintassi
cmd [/c|/k] [/s] [/q] [/d] [/a|/u] [/t:{<B><F>|<F>}] [/e:{on|off}] [/f:{on|off}] [/v:{on|off}] [<String>]
Parametri
| Parametro | Descrizione |
| /C | Esegue il comando specificato da String e poi si ferma. |
| /K | Esegue il comando specificato da String e continua. |
| /S | Modifica il trattamento di String dopo /c o /k. |
| /Q | Disattiva l'eco. |
| /D | Disabilita l'esecuzione dei comandi di esecuzione automatica. |
| /un | Formatta l'output del comando interno in una pipe o in un file come ANSI (American National Standards Institute). |
| /u | Formatta l'output del comando interno in una pipe o in un file come Unicode. |
| /t:{<B><F>|<F>} | Imposta i colori dello sfondo (B) e del primo piano (F). |
| /eone | Abilita le estensioni dei comandi. |
| /e: spento | Disabilita le estensioni dei comandi. |
| /f:on | Consente il completamento del nome di file e directory. |
| /f: disattivato | Disabilita il completamento del nome di file e directory. |
| /v:on | Consente l'espansione ritardata delle variabili di ambiente. |
| /v: disattivato | Disabilita l'espansione ritardata della variabile di ambiente. |
| <Stringa> | Specifica il comando che si desidera eseguire. |
| /? | Visualizza la guida al prompt dei comandi. |
La tabella seguente elenca le cifre esadecimali valide che è possibile utilizzare come valori per <B> e <F>
| Valore | Colore |
| 0 | Nero |
| 1 | Blu |
| 2 | Verde |
| 3 | Acqua |
| 4 | rosso |
| 5 | Viola |
| 6 | Giallo |
| 7 | bianco |
| 8 | Grigio |
| 9 | Azzurro |
| un | Verde chiaro |
| B | Acqua chiara |
| C | Rosso chiaro |
| D | Viola chiaro |
| e | Giallo chiaro |
| F | Bianco brillante |
Ecco un elenco completo dei comandi del prompt dei comandi. Puoi anche scaricare tutti i comandi con la loro sintassi dal link in fondo a questo articolo.
| Comando | Descrizione |
| Aggiungere | Il comando append può essere utilizzato dai programmi per aprire i file in un'altra directory come se si trovassero nella directory corrente. Il comando append è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando append non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| Arp | Il comando arp viene utilizzato per visualizzare o modificare le voci nella cache ARP. Il comando arp è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. |
| Assoc | Il comando assoc viene utilizzato per visualizzare o modificare il tipo di file associato a una particolare estensione di file. Il comando assoc è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| A | Il comando at viene utilizzato per pianificare comandi e altri programmi da eseguire in una data e ora specifica. Il comando at è disponibile in Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. A partire da Windows 8, la pianificazione delle attività della riga di comando dovrebbe invece essere completata con il comando schtasks. |
| Atmad | Il comando atmadm viene utilizzato per visualizzare le informazioni relative alle connessioni in modalità di trasferimento asincrono (ATM) sul sistema. Il comando atmadm è disponibile in Windows XP. Il supporto per ATM è stato rimosso a partire da Windows Vista, rendendo superfluo il comando atmadm. |
| Attributo | Il comando attrib viene utilizzato per modificare gli attributi di un singolo file o di una directory. Il comando attrib è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Auditpol | Il comando auditpol viene utilizzato per visualizzare o modificare le politiche di audit. Il comando auditpol è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Bcdboot | Il comando bcdboot viene utilizzato per copiare i file di avvio nella partizione di sistema e per creare un nuovo archivio BCD di sistema. Il comando bcdboot è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Bcdedit | Il comando bcdedit viene utilizzato per visualizzare o apportare modifiche ai dati di configurazione di avvio. Il comando bcdedit è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. Il comando bcdedit ha sostituito il comando bootcfg a partire da Windows Vista. |
| Bdehdcfg | Il comando bdehdcfg viene utilizzato per preparare un disco rigido per Crittografia unità BitLocker. Il comando bdehdcfg è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Bitsadmin | Il comando bitsadmin viene utilizzato per creare, gestire e monitorare i lavori di download e caricamento. Il comando bitsadmin è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. Sebbene il comando bitsadmin sia disponibile sia in Windows 8 che in Windows 7, viene gradualmente eliminato. È invece necessario utilizzare i cmdlet BITS PowerShell. |
| Bootcfg | Il comando bootcfg viene utilizzato per creare, modificare o visualizzare il contenuto del file boot.ini, un file nascosto utilizzato per identificare in quale cartella, su quale partizione e su quale disco rigido si trova Windows. Il comando bootcfg è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando bootcfg è stato sostituito dal comando bcdedit a partire da Windows Vista. Bootcfg è ancora disponibile in Windows 8, 7 e Vista, ma non ha alcun valore reale poiché boot.ini non viene utilizzato in questi sistemi operativi. |
| Bootsect | Il comando bootsect viene utilizzato per configurare il codice di avvio principale su uno compatibile con BOOTMGR (Vista e versioni successive) o NTLDR (XP e versioni precedenti). Il comando bootsect è disponibile in Windows 8. Il comando bootsect è disponibile anche in Windows 7 e Windows Vista, ma solo dal prompt dei comandi disponibile in Opzioni di ripristino del sistema. |
| Rottura | Il comando break imposta o cancella il controllo CTRL + C esteso sui sistemi DOS. Il comando break è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. Il comando break è disponibile in Windows XP e versioni successive di Windows per garantire la compatibilità con i file MS-DOS, ma non ha alcun effetto in Windows stesso. |
| Cacl | Il comando cacls viene utilizzato per visualizzare o modificare gli elenchi di controllo di accesso dei file. Il comando cacls è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando cacls viene gradualmente eliminato a favore del comando icacls, che dovrebbe essere utilizzato invece in tutte le versioni di Windows dopo Windows XP. |
| Chiamata | Il comando call viene utilizzato per eseguire uno script o un programma batch dall'interno di un altro script o programma batch. Il comando call è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. Il comando call non ha effetto al di fuori di uno script o di un file batch. In altre parole, l'esecuzione del comando di chiamata al prompt dei comandi o al prompt di MS-DOS non avrà alcun effetto. |
| Cd | Il comando cd è la versione abbreviata del comando chdir. Il comando cd è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Certoq | Il comando certreq viene utilizzato per eseguire varie funzioni di certificazione dell'autorità di certificazione (CA). Il comando certreq è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Certutil | Il comando certutil viene utilizzato per eseguire il dump e visualizzare le informazioni di configurazione dell'autorità di certificazione (CA) oltre ad altre funzioni della CA. Il comando certutil è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Modificare | Il comando di modifica modifica varie impostazioni del server terminal come le modalità di installazione, i mapping delle porte COM e gli accessi. Il comando di modifica è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| cap | Il comando chcp visualizza o configura il numero di codepage attivo. Il comando chcp è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Chdir | Il comando chdir viene utilizzato per visualizzare la lettera di unità e la cartella in cui ci si trova attualmente. Chdir può anche essere utilizzato per modificare l'unità e/o la directory in cui si desidera lavorare. Il comando chdir è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, come così come in MS-DOS. |
| Controllare l'isolamento della rete | Il comando checknetisolation viene utilizzato per testare le app che richiedono funzionalità di rete. Il comando checknetisolation è disponibile in Windows 8. |
| Chglogon | Il comando chglogon abilita, disabilita o svuota gli accessi alla sessione del server terminal. Il comando chglogon è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. L'esecuzione del comando chglogon equivale all'esecuzione di change logon. |
| Chgport | Il comando chgport può essere utilizzato per visualizzare o modificare i mapping delle porte COM per la compatibilità DOS. Il comando chgport è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. L'esecuzione del comando chgport equivale all'esecuzione di change port. |
| Chgusr | Il comando chgusr viene utilizzato per modificare la modalità di installazione per il server terminal. Il comando chgusr è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. L'esecuzione del comando chgusr equivale all'esecuzione di change user. |
| Chkdsk | Il comando chkdsk, spesso indicato come check disk, viene utilizzato per identificare e correggere determinati errori del disco rigido. Il comando chkdsk è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Chkntfs | Il comando chkntfs viene utilizzato per configurare o visualizzare il controllo dell'unità disco durante il processo di avvio di Windows. Il comando chkntfs è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Scelta | Il comando di scelta viene utilizzato all'interno di uno script o di un programma batch per fornire un elenco di scelte e restituire il valore di tale scelta al programma. Il comando di scelta è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni di Windows ad eccezione di Windows XP. Utilizzare il comando set con l'opzione /p al posto del comando choice nei file batch e negli script che si prevede di utilizzare in Windows XP. |
| Cifra | Il comando cipher mostra o modifica lo stato di crittografia di file e cartelle su partizioni NTFS. Il comando di cifratura è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Clip | Il comando clip viene utilizzato per reindirizzare l'output da qualsiasi comando agli appunti in Windows. Il comando clip è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| cl | Il comando cls cancella lo schermo da tutti i comandi immessi in precedenza e altro testo. Il comando cls è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| cmd | Il comando cmd avvia una nuova istanza dell'interprete dei comandi cmd.exe. Il comando cmd è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| tasto Cmd | Il comando cmdkey viene utilizzato per mostrare, creare e rimuovere i nomi utente e le password archiviati. Il comando cmdkey è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Cmstp | Il comando cmstp installa o disinstalla un profilo di servizio di Connection Manager. Il comando cmstp è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Colore | Il comando colore viene utilizzato per modificare i colori del testo e dello sfondo all'interno della finestra del prompt dei comandi. Il comando colore è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Comando | Il comando 'comando' avvia una nuova istanza dell'interprete dei comandi command.com. Il comando "comando" è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando "comando" non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| comp | Il comando comp viene utilizzato per confrontare il contenuto di due file o insiemi di file. Il comando comp è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Compatto | Il comando compact viene utilizzato per mostrare o modificare lo stato di compressione di file e directory su partizioni NTFS. Il comando compact è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Convertire | Il comando convert viene utilizzato per convertire i volumi formattati FAT o FAT32 nel formato NTFS. Il comando convert è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| copia | Il comando copy fa semplicemente questo: copia uno o più file da una posizione all'altra. Il comando copy è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. Il comando xcopy è considerato una versione più "potente" del comando copy. |
| Cscript | Il comando cscript viene utilizzato per eseguire script tramite Microsoft Script Host. Il comando cscript è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. Il comando cscript è comunemente usato per gestire le stampanti dalla riga di comando usando script come prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmngr.vbs e altri. |
| Ctty | Il comando ctty viene utilizzato per modificare i dispositivi di input e output predefiniti per il sistema. Il comando ctty è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95 nonché in MS-DOS. Le funzioni fornite dal comando ctty non erano più necessarie a partire da Windows XP perché l'interprete command.com (MS-DOS) non è più l'interprete della riga di comando predefinito. |
| Data | Il comando date viene utilizzato per mostrare o modificare la data corrente. Il comando date è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Dblspace | Il comando dblspace viene utilizzato per creare o configurare unità compresse DoubleSpace. Il comando dblspace è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. DriveSpace, eseguito utilizzando il comando drvspace, è una versione aggiornata di DoubleSpace. Windows gestisce nativamente la compressione a partire da Windows XP. |
| Debug | Il comando debug avvia Debug, un'applicazione a riga di comando utilizzata per testare e modificare i programmi. Il comando di debug è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando debug non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| deframmenta | Il comando deframmenta viene utilizzato per deframmentare un'unità specificata. Il comando deframmentazione è la versione da riga di comando dell'Utilità di deframmentazione dischi di Microsoft. Il comando deframmentazione è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Del | Il comando del viene utilizzato per eliminare uno o più file. Il comando del è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. Il comando del è lo stesso del comando di cancellazione. |
| Deltree | Il comando deltree viene utilizzato per eliminare una directory e tutti i file e le sottodirectory al suo interno. Il comando deltree è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. A partire da Windows XP, una cartella ei relativi file e sottocartelle possono essere rimossi utilizzando la funzione /s del comando rmdir. Deltree non era più necessario con questa nuova abilità rmdir, quindi il comando è stato rimosso. |
| Diantz | Il comando diantz viene utilizzato per comprimere senza perdita di dati uno o più file. Il comando diantz è talvolta chiamato Cabinet Maker. Il comando diantz è disponibile in Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando diantz è lo stesso del comando makecab. |
| Dir | Il comando dir viene utilizzato per visualizzare un elenco di file e cartelle contenuti all'interno della cartella in cui stai attualmente lavorando. Il comando dir mostra anche altre informazioni importanti come il numero di serie del disco rigido, il numero totale di file elencati, la loro dimensione combinata, la quantità totale di spazio libero rimasto sull'unità e altro ancora. Il comando dir è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Diskcomp | Il comando diskcomp viene utilizzato per confrontare il contenuto di due floppy disk. Il comando diskcomp è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Copia disco | Il comando diskcopy viene utilizzato per copiare l'intero contenuto di un floppy disk su un altro. Il comando diskcopy è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| parte del disco | Il comando diskpart viene utilizzato per creare, gestire ed eliminare le partizioni del disco rigido. Il comando diskpart è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando diskpart ha sostituito il comando fdisk a partire da Windows XP. |
| Diskperf | Il comando diskperf viene utilizzato per gestire in remoto i contatori delle prestazioni del disco. Il comando diskperf è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Discordia | Il comando diskraid avvia lo strumento DiskRAID utilizzato per gestire e configurare gli array RAID. Il comando diskraid è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Dism | Il comando dism avvia lo strumento di gestione e manutenzione delle immagini di distribuzione (DISM). Lo strumento DISM viene utilizzato per gestire le funzionalità nelle immagini di Windows. Il comando dism è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Dispdiag | Il comando dispdiag viene utilizzato per generare un registro di informazioni sul sistema di visualizzazione. Il comando dispdiag è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Dunisciti | Il comando djoin viene utilizzato per creare un nuovo account computer in un dominio. Il comando djoin è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Doskey | Il comando doskey viene utilizzato per modificare le righe di comando, creare macro e richiamare comandi immessi in precedenza. Il comando doskey è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Dosshell | Il comando dosshell avvia DOS Shell, uno strumento grafico di gestione dei file per MS-DOS. Il comando dosshell è disponibile in Windows 95 (in modalità MS-DOS) e anche in MS-DOS versione 6.0 e versioni successive di MS-DOS che sono state aggiornate dalle versioni precedenti che contenevano il comando dosshell. Un file manager grafico, Windows Explorer, è diventato parte integrante del sistema operativo a partire da Windows 95. |
| Dosx | Il comando dosx viene utilizzato per avviare DOS Protected Mode Interface (DPMI), una modalità speciale progettata per fornire alle applicazioni MS-DOS l'accesso a più dei 640 KB normalmente consentiti. Il comando dosx è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando dosx non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. Il comando dosx e DPMI sono disponibili solo in Windows per supportare i vecchi programmi MS-DOS. |
| Query driver | Il comando driverquery viene utilizzato per mostrare un elenco di tutti i driver installati. Il comando driverquery è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Drvspace | Il comando drvspace viene utilizzato per creare o configurare unità compresse DriveSpace. Il comando drvspace è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. DriveSpace è una versione aggiornata di DoubleSpace, eseguita utilizzando il comando dblspace. Windows gestisce nativamente la compressione a partire da Windows XP. |
| Eco | Il comando echo viene utilizzato per mostrare i messaggi, più comunemente da file di script o batch. Il comando echo può essere utilizzato anche per attivare o disattivare la funzione di eco. Il comando echo è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Modificare | Il comando di modifica avvia lo strumento Editor di MS-DOS utilizzato per creare e modificare file di testo. Il comando di modifica è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando di modifica non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| Edlin | Il comando edlin avvia lo strumento Edlin che viene utilizzato per creare e modificare file di testo dalla riga di comando. Il comando edlin è disponibile in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows ma non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. In MS-DOS, il comando edlin è disponibile solo fino a MS-DOS 5.0, quindi a meno che la versione successiva di MS-DOS non sia stata aggiornata da 5.0 o precedenti, non vedrai il comando edlin. |
| Emm386 | Il comando emm386 viene utilizzato per fornire a MS-DOS l'accesso a più di 640 KB di memoria. Il comando emm386 è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. Windows stesso ha accesso alla memoria estesa ed espansa a partire da Windows 95. |
| Endlocal | Il comando endlocal viene utilizzato per terminare la localizzazione delle modifiche all'ambiente all'interno di un batch o di un file di script. Il comando endlocal è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Cancellare | Il comando di cancellazione viene utilizzato per eliminare uno o più file. Il comando di cancellazione è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. Il comando di cancellazione è lo stesso del comando del. |
| Esentutl | Il comando esentutl viene utilizzato per gestire i database di Extensible Storage Engine. Il comando esentutl è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Creazione di eventi | Il comando eventcreate viene utilizzato per creare un evento personalizzato in un registro eventi. Il comando eventcreate è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Attivatori di eventi | Il comando eventtriggers viene utilizzato per configurare e visualizzare i trigger di eventi. Il comando eventtriggers è disponibile in Windows XP. A partire da Windows Vista, i trigger di eventi vengono creati utilizzando la funzionalità Allega attività a questo evento nel Visualizzatore eventi, rendendo superfluo il comando eventtriggers. |
| Exe2bin | Il comando exe2bin viene utilizzato per convertire un file di tipo EXE (file eseguibile) in un file binario. Il comando exe2bin è disponibile nelle versioni a 32 bit di Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando exe2bin non è disponibile in nessuna versione a 64 bit di Windows. |
| Uscita | Il comando exit viene utilizzato per terminare la sessione cmd.exe (Windows) o command.com (MS-DOS) in cui stai attualmente lavorando. Il comando exit è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS . |
| Espandere | Il comando di espansione viene utilizzato per estrarre i file e le cartelle contenuti nei file CAB (Microsoft Cabinet). Il comando expand è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni di Windows. Il comando expand non è disponibile nella versione a 64 bit di Windows XP. |
| Estrarre32 | Il comando extrac32 viene utilizzato per estrarre i file e le cartelle contenuti nei file Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Il comando extrac32 è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. Il comando extrac32 è in realtà un programma di estrazione CAB per l'utilizzo da Internet Explorer, ma può essere utilizzato per estrarre qualsiasi file Microsoft Cabinet. Se possibile, utilizzare il comando expand invece del comando extrac32. |
| Estratto | Il comando extract viene utilizzato per estrarre i file e le cartelle contenuti nei file CAB (Microsoft Cabinet). Il comando di estrazione è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95. Il comando di estrazione è stato sostituito dal comando di espansione a partire da Windows XP. |
| Aiuto veloce | Il comando fasthelp fornisce informazioni più dettagliate su qualsiasi altro comando MS-DOS. Il comando fasthelp è disponibile solo in MS-DOS. Il comando help ha sostituito il comando fasthelp a partire da Windows 95. |
| Fastopen | Il comando fastopen viene utilizzato per aggiungere la posizione del disco rigido di un programma a un elenco speciale archiviato in memoria, migliorando potenzialmente il tempo di avvio del programma eliminando la necessità di MS-DOS per individuare l'applicazione sull'unità. Il comando fastopen è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando fastopen non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. Fastopen è disponibile solo in Windows 8, 7, Vista e XP per supportare i file MS-DOS meno recenti. |
| FC | Il comando fc viene utilizzato per confrontare due singoli o insiemi di file e quindi mostrare le differenze tra di loro. Il comando fc è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Fdisk | Il comando fdisk viene utilizzato per creare, gestire ed eliminare le partizioni del disco rigido. Il comando fdisk è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. Il comando fdisk è stato sostituito dal comando diskpart a partire da Windows XP. La gestione delle partizioni è disponibile anche da Gestione disco in Windows 8, 7, Vista e XP. |
| Trovare | Il comando trova viene utilizzato per cercare una stringa di testo specificata in uno o più file. Il comando trova è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Trovastr | Il comando findstr viene utilizzato per trovare modelli di stringhe di testo in uno o più file. Il comando findstr è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Dito | Il comando finger viene utilizzato per restituire informazioni su uno o più utenti su un computer remoto che esegue il servizio Finger. Il comando finger è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Fltmc | Il comando fltmc viene utilizzato per caricare, scaricare, elencare e gestire in altro modo i driver del filtro. Il comando fltmc è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Fonduta | Il comando fonduta, abbreviazione di Features on Demand User Experience Tool, viene utilizzato per installare una delle numerose funzionalità opzionali di Windows dalla riga di comando. Il comando fonduta è disponibile in Windows 8. Le funzionalità di Windows opzionali possono anche essere installate dall'applet Programmi e funzionalità nel Pannello di controllo. |
| Per | Il comando for viene utilizzato per eseguire un comando specificato per ogni file in un set di file. Il comando for viene spesso utilizzato all'interno di un batch o di un file di script. Il comando for è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Forzati | Il comando forcedos viene utilizzato per avviare il programma specificato nel sottosistema MS-DOS. Il comando forcedos è disponibile solo nelle versioni a 32 bit di Windows XP. Il comando forcedos viene utilizzato solo per i programmi MS-DOS non riconosciuti come tali da Windows XP. |
| Forfile | Il comando forfiles seleziona uno o più file su cui eseguire un comando specificato. Il comando forfiles viene spesso utilizzato all'interno di un batch o di un file di script. Il comando forfiles è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Formato | Il comando format viene utilizzato per formattare un'unità nel file system specificato. Il comando format è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. La formattazione dell'unità è disponibile anche da Gestione disco in Windows 8, 7, Vista e XP. |
| Fsutil | Il comando fsutil viene utilizzato per eseguire varie attività del file system FAT e NTFS come la gestione dei punti di analisi e dei file sparsi, lo smontaggio di un volume e l'estensione di un volume. Il comando fsutil è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Ftp | Il comando ftp può essere utilizzato per trasferire file da e verso un altro computer. Il computer remoto deve funzionare come un server FTP. Il comando ftp è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. |
| Tipo F | Il comando ftype viene utilizzato per definire un programma predefinito per aprire un tipo di file specificato. Il comando ftype è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Getmac | Il comando getmac viene utilizzato per visualizzare l'indirizzo MAC (Media Access Control) di tutti i controller di rete su un sistema. Il comando getmac è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Vai a | Il comando goto viene utilizzato in un batch o in un file di script per indirizzare il processo del comando a una riga etichettata nello script. Il comando goto è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Gpresultato | Il comando gpresult viene utilizzato per visualizzare le impostazioni dei criteri di gruppo. Il comando gpresult è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Aggiornamento | Il comando gpupdate viene utilizzato per aggiornare le impostazioni dei criteri di gruppo. Il comando gpupdate è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Innestabile | Il comando graftabl viene utilizzato per consentire a Windows di visualizzare un set di caratteri esteso in modalità grafica. Il comando graftabl è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows e in MS-DOS fino alla versione 5.0. Il comando graftabl non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| Grafica | Il comando graphics viene utilizzato per caricare un programma in grado di stampare grafica. Il comando grafico è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando di grafica non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| Aiuto | Il comando della guida fornisce informazioni più dettagliate su qualsiasi altro prompt dei comandi o comandi MS-DOS. Il comando di aiuto è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Nome host | Il comando hostname visualizza il nome dell'host corrente. Il comando hostname è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Hwrcomp | Il comando hwrcomp viene utilizzato per compilare dizionari personalizzati per il riconoscimento della grafia. Il comando hwrcomp è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Hwrreg | Il comando hwrreg viene utilizzato per installare un dizionario personalizzato precedentemente compilato per il riconoscimento della grafia. Il comando hwrreg è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Icacl | Il comando icacls viene utilizzato per visualizzare o modificare gli elenchi di controllo di accesso dei file. Il comando icacls è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. Il comando icacls è una versione aggiornata del comando cacls. |
| Se | Il comando if viene utilizzato per eseguire funzioni condizionali in un file batch. Il comando if è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Interlink | Il comando interlnk viene utilizzato per collegare due computer tramite una connessione seriale o parallela per condividere file e stampanti. Il comando interlnk è disponibile solo in MS-DOS. La possibilità di collegare direttamente due computer è gestita dalle funzioni di rete in tutte le versioni di Windows. |
| Intersvr | Il comando intersvr viene utilizzato per avviare il server Interlnk e per copiare i file Interlnk da un computer all'altro. Il comando intersvr è disponibile solo in MS-DOS. La possibilità di collegare direttamente due computer è gestita dalle funzioni di rete in tutte le versioni di Windows. |
| Ipconfig | Il comando ipconfig viene utilizzato per visualizzare informazioni IP dettagliate per ciascuna scheda di rete che utilizza TCP/IP. Il comando ipconfig può essere utilizzato anche per rilasciare e rinnovare gli indirizzi IP sui sistemi configurati per riceverli tramite un server DHCP. Il comando ipconfig è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. |
| Ipxroute | Il comando ipxroute viene utilizzato per visualizzare e modificare le informazioni sulle tabelle di routing IPX. Il comando ipxroute è disponibile in Windows XP. Microsoft ha rimosso il client NetWare nativo a partire da Windows Vista, rimuovendo anche il comando ipxroute associato. |
| Irfp | Il comando irftp viene utilizzato per trasmettere file su un collegamento a infrarossi. Il comando irftp è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Iscsicli | Il comando iscsicli avvia Microsoft iSCSI Initiator, utilizzato per gestire iSCSI. Il comando iscsicli è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Kb16 | Il comando kb16 viene utilizzato per supportare i file MS-DOS che devono configurare una tastiera per una lingua specifica. Il comando kb16 è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando kb16 non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. Il comando kb16 ha sostituito il comando keyb a partire da Windows XP, ma esiste solo per supportare i file MS-DOS meno recenti. |
| Keyb | Il comando keyb viene utilizzato per configurare una tastiera per una lingua specifica. Il comando keyb è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. Vedere il comando kb16 per un comando equivalente nelle versioni successive di Windows. Le impostazioni della lingua della tastiera sono gestite dalle applet del Pannello di controllo di Regione e lingua o Opzioni internazionali e della lingua (a seconda della versione di Windows) in Windows a partire da Windows XP. |
| Klist | Il comando klist viene utilizzato per elencare i ticket di servizio Kerberos. Il comando klist può essere utilizzato anche per eliminare i ticket Kerberos. Il comando klist è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Ksetup | Il comando ksetup viene utilizzato per configurare le connessioni a un server Kerberos. Il comando ksetup è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. |
| Ktmutil | Il comando ktmutil avvia l'utilità Kernel Transaction Manager. Il comando ktmutil è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7 e Windows Vista. |
| Etichetta | Il comando label viene utilizzato per gestire l'etichetta del volume di un disco. Il comando label è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Lh | Il comando lh è la versione abbreviata del comando loadhigh. Il comando lh è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| Schema di licenza | Il comando licensingdiag è uno strumento utilizzato per generare un registro basato su testo e altri file di dati che contengono l'attivazione del prodotto e altre informazioni sulla licenza di Windows. Il comando licensingdiag è disponibile in Windows 8. |
| Loadfix | Il comando loadfix viene utilizzato per caricare il programma specificato nei primi 64 KB di memoria e quindi esegue il programma. Il comando loadfix è disponibile in MS-DOS e in tutte le versioni a 32 bit di Windows. Il comando loadfix non è disponibile nelle versioni a 64 bit di Windows. |
| Carico alto | Il comando loadhigh viene utilizzato per caricare un programma nella memoria elevata e di solito viene utilizzato all'interno del file autoexec.bat. Il comando loadhigh è disponibile in Windows 98 e 95, nonché in MS-DOS. L'utilizzo della memoria viene gestito automaticamente a partire da Windows XP. |
| Serratura | Il comando lock viene utilizzato per bloccare un'unità, consentendo l'accesso diretto al disco per un programma. Il comando di blocco è disponibile solo in Windows 98 e 95. Il blocco dell'unità non è più disponibile a partire da Windows XP. |
| Lodctr | Il comando lodctr viene utilizzato per aggiornare i valori del registro relativi ai contatori delle prestazioni. Il comando lodctr è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. |
| Logman | Il comando logman viene utilizzato per creare e gestire i registri delle sessioni di traccia degli eventi e delle prestazioni. Il comando logman supporta anche molte funzioni di Performance Monitor. Il comando logman è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Disconnettersi | Il comando di disconnessione viene utilizzato per terminare una sessione. Il comando di disconnessione è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. |
| Lpq | Il comando lpq visualizza lo stato di una coda di stampa su un computer che esegue Line Printer Daemon (LPD). Il comando lpq è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. Il comando lpq non è disponibile per impostazione predefinita in Windows 8, 7 o Vista, ma può essere abilitato attivando il servizio di stampa LPD e le funzionalità LPR Port Monitor da Programmi e funzionalità nel Pannello di controllo. |
| Lpr | Il comando lpr viene utilizzato per inviare un file a un computer che esegue Line Printer Daemon (LPD). Il comando lpr è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows. Il comando lpr non è disponibile per impostazione predefinita in Windows 8, 7 o Vista, ma può essere abilitato attivando il servizio di stampa LPD e le funzionalità LPR Port Monitor da Programmi e funzionalità nel Pannello di controllo. |
| Make-cab | Il comando makecab viene utilizzato per comprimere senza perdita di dati uno o più file. Il comando makecab è talvolta chiamato Cabinet Maker. Il comando makecab è disponibile in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista e Windows XP. Il comando makecab è lo stesso del comando diantz, un comando che è stato rimosso dopo Windows 7. |
| Gestisci-bde | Il comando manage-bde viene usato per configurare Crittografia unità BitLocker dalla riga di comando. Il comando manage-bde è disponibile in Windows 8 e Windows 7. Uno script con il nome manage-bde.wsf esiste in Windows Vista e può essere usato con il comando cscript per eseguire attività BitLocker dalla riga di comando in quel sistema operativo. |
| Md | Il comando md è la versione abbreviata del comando mkdir. Il comando md è disponibile in tutte le versioni di Windows, nonché in MS-DOS. |
| mem | The mem command shows information about used and free memory areas and programs that are currently loaded into memory in the MS-DOS subsystem. The mem command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The mem command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Memmaker | The memmaker command is used to start MemMaker, a memory optimization tool. The memaker command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is automatically optimized beginning in Windows XP. |
| Mkdir | The mkdir command is used to create a new folder. The mkdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mklink | The mklink command is used to create a symbolic link. The mklink command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Modalità | The mode command is used to configure system devices, most often COM and LPT ports. The mode command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mofcomp | The mofcomp command properly displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file. The mofcomp command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Di più | The more command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The more command can also be used to paginate the results of any other Command Prompt or MS-DOS command. The more command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mount | The mount command is used to mount Network File System (NFS) network shares. The mount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The mount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The mount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Mountvol | The mountvol command is used to display, create, or remove volume mount points. The mountvol command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Move | The move command is used to move one or files from one folder to another. The move command is also used to rename directories. The move command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mrinfo | The mrinfo command is used to provide information about a router's interfaces and neighbors. The mrinfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msav | The msav command starts Microsoft Antivirus. The msav command is only available in MS-DOS. Microsoft Antivirus was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Msbackup | The msbackup command starts Microsoft Backup, a tool used to back up and restore one or more files. The msbackup command is only available in MS-DOS. The msbackup command was replaced with Microsoft Backup beginning in Windows 95 and then Backup and Restore in later versions of Windows. |
| Mscdex | The mscdex command is used to provide CD-ROM access to MS-DOS. The mscdex command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows provides access to CD-ROM drives for the MS-DOS subsystem beginning in Windows XP, so the mscdex command is unnecessary in this and later operating systems. |
| Msd | The msd command starts Microsoft Diagnostics, a tool used to display information about your computer. The msd command is only available in MS-DOS. The msd command was replaced with System Information beginning in Windows 95. |
| Msg | The msg command is used to send a message to a user. The msg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msiexec | The msiexec command is used to start Windows Installer, a tool used to install and configure software. The msiexec command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Muiunattend | The muiunattend command starts the Multilanguage User Interface unattended setup process. The muiunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Nbtstat | The nbtstat command is used to show TCP/IP information and other statistical information about a remote computer. The nbtstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net | The net command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net1 | The net1 command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net1 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The net command should be used instead of the net1 command. The net1 command was made available in Windows NT and Windows 2000 as a temporary fix for a Y2K issue that the net command had, which was corrected before the release of Windows XP. The net1 command remains in later versions of Windows only for compatibility with older programs and scripts that utilized the command. |
| Netcfg | The netcfg command is used to install the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), a lightweight version of Windows used to deploy workstations. The netcfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Netsh | The netsh command is used to start Network Shell, a command-line utility used to manage the network configuration of the local, or a remote, computer. The netsh command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Netstat | The netstat command is most commonly used to display all open network connections and listening ports. The netstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Nfsadmin | The nfsadmin command is used to manage Server for NFS or Client for NFS from the command line. The nfsadmin command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The nfsadmin command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The nfsadmin command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Nlsfunc | The nlsfunc command is used to load information specific to a particular country or region. The nlsfunc command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The nlsfunc command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Nlsfunc is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Nltest | The nltest command is used to test secure channels between Windows computers in a domain and between domain controllers that are trusting other domains. The nltest command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Nslookup | The nslookup is most commonly used to display the hostname of an entered IP address. The nslookup command queries your configured DNS server to discover the IP address. The nslookup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ntbackup | The ntbackup command is used to perform various backup functions from the Command Prompt or from within a batch or script file. The ntbackup command is available in Windows XP. The ntbackup command was replaced with the wbadmin beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Ntsd | The ntsd command is used to perform certain command line debugging tasks. The ntsd command is available in Windows XP. The ntsd command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the addition of dump file support in Task Manager. |
| Ocsetup | The ocsetup command starts the Windows Optional Component Setup tool, used to install additional Windows features. The ocsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Beginning in Windows 8, Microsoft is depreciating the ocsetup command in favor of the dism command. |
| Openfiles | The openfiles command is used to display and disconnect open files and folders on a system. The openfiles command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Sentiero | The path command is used to display or set a specific path available to executable files. The path command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pathping | The pathping command functions much like the tracert command but will also report information about network latency and loss at each hop. The pathping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pausa | The pause command is used within a batch or script file to pause the processing of the file. When the pause command is used, a “Press any key to continue…” message displays in the command window. The pause command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pentnt | The pentnt command is used to detect floating point division errors in the Intel Pentium chip. The pentnt command is also used to enable floating point emulation and disable floating point hardware. The pentnt command is available in Windows XP. The pentnt command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the lack of Intel Pentium CPU use at the time of this operating system release. |
| Ping | The ping command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity. The ping command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Pkgmgr | The pkgmgr command is used to start the Windows Package Manager from the Command Prompt. Package Manager installs, uninstalls, configures, and updates features and packages for Windows. The pkgmgr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnpunattend | The pnpunattend command is used to automate the installation of hardware device drivers. The pnpunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnputil | The pnputil command is used to start the Microsoft PnP Utility, a tool used to install a Plug and Play device from the command line. The pnputil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Popd | The popd command is used to change the current directory to the one most recently stored by the pushd command. The popd command is most often utilized from within a batch or script file. The popd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Potenza | The power command is used to reduce the power consumed by a computer by monitoring software and hardware devices. The power command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The power command was replaced by operating system integrated power management functions beginning in Windows XP. |
| Powercfg | The powercfg command is used to manage the Windows power management settings from the command line. The powercfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Stampa | The print command is used to print a specified text file to a specified printing device. The print command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Prompt | The prompt command is used to customize the appearance of the prompt text in Command Prompt or MS-DOS. The prompt command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pushd | The pushd command is used to store a directory for use, most commonly from within a batch or script program. The pushd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pwlauncher | The pwlauncher command is used to enable, disable, or show the status of your Windows To Go startup options. The pwlauncher command is available in Windows 8. |
| Qappsrv | The qappsrv command is used to display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers available on the network. The qappsrv command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Qbasic | The qbasic command starts QBasic, the MS-DOS based programming environment for the BASIC programming language. The qbasic command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The qbasic command is not installed by default with Windows 98 or 95 but is available from the installation disc or disks. |
| Qprocess | The qprocess command is used to display information about running processes. The qprocess command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Domanda | The query command is used to display the status of a specified service. The query command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Quser | The quser command is used to display information about users currently logged on to the system. The quser command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Qwinsta | The qwinsta command is used to display information about open Remote Desktop Sessions. The qwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasautou | The rasautou command is used to manage Remote Access Dialer AutoDial addresses. The rasautou command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasdial | The rasdial command is used to start or end a network connection for a Microsoft client. The rasdial command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rcp | The rcp command is used to copy files between a Windows computer and a system running the rshd daemon. The rcp command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rcp command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rcp command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rd | The rd command is the shorthand version of the rmdir command. The rd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rdpsign | The rdpsign command is used to sign a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) file. The rdpsign command is available in Windows 7. |
| Reagentc | The reagentc command is used to configure the Windows Recovery Environment (RE). The reagentc command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Recimg | The recimg command is used to create a custom refresh image. The recimg command is available in Windows 8. |
| Recuperare | The recover command is used to recover readable data from a bad or defective disk. The recover command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Reg | The reg command is used to manage the Windows Registry from the command line. The reg command can perform common registry functions like adding registry keys, exporting the registry, etc. The reg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Regini | The regini command is used to set or change registry permissions and registry values from the command line. The regini command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Register-cimprovider | The register-cimprovider command is used to register a Common Information Model (CIM) Provider in Windows. The register-cimprovider command is available in Windows 8. |
| Regsvr32 | The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file as a command component in the Windows Registry. The regsvr32 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Relog | The relog command is used to create new performance logs from data in existing performance logs. The relog command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rem | The rem command is used to record comments or remarks in a batch or script file. The rem command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Ren | The ren command is the shorthand version of the rename command. The ren command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rename | The rename command is used to change the name of the individual file that you specify. The rename command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Repair-bde | The repair-bde command is used to repair or decrypt a damaged drive that's been encrypted using BitLocker. The repair-bde command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Replace | The replace command is used to replace one or more files with one or more other files. The replace command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Ripristina | The reset command, executed as reset session, is used to reset the session subsystem software and hardware to known initial values. The reset command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Restore | The restore command is used to restore files that were backed up using the backup command. The restore command is only available in MS-DOS. The backup command was only available up to MS-DOS 5.00 but the restore command was included by default with later versions of MS-DOS to provide a way to restore files that were backed up in previous versions of MS-DOS. |
| Rexec | The rexec command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rexec daemon. The rexec command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here. The rexec command is not available in Windows 7 but can be executed in Windows XP via Windows XP Mode if need be. |
| Rmdir | The rmdir command is used to delete an existing or completely empty folder. The rmdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Robocopy | The robocopy command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. This command is also called Robust File Copy. The robocopy command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The robocopy command is superior to both the copy command and the xcopy command because robocopy supports many more options. |
| Route | The route command is used to manipulate network routing tables. The route command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Rpcinfo | The rpcinfo command makes a remote procedure call (RPC) to an RPC server and reports what it finds. The rpcinfo command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The rpcinfo command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The rpcinfo command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rpcping | The rpcping command is used to ping a server using RPC. The rpcping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Rsh | The rsh command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rsh daemon. The rsh command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rsh command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rsm | The rsm command is used to manage media resources using Removable Storage. The rsm command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsm command was optional in Windows Vista and then removed in Windows 7 due to Removable Storage Manager being removed from the operating system. Search for the rsm command in the C:\Windows\winsxs folder in Windows Vista if you're having trouble executing the command. |
| Runas | The runas command is used to execute a program using another user's credentials. The runas command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rwinsta | The rwinsta command is the shorthand version of the reset session command. The rwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Sc | The sc command is used to configure information about services. The sc command communicates with the Service Control Manager. The sc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Scandisk | The scandisk command is used to start Microsoft ScanDisk, a disk repair program. The scandisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The scandisk command was replaced by the chkdsk command beginning in Windows XP. |
| Scanreg | The scanreg command starts Windows Registry Checker, a basic registry repair program and backup utility. The scanreg command is available in Windows 98 and Windows 95. The functions provided by the scanreg command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP due to changes in how the Windows Registry functions. |
| Schtasks | The schtasks command is used to schedule specified programs or commands to run at certain times. The schtasks command can be used to create, delete, query, change, run, and end scheduled tasks. The schtasks command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.? |
| Sdbinst | The sdbinst command is used to deploy customized SDB database files. The sdbinst command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Secedit | The secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security by comparing the current security configuration to a template. The secedit command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Set | The set command is used to display, enable, or disable environment variables in MS-DOS or from the Command Prompt. The set command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Setlocal | The setlocal command is used to start the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The setlocal command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Setspn | The setspn command is used to manage the Service Principal Names (SPN) for an Active Directory (AD) service account. The setspn command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Setver | The setver command is used to set the MS-DOS version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. The setver command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The setver command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Setx | The setx command is used to create or change environment variables in the user environment or the system environment. The setx command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sfc | The sfc command is used to verify and replace important Windows system files. The sfc command is also referred to as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker, depending on the operating system. The sfc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Shadow | The shadow command is used to monitor another Remote Desktop Services session. The shadow command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Condividere | The share command is used to install file locking and file sharing functions in MS-DOS. The share command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The share command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Share is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Cambio | The shift command is used to change the position of replaceable parameters in a batch or script file. The shift command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Showmount | The showmount command is used to display information about NFS mounted file systems. The showmount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The showmount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The showmount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Shutdown | The shutdown command can be used to shut down, restart, or log off the current system or a remote computer. The shutdown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Smartdrv | The smartdrv command installs and configures SMARTDrive, a disk caching utility for MS-DOS. The smartdrv command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Caching is automatic beginning in Windows XP, making the smartdrv command unnecessary. |
| Ordinare | The sort command is used to read data from a specified input, sort that data, and return the results of that sort to the Command Prompt screen, a file, or another output device. The sort command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Inizio | The start command is used to open a new command line window to run a specified program or command. The start command can also be used to start an application without creating a new window. The start command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Subst | The subst command is used to associate a local path with a drive letter. The subst command is a lot like the net use command except a local path is used instead of a shared network path. The subst command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The subst command replaced the assign command beginning with MS-DOS 6.0. |
| Sxstrace | The sxstrace command is used to start the WinSxs Tracing Utility, a programming diagnostic tool. The sxstrace command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sys | The sys command is used to copy the MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk. The sys command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The sys command is used most often to create a simple bootable disk or hard drive. The necessary system files for Windows are too large to fit on a disk, so the sys command was removed beginning in Windows XP. |
| Systeminfo | The systeminfo command is used to display basic Windows configuration information for the local or a remote computer. The systeminfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Takeown | The takedown command is used to regain access to a file that that an administrator was denied access to when reassigning ownership of the file. The takeown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Taskkill | The taskkill command is used to terminate a running task. The taskkill command is the command line equivalent of ending a process in Task Manager in Windows. The taskkill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tasklist | Displays a list of applications, services, and the Process ID (PID) currently running on either a local or a remote computer. The tasklist command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tcmsetup | The tcmsetup command is used to set up or disable the Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) client. The tcmsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Telnet | The telnet command is used to communicate with remote computers that use the Telnet protocol. The telnet command is available in all versions of Windows. The telnet command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tftp | The tftp command is used to transfer files to and from a remote computer that's running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) service or daemon. The tftp command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tftp command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the TFTP Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Volta | The time command is used to show or change the current time. The time command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Tempo scaduto | The timeout command is typically used in a batch or script file to provide a specified timeout value during a procedure. The timeout command can also be used to ignore keypresses. The timeout command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Titolo | The title command is used to set the Command Prompt window title. The title command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tlntadmn | The tlntadmn command is used to administer a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. The tlntadmn command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tlntadmn command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Server Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tpmvscmgr | The tpmvscmgr command is used to create and destroy TPM virtual smart cards. The tpmvscmgr command is available in Windows 8. |
| Tracerpt | The tracerpt command is used to process event trace logs or real-time data from instrumented event trace providers. The tracerpt command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tracert | The tracert command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to a specified remote computer with increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values and displays the IP address and hostname, if available, of the router interfaces between the source and destination. The tracert command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Tree | The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path. The tree command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Tscon | The tscon command is used to attach a user session to a Remote Desktop session. The tscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsdiscon | The tsdiscon command is used to disconnect a Remote Desktop session. The tsdiscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tskill | The tskill command is used to end the specified process. The tskill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsshutdn | The tsshutdn command is used to remotely shut down or restart a terminal server. The tsshutdn command is available in Windows XP. The ability to shut down a computer remotely is also available in the more powerful shutdown command, so tsshutdn was removed beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Tipo | The type command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The type command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Typeperf | The typerperf command displays performance data in the Command Prompt window or writes the data to specified log file. The typeperf command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tzutil | The tzutil command is used to display or configure the current system's time zone. The tzutil command can also be used to enable or disable Daylight Saving Time adjustments. The tzutil command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Umount | The umount command is used to remove Network File System (NFS) mounted network shares. The umount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The umount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The umount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Annulla eliminazione | The undelete command is used to undo a deletion performed with the MS-DOS delete command. The undelete command is only available in MS-DOS. The undelete command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to the availability of the Recycle Bin in Windows. Additionally, free file recovery programs are available from third-party software makers. |
| Unformat | The unformat command is used to undo the formatting on a drive performed by the MS-DOS format command. The unformat command is only available in MS-DOS. The unformat command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to file system changes. |
| Sbloccare | The unlock command is used to unlock a drive, disabling direct disk access for a program. The unlock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP. |
| Unlodctr | The unlodctr command removes Explain text and Performance counter names for a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. The unlodctr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Vaultcmd | The vaultcmd command is used to create, remove, and show stored credentials. The vaultcmd command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Ver | The ver command is used to display the current Windows or MS-DOS version number. The ver command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Verificare | The verify command is used to enable or disable the ability of Command Prompt, or MS-DOS, to verify that files are written correctly to a disk. The verify command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vol | The vol command shows the volume label and serial number of a specified disk, assuming this information exists. The vol command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vsafe | The vsafe command is used to start VSafe, a basic virus protection system for MS-DOS. The vsafe command is only available in MS-DOS. VSafe was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Vssadmin | The vssadmin command starts the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool which displays current volume shadow copy backups and all installed shadow copy writers and providers. The vssadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| W32tm | The w32tm command is used to diagnose issues with Windows Time. The w32tm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Waitfor | The waitfor command is used to send or wait for a signal on a system. The waitfor command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wbadmin | The wbadmin command is used to start and stop backup jobs, display details about a previous backup, list the items within a backup, and report on the status of a currently running backup. The wbadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The wbadmin command replaced the ntbackup command beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Wecutil | The wecutil command is used to manage subscriptions to events that are forwarded from WS-Management supported computers. The wecutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wevtutil | The wevtutil command starts the Windows Events Command Line Utility which is used to manage event logs and publishers. The wevtutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Dove | The where command is used to search for files that match a specified pattern. The where command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Whoami | The whoami command is used to retrieve user name and group information on a network. The whoami command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winmgmt | The winmgmt command starts the command line version of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. The winmgmt command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Winrm | The winrm command is used to start the command line version of Windows Remote Management, used to manage secure communications with local and remote computers using web services. The winrm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winrs | The winrs command is used to open a secure command window with a remote host. The winrs command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winsat | The winsat command starts the Windows System Assessment Tool, a program that assesses various features, attributes, and capabilities of a computer running Windows. The winsat command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wmic | The wmic command starts the Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC), a scripting interface that simplifies the use of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and systems managed via WMI. The wmic command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Wsmanhttpconfig | The wsmanhttpconfig command is used to manage aspects of the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service. The wsmanhttpconfig command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Xcopy | The xcopy command can copy one or more files or directory trees from one location to another. The xcopy command is generally considered a more “powerful” version of the copy command through the robocopy command trumps even xcopy. The xcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. A command by the name of xcopy32 existed in Windows 95 and Windows 98. To avoid a long and confusing explanation here, just know that no matter if you executed the xcopy command or the xcopy32 command, you were always executing the most updated version of the command. |
| Xwizard | The xwizard command, short for Extensible Wizard, is used to register data in Windows, often from a preconfigured XML file. The xwizard command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
The above list is a set of most essential commands of command prompt. To view or download a PDF version of complete set of windows commands, please click on the below button.

Scarica come PDF
Per ulteriori suggerimenti, trucchi e aggiornamenti relativi alla tecnologia iscriviti alla Libreria di Tweak e se ti piacciono di più i video relativi alla tecnologia, guarda e iscriviti al nostro canale YouTube . Puoi raggiungerci anche su Facebook e Pinterest .
