Używaj wiersza poleceń jak profesjonalista – wszystko o wierszu poleceń
Opublikowany: 2019-05-21Wraz z uruchomieniem systemu Windows 10 firma Microsoft powoli wypchnęła wiersz poleceń z interfejsu systemu Windows. Powodem tego było to, że wiersz poleceń był przestarzałym i najbardziej niepotrzebnym narzędziem z ery wprowadzania tekstu. Jednak wiele poleceń jest nadal przydatnych, a system Windows 10 dodał nawet nowe funkcje do świata wiersza poleceń. Teraz wiersz polecenia został przeprojektowany do programu PowerShell, aplikacji, której można używać tak samo jak wiersza polecenia. Jest to kolorowa aplikacja, która może zastąpić wiersz poleceń, chociaż nadal możesz korzystać z wiersza poleceń. Te sztuczki wiersza polecenia są naprawdę przydatne dla administratorów komputerów i dają im dostęp do profesjonalnego wykonywania kilku zadań.
Jak otworzyć wiersz polecenia
Naciśnij Win + R -> wpisz „cmd” -> naciśnij „Enter”
W pasku wyszukiwania wpisz „cmd” naciśnij „Enter”.
Jeśli chcesz otworzyć wiersz poleceń jako administrator, w pasku wyszukiwania wpisz „cmd”, a gdy tylko pojawi się „Aplikacja poleceń”, kliknij go prawym przyciskiem myszy i kliknij „Uruchom jako administrator”.
Przeczytaj także: Wszystko o skrótach klawiaturowych systemu Windows 10
Jak znaleźć wszystkie polecenia w wierszu polecenia
Aby znaleźć odpowiednie polecenia i ich składnię w wierszu poleceń, możemy wpisać „cmd /?” lub wpisz polecenie, po którym następuje „/?” na przykład 'ipconfig /?' otwiera listę opcji i składni z ich akcjami. Ten interpreter poleceń jest przydatny do nauki nowych poleceń w wierszu poleceń.
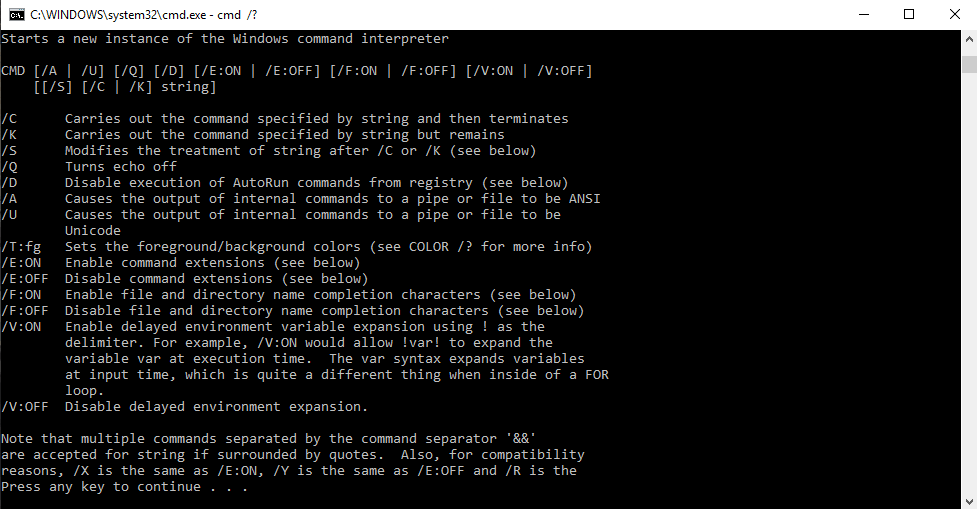
Korzystanie ze składni
cmd [/c|/k] [/s] [/q] [/d] [/a|/u] [/t:{<B><F>|<F>}] [/e:{on|off}] [/f:{on|off}] [/v:{on|off}] [<String>]
Parametry
| Parametr | Opis |
| /C | Wykonuje polecenie określone przez String, a następnie zatrzymuje się. |
| /k | Wykonuje polecenie określone przez String i kontynuuje. |
| /s | Modyfikuje traktowanie String po /c lub /k. |
| /Q | Wyłącza echo. |
| /D | Wyłącza wykonywanie poleceń AutoRun. |
| /a | Formatuje dane wyjściowe poleceń wewnętrznych do potoku lub pliku jako American National Standards Institute (ANSI). |
| /u | Formatuje dane wyjściowe poleceń wewnętrznych do potoku lub pliku jako Unicode. |
| /t:{<B><F>|<F>} | Ustawia kolory tła (B) i pierwszego planu (F). |
| /wieczność | Włącza rozszerzenia poleceń. |
| /e:wyłączone | Wyłącza rozszerzenia poleceń. |
| /f:wł. | Umożliwia uzupełnianie nazw plików i katalogów. |
| /f:wył. | Wyłącza uzupełnianie nazw plików i katalogów. |
| /v:wł. | Włącza opóźnione rozwijanie zmiennych środowiskowych. |
| /v:wył | Wyłącza opóźnione rozwijanie zmiennych środowiskowych. |
| <Ciąg> | Określa polecenie, które chcesz wykonać. |
| /? | Wyświetla pomoc w wierszu polecenia. |
W poniższej tabeli wymieniono prawidłowe cyfry szesnastkowe, których można użyć jako wartości dla <B> i <F>
| Wartość | Kolor |
| 0 | Czarny |
| 1 | Niebieski |
| 2 | Zielony |
| 3 | wodny |
| 4 | czerwony |
| 5 | Fioletowy |
| 6 | Żółty |
| 7 | biały |
| 8 | Szary |
| 9 | Jasny niebieski |
| a | Jasnozielony |
| b | Jasny wodny |
| C | Jasnoczerwony |
| D | Jasny fiolet |
| mi | Jasny zółty |
| F | Jasny biały |
Oto pełna lista poleceń wiersza polecenia. Możesz również pobrać wszystkie polecenia wraz z ich składnią, korzystając z łącza na dole tego artykułu.
| Komenda | Opis |
| Dodać | Polecenie append może być używane przez programy do otwierania plików w innym katalogu, tak jakby znajdowały się w bieżącym katalogu. Polecenie append jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS oraz we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie append nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Arp | Polecenie arp służy do wyświetlania lub zmiany wpisów w pamięci podręcznej ARP. Polecenie arp jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Doc | Polecenie assoc służy do wyświetlania lub zmiany typu pliku skojarzonego z określonym rozszerzeniem pliku. Polecenie assoc jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Na | Polecenie at służy do planowania poleceń i innych programów, które mają być uruchamiane w określonym dniu i czasie. Polecenie at jest dostępne w systemach Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Począwszy od systemu Windows 8, planowanie zadań wiersza polecenia powinno być wykonywane za pomocą polecenia schtasks. |
| Atmadm | Polecenie atmadm służy do wyświetlania informacji związanych z połączeniami w trybie transferu asynchronicznego (ATM) w systemie. Polecenie atmadm jest dostępne w systemie Windows XP. Obsługa ATM została usunięta począwszy od systemu Windows Vista, przez co polecenie atmadm stało się zbędne. |
| Atrybut | Komenda attrib służy do zmiany atrybutów pojedynczego pliku lub katalogu. Polecenie attrib jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Auditpol | Komenda auditpol służy do wyświetlania lub zmiany strategii kontroli. Polecenie auditpol jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Bcdboot | Polecenie bcdboot służy do kopiowania plików rozruchowych na partycję systemową i tworzenia nowego systemowego magazynu BCD. Polecenie bcdboot jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Bcdedit | Polecenie bcdedit służy do przeglądania lub wprowadzania zmian w danych konfiguracji rozruchu. Polecenie bcdedit jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. Polecenie bcdedit zastąpiło polecenie bootcfg rozpoczynające się w systemie Windows Vista. |
| Bdehdcfg | Polecenie bdehdcfg służy do przygotowania dysku twardego do szyfrowania dysków funkcją BitLocker. Polecenie bdehdcfg jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Bitsadmin | Polecenie bitsadmin służy do tworzenia, zarządzania i monitorowania zadań pobierania i przesyłania. Polecenie bitsadmin jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. Chociaż polecenie bitsadmin jest dostępne zarówno w systemie Windows 8, jak i Windows 7, jest wycofywane. Zamiast tego należy używać poleceń cmdlet programu BITS PowerShell. |
| Bootcfg | Polecenie bootcfg służy do tworzenia, modyfikowania lub przeglądania zawartości pliku boot.ini, ukrytego pliku używanego do identyfikowania w jakim folderze, na której partycji i na jakim dysku twardym znajduje się system Windows. Polecenie bootcfg jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie bootcfg zostało zastąpione poleceniem bcdedit rozpoczynającym się w systemie Windows Vista. Bootcfg jest nadal dostępny w systemach Windows 8, 7 i Vista, ale nie ma żadnej rzeczywistej wartości, ponieważ boot.ini nie jest używany w tych systemach operacyjnych. |
| Bootsect | Polecenie bootsect służy do konfiguracji głównego kodu rozruchowego zgodnego z BOOTMGR (Vista i nowsze) lub NTLDR (XP i wcześniejsze). Polecenie bootsect jest dostępne w systemie Windows 8. Polecenie bootsect jest również dostępne w systemach Windows 7 i Windows Vista, ale tylko z wiersza polecenia dostępnego w opcjach odzyskiwania systemu. |
| Złamać | Polecenie break ustawia lub czyści rozszerzone sprawdzanie CTRL + C w systemach DOS. Polecenie break jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach Windows, a także w MS-DOS. Polecenie przerwania jest dostępne w systemie Windows XP i nowszych wersjach systemu Windows, aby zapewnić zgodność z plikami MS-DOS, ale nie działa w samym systemie Windows. |
| Cacls | Polecenie cacls służy do wyświetlania lub zmiany list kontroli dostępu do plików. Polecenie cacls jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie cacls jest wycofywane na rzecz polecenia icacls, które powinno być używane zamiast tego we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows po systemie Windows XP. |
| Połączenie | Polecenie call służy do uruchamiania skryptu lub programu wsadowego z innego skryptu lub programu wsadowego. Polecenie call jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. Polecenie call nie działa poza skryptem lub plikiem wsadowym. Innymi słowy, uruchomienie polecenia wywołania w wierszu polecenia lub wierszu MS-DOS nic nie da. |
| Płyta CD | Polecenie cd jest skróconą wersją polecenia chdir. Polecenie cd jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Certreq | Polecenie certreq służy do wykonywania różnych funkcji certyfikacji urzędu certyfikacji (CA). Polecenie certreq jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Certutil | Komenda certutil służy do zrzutu i wyświetlenia informacji o konfiguracji urzędu certyfikacji (CA) oraz innych funkcji urzędu certyfikacji. Polecenie certutil jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Zmiana | Polecenie change zmienia różne ustawienia serwera terminali, takie jak tryby instalacji, mapowania portów COM i logowania. Polecenie zmiany jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Chcp | Polecenie chcp wyświetla lub konfiguruje numer aktywnej strony kodowej. Polecenie chcp jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Chdir | Polecenie chdir służy do wyświetlania litery dysku i folderu, w którym aktualnie się znajdujesz. Chdir można również użyć do zmiany dysku i/lub katalogu, w którym chcesz pracować. Polecenie chdir jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, jako jak również w MS-DOS. |
| Checknetizolacja | Polecenie checknetisolation służy do testowania aplikacji wymagających możliwości sieciowych. Polecenie checknetisolation jest dostępne w systemie Windows 8. |
| Chglogon | Komenda chglogon włącza, wyłącza lub opróżnia logowanie w sesji serwera terminali. Polecenie chglogon jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. Wykonywanie komendy chglogon jest takie samo, jak wykonywanie logowania do zmiany. |
| Chgport | Polecenia chgport można użyć do wyświetlenia lub zmiany mapowań portów COM w celu zapewnienia zgodności z systemem DOS. Polecenie chgport jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. Wykonanie komendy chgport jest takie samo, jak wykonanie polecenia change port. |
| Chgusr | Komenda chgusr służy do zmiany trybu instalacji serwera terminali. Polecenie chgusr jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. Wykonanie komendy chgusr jest takie samo, jak wykonanie polecenia change user. |
| Czkdsk | Polecenie chkdsk, często nazywane sprawdzaniem dysku, służy do identyfikowania i korygowania niektórych błędów dysku twardego. Polecenie chkdsk jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w systemie MS-DOS. |
| Chkntfs | Polecenie chkntfs służy do konfigurowania lub wyświetlania sprawdzania dysku podczas procesu uruchamiania systemu Windows. Polecenie chkntfs jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Wybór | Polecenie wyboru jest używane w skrypcie lub programie wsadowym w celu dostarczenia listy wyborów i zwrócenia wartości tego wyboru do programu. Polecenie wyboru jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS i we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows z wyjątkiem Windows XP. Użyj polecenia set z przełącznikiem /p zamiast polecenia wyboru w plikach wsadowych i skryptach, których planujesz używać w systemie Windows XP. |
| Szyfr | Polecenie cipher pokazuje lub zmienia stan szyfrowania plików i folderów na partycjach NTFS. Polecenie cipher jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Spinacz | Polecenie clip służy do przekierowania danych wyjściowych z dowolnego polecenia do schowka w systemie Windows. Polecenie przycinania jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Cls | Polecenie cls czyści ekran ze wszystkich wcześniej wprowadzonych poleceń i innego tekstu. Polecenie cls jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Polecenie | Polecenie cmd uruchamia nowe wystąpienie interpretera poleceń cmd.exe. Polecenie cmd jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Cmdkey | Polecenie cmdkey służy do wyświetlania, tworzenia i usuwania zapisanych nazw użytkowników i haseł. Polecenie cmdkey jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Cmstp | Polecenie cmstp instaluje lub odinstalowuje profil usługi Menedżera połączeń. Polecenie cmstp jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Kolor | Polecenie kolor służy do zmiany kolorów tekstu i tła w oknie wiersza polecenia. Polecenie koloru jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Komenda | Polecenie „command” uruchamia nową instancję interpretera poleceń command.com. Polecenie „polecenie” jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS oraz we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie „polecenie” nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Comp | Komenda comp służy do porównywania zawartości dwóch plików lub zestawów plików. Polecenie comp jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Kompaktowy | Polecenie compact służy do pokazywania lub zmieniania stanu kompresji plików i katalogów na partycjach NTFS. Kompaktowe polecenie jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Konwertować | Polecenie convert służy do konwersji woluminów w formacie FAT lub FAT32 na format NTFS. Polecenie konwertuj jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Kopiuj | Polecenie kopiowania po prostu to robi — kopiuje jeden lub więcej plików z jednej lokalizacji do drugiej. Polecenie kopiowania jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. Polecenie xcopy jest uważane za bardziej „potężną” wersję polecenia kopiowania. |
| Cscript | Polecenie cscript służy do wykonywania skryptów za pośrednictwem Microsoft Script Host. Polecenie cscript jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie cscript jest najczęściej używane do zarządzania drukarkami z wiersza poleceń za pomocą skryptów takich jak prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmngr.vbs i innych. |
| Ctty | Polecenie ctty służy do zmiany domyślnych urządzeń wejściowych i wyjściowych systemu. Polecenie ctty jest dostępne w Windows 98 i 95 oraz w MS-DOS. Funkcje zapewniane przez polecenie ctty nie były już potrzebne począwszy od systemu Windows XP, ponieważ interpreter command.com (MS-DOS) nie jest już domyślnym interpreterem wiersza poleceń. |
| Data | Polecenie date służy do pokazywania lub zmiany bieżącej daty. Polecenie date jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Dblspace | Polecenie dblspace służy do tworzenia lub konfigurowania skompresowanych dysków DoubleSpace. Polecenie dblspace jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. DriveSpace, wykonywany za pomocą polecenia drvspace, jest zaktualizowaną wersją DoubleSpace. System Windows natywnie obsługuje kompresję, począwszy od systemu Windows XP. |
| Odpluskwić | Polecenie debug uruchamia Debug, aplikację wiersza poleceń używaną do testowania i edycji programów. Polecenie debug jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS, a także we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie debug nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Defragmentuj | Polecenie defrag służy do defragmentacji określonego dysku. Polecenie defrag to wersja wiersza poleceń programu Defragmentator dysków firmy Microsoft. Polecenie defrag jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Del | Polecenie del służy do usuwania jednego lub więcej plików. Polecenie del jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. Polecenie del jest tym samym, co polecenie kasowania. |
| Deltree | Polecenie deltree służy do usuwania katalogu oraz wszystkich znajdujących się w nim plików i podkatalogów. Polecenie deltree jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. Począwszy od systemu Windows XP folder oraz jego pliki i podfoldery można usunąć za pomocą funkcji /s polecenia rmdir. Deltree nie było już potrzebne z tą nową umiejętnością rmdir, więc polecenie zostało usunięte. |
| Diantz | Polecenie diantz służy do bezstratnej kompresji jednego lub więcej plików. Polecenie diantz jest czasami nazywane Cabinet Maker. Polecenie diantz jest dostępne w systemach Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie diantz jest takie samo, jak polecenie makecab. |
| Dir | Polecenie dir służy do wyświetlania listy plików i folderów zawartych w folderze, w którym aktualnie pracujesz. Polecenie dir wyświetla również inne ważne informacje, takie jak numer seryjny dysku twardego, całkowita liczba wymienionych plików, ich łączny rozmiar, całkowita ilość wolnego miejsca na dysku i nie tylko. Polecenie dir jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Diskcomp | Polecenie diskcomp służy do porównania zawartości dwóch dyskietek. Polecenie diskcomp jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Kopia dyskowa | Polecenie diskcopy służy do kopiowania całej zawartości jednej dyskietki na drugą. Polecenie diskcopy jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Diskpart | Polecenie diskpart służy do tworzenia, zarządzania i usuwania partycji dysku twardego. Polecenie diskpart jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie diskpart zastąpiło polecenie fdisk począwszy od systemu Windows XP. |
| Diskperf | Polecenie diskperf służy do zdalnego zarządzania licznikami wydajności dysku. Polecenie diskperf jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Diskraid | Polecenie diskraid uruchamia narzędzie DiskRAID, które służy do zarządzania i konfiguracji macierzy RAID. Polecenie diskraid jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Dism | Polecenie dism uruchamia narzędzie do obsługi i zarządzania obrazami wdrażania (DISM). Narzędzie DISM służy do zarządzania funkcjami w obrazach systemu Windows. Polecenie dism jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Dispdiag | Polecenie dispdiag służy do wyprowadzania dziennika informacji o systemie wyświetlania. Polecenie dispdiag jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Djoin | Polecenie djoin służy do tworzenia nowego konta komputera w domenie. Polecenie djoin jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Doskey | Polecenie doskey służy do edycji wierszy poleceń, tworzenia makr i przywoływania wcześniej wprowadzonych poleceń. Polecenie doskey jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Dosshell | Polecenie dosshell uruchamia DOS Shell, graficzne narzędzie do zarządzania plikami dla MS-DOS. Polecenie dosshell jest dostępne w systemie Windows 95 (w trybie MS-DOS), a także w systemie MS-DOS w wersji 6.0 i nowszych wersjach MS-DOS, które zostały uaktualnione z poprzednich wersji, które zawierały polecenie dosshell. Graficzny menedżer plików, Eksplorator Windows, stał się integralną częścią systemu operacyjnego począwszy od Windows 95. |
| Dosx | Polecenie dosx służy do uruchamiania interfejsu trybu chronionego DOS (DPMI), specjalnego trybu zaprojektowanego w celu zapewnienia aplikacjom MS-DOS dostępu do więcej niż normalnie dozwolone 640 KB. Polecenie dosx jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie dosx nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie dosx i DPMI są dostępne tylko w systemie Windows do obsługi starszych programów MS-DOS. |
| Zapytanie kierowcy | Polecenie driverquery służy do wyświetlenia listy wszystkich zainstalowanych sterowników. Polecenie driverquery jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Drvspace | Polecenie drvspace służy do tworzenia lub konfigurowania skompresowanych dysków DriveSpace. Polecenie drvspace jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. DriveSpace to zaktualizowana wersja DoubleSpace, uruchamiana za pomocą polecenia dblspace. System Windows natywnie obsługuje kompresję, począwszy od systemu Windows XP. |
| Echo | Polecenie echo służy do wyświetlania komunikatów, najczęściej z poziomu skryptów lub plików wsadowych. Polecenie echo może być również używane do włączania lub wyłączania funkcji echa. Polecenie echo jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Edytować | Polecenie edit uruchamia narzędzie MS-DOS Editor, które służy do tworzenia i modyfikowania plików tekstowych. Polecenie edycji jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS, a także we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie edycji nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Edlin | Polecenie edlin uruchamia narzędzie Edlin, które służy do tworzenia i modyfikowania plików tekstowych z wiersza poleceń. Polecenie edlin jest dostępne we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows, ale nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. W MS-DOS polecenie edlin jest dostępne tylko do MS-DOS 5.0, więc jeśli nowsza wersja MS-DOS nie została uaktualniona z wersji 5.0 lub wcześniejszej, nie zobaczysz polecenia edlin. |
| Emm386 | Polecenie emm386 umożliwia systemowi MS-DOS dostęp do ponad 640 KB pamięci. Polecenie emm386 jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. Sam system Windows ma dostęp do rozszerzonej i rozszerzonej pamięci począwszy od systemu Windows 95. |
| Endlokalny | Polecenie endlocal służy do zakończenia lokalizacji zmian środowiska wewnątrz pliku wsadowego lub skryptu. Polecenie endlocal jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Usuwać | Polecenie kasowania służy do usuwania jednego lub więcej plików. Polecenie kasowania jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w systemie MS-DOS. Polecenie kasowania jest takie samo, jak polecenie del. |
| Esentutl | Komenda esentutl służy do zarządzania bazami danych Extensible Storage Engine. Polecenie esentutl jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Utwórz wydarzenie | Polecenie eventcreate służy do tworzenia niestandardowego zdarzenia w dzienniku zdarzeń. Polecenie eventcreate jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Wyzwalacze zdarzeń | Polecenie eventtriggers służy do konfigurowania i wyświetlania wyzwalaczy zdarzeń. Polecenie eventtriggers jest dostępne w systemie Windows XP. Począwszy od systemu Windows Vista, wyzwalacze zdarzeń są tworzone za pomocą funkcji Dołącz zadanie do tego zdarzenia w Podglądzie zdarzeń, dzięki czemu polecenie eventtriggers jest niepotrzebne. |
| Exe2bin | Polecenie exe2bin służy do konwersji pliku typu EXE (plik wykonywalny) na plik binarny. Polecenie exe2bin jest dostępne w 32-bitowych wersjach systemów Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie exe2bin nie jest dostępne w żadnej 64-bitowej wersji systemu Windows. |
| Wyjście | Polecenie wyjścia służy do zakończenia sesji cmd.exe (Windows) lub command.com (MS-DOS), w której aktualnie pracujesz. Polecenie wyjścia jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS . |
| Zwiększać | Polecenie expand służy do wyodrębniania plików i folderów zawartych w plikach Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Polecenie expand jest dostępne w MS-DOS, jak również we wszystkich wersjach Windows. Polecenie expand nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowej wersji systemu Windows XP. |
| Wyciąg32 | Polecenie extrac32 służy do wyodrębniania plików i folderów zawartych w plikach Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Polecenie extrac32 jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie extrac32 jest w rzeczywistości programem do ekstrakcji CAB do użytku przez Internet Explorer, ale może być użyte do wyodrębnienia dowolnego pliku Microsoft Cabinet. Jeśli to możliwe, użyj polecenia expand zamiast polecenia extrac32. |
| Wyciąg | Polecenie wyodrębniania służy do wyodrębniania plików i folderów zawartych w plikach Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). Polecenie wyodrębniania jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95. Polecenie wyodrębniania zostało zastąpione poleceniem expand, rozpoczynającym się w systemie Windows XP. |
| Szybka pomoc | Polecenie fasthelp dostarcza bardziej szczegółowych informacji o innych poleceniach systemu MS-DOS. Polecenie fasthelp jest dostępne tylko w systemie MS-DOS. Polecenie help zastąpiło polecenie fasthelp rozpoczynające się w systemie Windows 95. |
| Fastopen | Polecenie fastopen służy do dodawania lokalizacji dysku twardego programu do specjalnej listy przechowywanej w pamięci, potencjalnie skracając czas uruchamiania programu przez eliminację konieczności lokalizowania aplikacji na dysku przez system MS-DOS. Polecenie fastopen jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS oraz we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie fastopen nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Fastopen jest dostępny tylko w systemach Windows 8, 7, Vista i XP do obsługi starszych plików MS-DOS. |
| Fc | Polecenie fc służy do porównania dwóch pojedynczych lub zestawów plików, a następnie pokazania różnic między nimi. Polecenie fc jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Fdisk | Polecenie fdisk służy do tworzenia, zarządzania i usuwania partycji dysku twardego. Polecenie fdisk jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. Polecenie fdisk zostało zastąpione poleceniem diskpart rozpoczynającym się w systemie Windows XP. Zarządzanie partycjami jest również dostępne w przystawce Zarządzanie dyskami w systemach Windows 8, 7, Vista i XP. |
| Znajdować | Polecenie find służy do wyszukiwania określonego ciągu tekstowego w jednym lub kilku plikach. Polecenie find jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Findstr | Polecenie findstr służy do wyszukiwania wzorców ciągów tekstowych w jednym lub kilku plikach. Polecenie findstr jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Palec | Polecenie finger służy do zwracania informacji o co najmniej jednym użytkowniku na komputerze zdalnym z uruchomioną usługą Finger. Polecenie finger jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Fltmc | Polecenie fltmc służy do ładowania, rozładowywania, wyświetlania i innego zarządzania sterownikami filtrów. Polecenie fltmc jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Fondue | Polecenie fondue, skrót od Functions on Demand User Experience Tool, służy do instalowania dowolnej z kilku opcjonalnych funkcji systemu Windows z wiersza polecenia. Polecenie fondue jest dostępne w systemie Windows 8. Opcjonalne funkcje systemu Windows można również zainstalować z apletu Programy i funkcje w Panelu sterowania. |
| Do | Polecenie for służy do uruchamiania określonego polecenia dla każdego pliku w zestawie plików. Polecenie for jest najczęściej używane w pliku wsadowym lub w skrypcie. Polecenie for jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w systemie MS-DOS. |
| Forcedos | Polecenie forceos służy do uruchomienia określonego programu w podsystemie MS-DOS. Polecenie forcedos jest dostępne tylko w 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows XP. Polecenie forceos jest używane tylko w przypadku programów MS-DOS, które nie są rozpoznawane jako takie przez system Windows XP. |
| Forfiles | Polecenie forfiles wybiera jeden lub więcej plików do wykonania określonego polecenia. Polecenie forfiles jest najczęściej używane w pliku wsadowym lub w skrypcie. Polecenie forfiles jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Format | Polecenie format służy do formatowania dysku w określonym systemie plików. Polecenie format jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. Formatowanie dysku jest również dostępne w Zarządzaniu dyskami w systemie Windows 8, 7, Vista i XP. |
| Fsutil | Polecenie fsutil służy do wykonywania różnych zadań związanych z systemem plików FAT i NTFS, takich jak zarządzanie punktami ponownej analizy i rozrzedzonymi plikami, odmontowywanie woluminu i rozszerzanie woluminu. Polecenie fsutil jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| FTP | Polecenia ftp można używać do przesyłania plików do iz innego komputera. Komputer zdalny musi działać jako serwer FTP. Polecenie ftp jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Ftyp | Polecenie ftype służy do zdefiniowania domyślnego programu do otwierania określonego typu pliku. Polecenie ftype jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Getmac | Polecenie getmac służy do wyświetlania adresu kontroli dostępu do nośnika (MAC) wszystkich kontrolerów sieciowych w systemie. Polecenie getmac jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Iść do | Polecenie goto jest używane w pliku wsadowym lub skrypcie, aby skierować proces polecenia do oznaczonej linii w skrypcie. Polecenie goto jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Gpresult | Polecenie gpresult służy do wyświetlania ustawień zasad grupy. Polecenie gpresult jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Gpupdate | Polecenie gpupdate służy do aktualizacji ustawień zasad grupy. Polecenie gpupdate jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Graftabl | Polecenie graftabl służy do włączania w systemie Windows wyświetlania rozszerzonego zestawu znaków w trybie graficznym. Polecenie graftabl jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach Windows i MS-DOS do wersji 5.0. Polecenie graftabl nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Grafika | Polecenie grafika służy do załadowania programu, który może drukować grafikę. Polecenie grafiki jest dostępne w systemie MS-DOS, jak również we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie grafiki nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Pomoc | Polecenie pomocy zawiera bardziej szczegółowe informacje na temat innych poleceń wiersza polecenia lub systemu MS-DOS. Polecenie help jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Nazwa hosta | Polecenie hostname wyświetla nazwę bieżącego hosta. Polecenie hostname jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Hwrcomp | Polecenie hwrcomp służy do kompilowania niestandardowych słowników do rozpoznawania pisma ręcznego. Polecenie hwrcomp jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Hwrreg | Polecenie hwrreg służy do instalowania wcześniej skompilowanego słownika niestandardowego do rozpoznawania pisma ręcznego. Polecenie hwrreg jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Icacls | Polecenie icacls służy do wyświetlania lub zmiany list kontroli dostępu do plików. Polecenie icacls jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. Polecenie icacls jest zaktualizowaną wersją polecenia cacls. |
| Jeśli | Polecenie if służy do wykonywania funkcji warunkowych w pliku wsadowym. Polecenie if jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Interlnk | Polecenie interlnk służy do łączenia dwóch komputerów przez połączenie szeregowe lub równoległe w celu udostępniania plików i drukarek. Polecenie interlnk jest dostępne tylko w systemie MS-DOS. Możliwość bezpośredniego połączenia dwóch komputerów jest obsługiwana przez funkcje sieciowe we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Intersvr | Polecenie intersvr służy do uruchamiania serwera Interlnk i kopiowania plików Interlnk z jednego komputera na drugi. Polecenie intersvr jest dostępne tylko w systemie MS-DOS. Możliwość bezpośredniego połączenia dwóch komputerów jest obsługiwana przez funkcje sieciowe we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Konfiguracja ip | Polecenie ipconfig służy do wyświetlania szczegółowych informacji o IP dla każdej karty sieciowej korzystającej z protokołu TCP/IP. Polecenia ipconfig można również użyć do zwolnienia i odnowienia adresów IP w systemach skonfigurowanych do odbierania ich przez serwer DHCP. Polecenie ipconfig jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Ipxroute | Polecenie ipxroute służy do wyświetlania i zmiany informacji o tablicach routingu IPX. Polecenie ipxroute jest dostępne w systemie Windows XP. Microsoft usunął swojego rodzimego klienta NetWare, począwszy od systemu Windows Vista, usuwając również powiązane polecenie ipxroute. |
| Irftp | Polecenie irftp służy do przesyłania plików przez łącze podczerwieni. Polecenie irftp jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Iscsicli | Polecenie iscsicli uruchamia inicjator iSCSI firmy Microsoft, używany do zarządzania iSCSI. Polecenie iscsicli jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Kb16 | Polecenie kb16 służy do obsługi plików MS-DOS, które wymagają skonfigurowania klawiatury dla określonego języka. Polecenie kb16 jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie kb16 nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie kb16 zastąpiło polecenie keyb począwszy od systemu Windows XP, ale istnieje tylko w celu obsługi starszych plików MS-DOS. |
| Keyb | Polecenie keyb służy do konfigurowania klawiatury dla określonego języka. Polecenie keyb jest dostępne w systemach Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. Zobacz polecenie kb16, aby uzyskać równoważne polecenie w nowszych wersjach systemu Windows. Ustawienia języka klawiatury są obsługiwane przez aplety Panelu sterowania Region i język lub Opcje regionalne i językowe (w zależności od wersji systemu Windows) w systemie Windows, począwszy od systemu Windows XP. |
| Klist | Komenda klist służy do wyświetlania biletów usługi Kerberos. Polecenia klist można również użyć do usunięcia biletów Kerberos. Polecenie klist jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Ksetup | Polecenie ksetup służy do konfigurowania połączeń z serwerem Kerberos. Polecenie ksetup jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. |
| Ktmutil .Name | Komenda ktmutil uruchamia narzędzie Kernel Transaction Manager. Polecenie ktmutil jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7 i Windows Vista. |
| Etykieta | Polecenie label służy do zarządzania etykietą woluminu dysku. Polecenie label jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Lh | Polecenie lh jest skróconą wersją polecenia loadhigh. Polecenie lh jest dostępne w Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Diagnostyka licencji | Polecenie licensediag to narzędzie służące do generowania dziennika tekstowego i innych plików danych zawierających informacje o aktywacji produktu i inne informacje dotyczące licencjonowania systemu Windows. Polecenie licensediag jest dostępne w systemie Windows 8. |
| Obciążenie | Polecenie loadfix służy do załadowania określonego programu do pierwszych 64 KB pamięci, a następnie uruchamia program. Polecenie loadfix jest dostępne w MS-DOS, jak również we wszystkich 32-bitowych wersjach Windows. Polecenie loadfix nie jest dostępne w 64-bitowych wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Loadhigh | Polecenie loadhigh służy do ładowania programu do wysokiej pamięci i jest zwykle używane z pliku autoexec.bat. Polecenie loadhigh jest dostępne w Windows 98 i 95, a także w MS-DOS. Użycie pamięci jest obsługiwane automatycznie, począwszy od systemu Windows XP. |
| Zamek | Polecenie lock służy do zablokowania dysku, umożliwiając programowi bezpośredni dostęp do dysku. Polecenie blokady jest dostępne tylko w systemie Windows 98 i 95. Blokowanie dysku nie jest już dostępne w systemie Windows XP. |
| Lodctr | Polecenie lodctr służy do aktualizowania wartości rejestru związanych z licznikami wydajności. Polecenie lodctr jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. |
| Logman | Polecenie logman służy do tworzenia dzienników sesji śledzenia zdarzeń i wydajności oraz zarządzania nimi. Polecenie logman obsługuje również wiele funkcji Monitora wydajności. Polecenie logman jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Wyloguj | Polecenie wylogowania służy do zakończenia sesji. Polecenie wylogowania jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. |
| Lpq | Polecenie lpq wyświetla stan kolejki drukowania na komputerze z uruchomionym programem Line Printer Daemon (LPD). Polecenie lpq jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie lpq nie jest domyślnie dostępne w systemach Windows 8, 7 lub Vista, ale można je włączyć, włączając funkcje Usługi drukowania LPD i Monitor portu LPR w Panelu sterowania i Programy. |
| Lpr | Polecenie lpr służy do wysłania pliku do komputera z uruchomionym programem Line Printer Daemon (LPD). Polecenie lpr jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows. Polecenie lpr nie jest domyślnie dostępne w systemach Windows 8, 7 lub Vista, ale można je włączyć, włączając funkcje Usługi drukowania LPD i Monitor portów LPR w Panelu sterowania i Programy. |
| Makecab | Polecenie makecab służy do bezstratnej kompresji jednego lub więcej plików. Polecenie makecab jest czasami nazywane Cabinet Maker. Polecenie makecab jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista i Windows XP. Polecenie makecab jest takie samo, jak polecenie diantz, polecenie, które zostało usunięte po systemie Windows 7. |
| Zarządzaj-bde | Polecenie manage-bde służy do konfigurowania szyfrowania dysków funkcją BitLocker z wiersza polecenia. Polecenie manage-bde jest dostępne w systemach Windows 8 i Windows 7. Skrypt o nazwie manage-bde.wsf istnieje w systemie Windows Vista i można go używać z poleceniem cscript do wykonywania zadań funkcji BitLocker z wiersza polecenia w tym systemie operacyjnym. |
| Md | Polecenie md jest skróconą wersją polecenia mkdir. Polecenie md jest dostępne we wszystkich wersjach systemu Windows, a także w MS-DOS. |
| Mem | The mem command shows information about used and free memory areas and programs that are currently loaded into memory in the MS-DOS subsystem. The mem command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The mem command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Memmaker | The memmaker command is used to start MemMaker, a memory optimization tool. The memaker command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is automatically optimized beginning in Windows XP. |
| Mkdir | The mkdir command is used to create a new folder. The mkdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mklink | The mklink command is used to create a symbolic link. The mklink command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Mode | The mode command is used to configure system devices, most often COM and LPT ports. The mode command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mofcomp | The mofcomp command properly displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file. The mofcomp command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| More | The more command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The more command can also be used to paginate the results of any other Command Prompt or MS-DOS command. The more command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mount | The mount command is used to mount Network File System (NFS) network shares. The mount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The mount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The mount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Mountvol | The mountvol command is used to display, create, or remove volume mount points. The mountvol command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ruszaj się | The move command is used to move one or files from one folder to another. The move command is also used to rename directories. The move command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mrinfo | The mrinfo command is used to provide information about a router's interfaces and neighbors. The mrinfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msav | The msav command starts Microsoft Antivirus. The msav command is only available in MS-DOS. Microsoft Antivirus was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Msbackup | The msbackup command starts Microsoft Backup, a tool used to back up and restore one or more files. The msbackup command is only available in MS-DOS. The msbackup command was replaced with Microsoft Backup beginning in Windows 95 and then Backup and Restore in later versions of Windows. |
| Mscdex | The mscdex command is used to provide CD-ROM access to MS-DOS. The mscdex command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows provides access to CD-ROM drives for the MS-DOS subsystem beginning in Windows XP, so the mscdex command is unnecessary in this and later operating systems. |
| Msd | The msd command starts Microsoft Diagnostics, a tool used to display information about your computer. The msd command is only available in MS-DOS. The msd command was replaced with System Information beginning in Windows 95. |
| Msg | The msg command is used to send a message to a user. The msg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msiexec | The msiexec command is used to start Windows Installer, a tool used to install and configure software. The msiexec command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Muiunattend | The muiunattend command starts the Multilanguage User Interface unattended setup process. The muiunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Nbtstat | The nbtstat command is used to show TCP/IP information and other statistical information about a remote computer. The nbtstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Internet | The net command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net1 | The net1 command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net1 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The net command should be used instead of the net1 command. The net1 command was made available in Windows NT and Windows 2000 as a temporary fix for a Y2K issue that the net command had, which was corrected before the release of Windows XP. The net1 command remains in later versions of Windows only for compatibility with older programs and scripts that utilized the command. |
| Netcfg | The netcfg command is used to install the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), a lightweight version of Windows used to deploy workstations. The netcfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Netsh | The netsh command is used to start Network Shell, a command-line utility used to manage the network configuration of the local, or a remote, computer. The netsh command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Netstat | The netstat command is most commonly used to display all open network connections and listening ports. The netstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Nfsadmin | The nfsadmin command is used to manage Server for NFS or Client for NFS from the command line. The nfsadmin command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The nfsadmin command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The nfsadmin command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Nlsfunc | The nlsfunc command is used to load information specific to a particular country or region. The nlsfunc command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The nlsfunc command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Nlsfunc is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Nltest | The nltest command is used to test secure channels between Windows computers in a domain and between domain controllers that are trusting other domains. The nltest command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Nslookup | The nslookup is most commonly used to display the hostname of an entered IP address. The nslookup command queries your configured DNS server to discover the IP address. The nslookup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ntbackup | The ntbackup command is used to perform various backup functions from the Command Prompt or from within a batch or script file. The ntbackup command is available in Windows XP. The ntbackup command was replaced with the wbadmin beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Ntsd | The ntsd command is used to perform certain command line debugging tasks. The ntsd command is available in Windows XP. The ntsd command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the addition of dump file support in Task Manager. |
| Ocsetup | The ocsetup command starts the Windows Optional Component Setup tool, used to install additional Windows features. The ocsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Beginning in Windows 8, Microsoft is depreciating the ocsetup command in favor of the dism command. |
| Openfiles | The openfiles command is used to display and disconnect open files and folders on a system. The openfiles command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ścieżka | The path command is used to display or set a specific path available to executable files. The path command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pathping | The pathping command functions much like the tracert command but will also report information about network latency and loss at each hop. The pathping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pause | The pause command is used within a batch or script file to pause the processing of the file. When the pause command is used, a “Press any key to continue…” message displays in the command window. The pause command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pentnt | The pentnt command is used to detect floating point division errors in the Intel Pentium chip. The pentnt command is also used to enable floating point emulation and disable floating point hardware. The pentnt command is available in Windows XP. The pentnt command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the lack of Intel Pentium CPU use at the time of this operating system release. |
| Świst | The ping command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity. The ping command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Pkgmgr | The pkgmgr command is used to start the Windows Package Manager from the Command Prompt. Package Manager installs, uninstalls, configures, and updates features and packages for Windows. The pkgmgr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnpunattend | The pnpunattend command is used to automate the installation of hardware device drivers. The pnpunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnputil | The pnputil command is used to start the Microsoft PnP Utility, a tool used to install a Plug and Play device from the command line. The pnputil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Popd | The popd command is used to change the current directory to the one most recently stored by the pushd command. The popd command is most often utilized from within a batch or script file. The popd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Power | The power command is used to reduce the power consumed by a computer by monitoring software and hardware devices. The power command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The power command was replaced by operating system integrated power management functions beginning in Windows XP. |
| Powercfg | The powercfg command is used to manage the Windows power management settings from the command line. The powercfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| The print command is used to print a specified text file to a specified printing device. The print command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. | |
| Prompt | The prompt command is used to customize the appearance of the prompt text in Command Prompt or MS-DOS. The prompt command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pushd | The pushd command is used to store a directory for use, most commonly from within a batch or script program. The pushd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pwlauncher | The pwlauncher command is used to enable, disable, or show the status of your Windows To Go startup options. The pwlauncher command is available in Windows 8. |
| Qappsrv | The qappsrv command is used to display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers available on the network. The qappsrv command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Qbasic | The qbasic command starts QBasic, the MS-DOS based programming environment for the BASIC programming language. The qbasic command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The qbasic command is not installed by default with Windows 98 or 95 but is available from the installation disc or disks. |
| Qprocess | The qprocess command is used to display information about running processes. The qprocess command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Zapytanie | The query command is used to display the status of a specified service. The query command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Quser | The quser command is used to display information about users currently logged on to the system. The quser command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Qwinsta | The qwinsta command is used to display information about open Remote Desktop Sessions. The qwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasautou | The rasautou command is used to manage Remote Access Dialer AutoDial addresses. The rasautou command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasdial | The rasdial command is used to start or end a network connection for a Microsoft client. The rasdial command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rcp | The rcp command is used to copy files between a Windows computer and a system running the rshd daemon. The rcp command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rcp command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rcp command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rd | The rd command is the shorthand version of the rmdir command. The rd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rdpsign | The rdpsign command is used to sign a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) file. The rdpsign command is available in Windows 7. |
| Reagentc | The reagentc command is used to configure the Windows Recovery Environment (RE). The reagentc command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Recimg | The recimg command is used to create a custom refresh image. The recimg command is available in Windows 8. |
| Recover | The recover command is used to recover readable data from a bad or defective disk. The recover command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Reg | The reg command is used to manage the Windows Registry from the command line. The reg command can perform common registry functions like adding registry keys, exporting the registry, etc. The reg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Regini | The regini command is used to set or change registry permissions and registry values from the command line. The regini command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Register-cimprovider | The register-cimprovider command is used to register a Common Information Model (CIM) Provider in Windows. The register-cimprovider command is available in Windows 8. |
| Regsvr32 | The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file as a command component in the Windows Registry. The regsvr32 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Relog | The relog command is used to create new performance logs from data in existing performance logs. The relog command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rem | The rem command is used to record comments or remarks in a batch or script file. The rem command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Ren | The ren command is the shorthand version of the rename command. The ren command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rename | The rename command is used to change the name of the individual file that you specify. The rename command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Repair-bde | The repair-bde command is used to repair or decrypt a damaged drive that's been encrypted using BitLocker. The repair-bde command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Replace | The replace command is used to replace one or more files with one or more other files. The replace command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Reset | The reset command, executed as reset session, is used to reset the session subsystem software and hardware to known initial values. The reset command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Restore | The restore command is used to restore files that were backed up using the backup command. The restore command is only available in MS-DOS. The backup command was only available up to MS-DOS 5.00 but the restore command was included by default with later versions of MS-DOS to provide a way to restore files that were backed up in previous versions of MS-DOS. |
| Rexec | The rexec command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rexec daemon. The rexec command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here. The rexec command is not available in Windows 7 but can be executed in Windows XP via Windows XP Mode if need be. |
| Rmdir | The rmdir command is used to delete an existing or completely empty folder. The rmdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Robocopy | The robocopy command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. This command is also called Robust File Copy. The robocopy command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The robocopy command is superior to both the copy command and the xcopy command because robocopy supports many more options. |
| Route | The route command is used to manipulate network routing tables. The route command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Rpcinfo | The rpcinfo command makes a remote procedure call (RPC) to an RPC server and reports what it finds. The rpcinfo command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The rpcinfo command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The rpcinfo command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rpcping | The rpcping command is used to ping a server using RPC. The rpcping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Rsh | The rsh command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rsh daemon. The rsh command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rsh command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rsm | The rsm command is used to manage media resources using Removable Storage. The rsm command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsm command was optional in Windows Vista and then removed in Windows 7 due to Removable Storage Manager being removed from the operating system. Search for the rsm command in the C:\Windows\winsxs folder in Windows Vista if you're having trouble executing the command. |
| Runas | The runas command is used to execute a program using another user's credentials. The runas command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rwinsta | The rwinsta command is the shorthand version of the reset session command. The rwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Sc | The sc command is used to configure information about services. The sc command communicates with the Service Control Manager. The sc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Scandisk | The scandisk command is used to start Microsoft ScanDisk, a disk repair program. The scandisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The scandisk command was replaced by the chkdsk command beginning in Windows XP. |
| Scanreg | The scanreg command starts Windows Registry Checker, a basic registry repair program and backup utility. The scanreg command is available in Windows 98 and Windows 95. The functions provided by the scanreg command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP due to changes in how the Windows Registry functions. |
| Schtasks | The schtasks command is used to schedule specified programs or commands to run at certain times. The schtasks command can be used to create, delete, query, change, run, and end scheduled tasks. The schtasks command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.? |
| Sdbinst | The sdbinst command is used to deploy customized SDB database files. The sdbinst command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Secedit | The secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security by comparing the current security configuration to a template. The secedit command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ustawić | The set command is used to display, enable, or disable environment variables in MS-DOS or from the Command Prompt. The set command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Setlocal | The setlocal command is used to start the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The setlocal command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Setspn | The setspn command is used to manage the Service Principal Names (SPN) for an Active Directory (AD) service account. The setspn command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Setver | The setver command is used to set the MS-DOS version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. The setver command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The setver command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Setx | The setx command is used to create or change environment variables in the user environment or the system environment. The setx command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sfc | The sfc command is used to verify and replace important Windows system files. The sfc command is also referred to as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker, depending on the operating system. The sfc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Cień | The shadow command is used to monitor another Remote Desktop Services session. The shadow command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Udział | The share command is used to install file locking and file sharing functions in MS-DOS. The share command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The share command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Share is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Shift | The shift command is used to change the position of replaceable parameters in a batch or script file. The shift command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Showmount | The showmount command is used to display information about NFS mounted file systems. The showmount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The showmount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The showmount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Zamknąć | The shutdown command can be used to shut down, restart, or log off the current system or a remote computer. The shutdown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Smartdrv | The smartdrv command installs and configures SMARTDrive, a disk caching utility for MS-DOS. The smartdrv command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Caching is automatic beginning in Windows XP, making the smartdrv command unnecessary. |
| Sortować | The sort command is used to read data from a specified input, sort that data, and return the results of that sort to the Command Prompt screen, a file, or another output device. The sort command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Początek | The start command is used to open a new command line window to run a specified program or command. The start command can also be used to start an application without creating a new window. The start command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Subst | The subst command is used to associate a local path with a drive letter. The subst command is a lot like the net use command except a local path is used instead of a shared network path. The subst command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The subst command replaced the assign command beginning with MS-DOS 6.0. |
| Sxstrace | The sxstrace command is used to start the WinSxs Tracing Utility, a programming diagnostic tool. The sxstrace command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sys | The sys command is used to copy the MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk. The sys command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The sys command is used most often to create a simple bootable disk or hard drive. The necessary system files for Windows are too large to fit on a disk, so the sys command was removed beginning in Windows XP. |
| Systeminfo | The systeminfo command is used to display basic Windows configuration information for the local or a remote computer. The systeminfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Takeown | The takedown command is used to regain access to a file that that an administrator was denied access to when reassigning ownership of the file. The takeown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Taskkill | The taskkill command is used to terminate a running task. The taskkill command is the command line equivalent of ending a process in Task Manager in Windows. The taskkill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tasklist | Displays a list of applications, services, and the Process ID (PID) currently running on either a local or a remote computer. The tasklist command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tcmsetup | The tcmsetup command is used to set up or disable the Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) client. The tcmsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Telnet | The telnet command is used to communicate with remote computers that use the Telnet protocol. The telnet command is available in all versions of Windows. The telnet command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tftp | The tftp command is used to transfer files to and from a remote computer that's running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) service or daemon. The tftp command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tftp command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the TFTP Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Time | The time command is used to show or change the current time. The time command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Koniec czasu | The timeout command is typically used in a batch or script file to provide a specified timeout value during a procedure. The timeout command can also be used to ignore keypresses. The timeout command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Tytuł | The title command is used to set the Command Prompt window title. The title command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tlntadmn | The tlntadmn command is used to administer a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. The tlntadmn command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tlntadmn command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Server Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tpmvscmgr | The tpmvscmgr command is used to create and destroy TPM virtual smart cards. The tpmvscmgr command is available in Windows 8. |
| Tracerpt | The tracerpt command is used to process event trace logs or real-time data from instrumented event trace providers. The tracerpt command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tracert | The tracert command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to a specified remote computer with increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values and displays the IP address and hostname, if available, of the router interfaces between the source and destination. The tracert command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Drzewo | The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path. The tree command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Tscon | The tscon command is used to attach a user session to a Remote Desktop session. The tscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsdiscon | The tsdiscon command is used to disconnect a Remote Desktop session. The tsdiscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tskill | The tskill command is used to end the specified process. The tskill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsshutdn | The tsshutdn command is used to remotely shut down or restart a terminal server. The tsshutdn command is available in Windows XP. The ability to shut down a computer remotely is also available in the more powerful shutdown command, so tsshutdn was removed beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Rodzaj | The type command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The type command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Typeperf | The typerperf command displays performance data in the Command Prompt window or writes the data to specified log file. The typeperf command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tzutil | The tzutil command is used to display or configure the current system's time zone. The tzutil command can also be used to enable or disable Daylight Saving Time adjustments. The tzutil command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Umount | The umount command is used to remove Network File System (NFS) mounted network shares. The umount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The umount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The umount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Undelete | The undelete command is used to undo a deletion performed with the MS-DOS delete command. The undelete command is only available in MS-DOS. The undelete command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to the availability of the Recycle Bin in Windows. Additionally, free file recovery programs are available from third-party software makers. |
| Unformat | The unformat command is used to undo the formatting on a drive performed by the MS-DOS format command. The unformat command is only available in MS-DOS. The unformat command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to file system changes. |
| Unlock | The unlock command is used to unlock a drive, disabling direct disk access for a program. The unlock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP. |
| Unlodctr | The unlodctr command removes Explain text and Performance counter names for a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. The unlodctr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Vaultcmd | The vaultcmd command is used to create, remove, and show stored credentials. The vaultcmd command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Ver | The ver command is used to display the current Windows or MS-DOS version number. The ver command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Verify | The verify command is used to enable or disable the ability of Command Prompt, or MS-DOS, to verify that files are written correctly to a disk. The verify command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vol | The vol command shows the volume label and serial number of a specified disk, assuming this information exists. The vol command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vsafe | The vsafe command is used to start VSafe, a basic virus protection system for MS-DOS. The vsafe command is only available in MS-DOS. VSafe was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Vssadmin | The vssadmin command starts the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool which displays current volume shadow copy backups and all installed shadow copy writers and providers. The vssadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| W32tm | The w32tm command is used to diagnose issues with Windows Time. The w32tm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Waitfor | The waitfor command is used to send or wait for a signal on a system. The waitfor command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wbadmin | The wbadmin command is used to start and stop backup jobs, display details about a previous backup, list the items within a backup, and report on the status of a currently running backup. The wbadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The wbadmin command replaced the ntbackup command beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Wecutil | The wecutil command is used to manage subscriptions to events that are forwarded from WS-Management supported computers. The wecutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wevtutil | The wevtutil command starts the Windows Events Command Line Utility which is used to manage event logs and publishers. The wevtutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Where | The where command is used to search for files that match a specified pattern. The where command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Whoami | The whoami command is used to retrieve user name and group information on a network. The whoami command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winmgmt | The winmgmt command starts the command line version of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. The winmgmt command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Winrm | The winrm command is used to start the command line version of Windows Remote Management, used to manage secure communications with local and remote computers using web services. The winrm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winrs | The winrs command is used to open a secure command window with a remote host. The winrs command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winsat | The winsat command starts the Windows System Assessment Tool, a program that assesses various features, attributes, and capabilities of a computer running Windows. The winsat command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wmic | The wmic command starts the Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC), a scripting interface that simplifies the use of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and systems managed via WMI. The wmic command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Wsmanhttpconfig | The wsmanhttpconfig command is used to manage aspects of the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service. The wsmanhttpconfig command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Xcopy | The xcopy command can copy one or more files or directory trees from one location to another. The xcopy command is generally considered a more “powerful” version of the copy command through the robocopy command trumps even xcopy. The xcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. A command by the name of xcopy32 existed in Windows 95 and Windows 98. To avoid a long and confusing explanation here, just know that no matter if you executed the xcopy command or the xcopy32 command, you were always executing the most updated version of the command. |
| Xwizard | The xwizard command, short for Extensible Wizard, is used to register data in Windows, often from a preconfigured XML file. The xwizard command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
The above list is a set of most essential commands of command prompt. To view or download a PDF version of complete set of windows commands, please click on the below button.

Pobierz jako PDF
Aby uzyskać więcej takich wskazówek, sztuczek i aktualizacji związanych z technologią, zasubskrybuj Tweak Library , a jeśli bardziej interesują Cię filmy związane z technologią, obejrzyj i zasubskrybuj nasz kanał YouTube . Możesz również skontaktować się z nami na Facebooku i Pintereście .
