Utilisez l'invite de commande comme un pro - Tout sur l'invite de commande
Publié: 2019-05-21Avec le lancement de Windows 10, Microsoft a lentement poussé la ligne de commande hors de l'interface Windows. La raison derrière cela était que la ligne de commande était un outil obsolète et des plus inutiles d'une ère de saisie textuelle. Cependant, de nombreuses commandes sont toujours utiles, et Windows 10 a même ajouté de nouvelles fonctionnalités au monde de la ligne de commande. Maintenant, l'invite de commande est repensée en PowerShell, une application qui peut être utilisée de la même manière que l'invite de commande. C'est une application colorée qui remplace l'invite de commande, bien que vous puissiez toujours utiliser l'invite de commande à partir de maintenant. Ces astuces d'invite de commande sont vraiment utiles pour les administrateurs d'ordinateurs et leur permettent d'accomplir professionnellement plusieurs tâches.
Comment ouvrir l'invite de commande
Appuyez sur Win + R -> tapez 'cmd' -> appuyez sur 'Entrée'
Dans la barre de recherche, tapez 'cmd' appuyez sur 'Entrée'.
Si vous souhaitez ouvrir l'invite de commande en tant qu'administrateur, dans la barre de recherche, tapez 'cmd' et dès qu'il affiche 'Application de commande', faites un clic droit dessus et cliquez sur 'Exécuter en tant qu'administrateur'.
A lire également : Tout sur les raccourcis clavier de Windows 10
Comment trouver toutes les commandes sur l'invite de commande
Pour trouver les commandes pertinentes et leur syntaxe dans l'invite de commande, nous pouvons taper 'cmd /?' ou tapez une commande suivie de '/?' par exemple 'ipconfig /?' ouvre la liste des options et la syntaxe avec leurs actions. Cet interpréteur de commandes nous est utile pour apprendre de nouvelles commandes sur l'invite de commande.
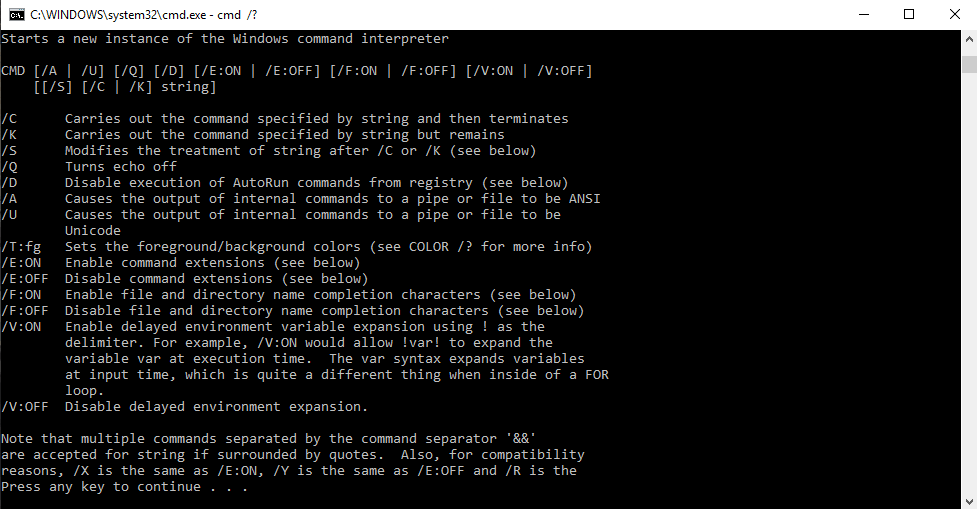
Utilisation de la syntaxe
cmd [/c|/k] [/s] [/q] [/d] [/a|/u] [/t:{<B><F>|<F>}] [/e:{on|off}] [/f:{on|off}] [/v:{on|off}] [<String>]
Paramètres
| Paramètre | La description |
| /c | Exécute la commande spécifiée par String puis s'arrête. |
| /k | Exécute la commande spécifiée par String et continue. |
| /s | Modifie le traitement de String après /c ou /k. |
| /q | Désactive l'écho. |
| /ré | Désactive l'exécution des commandes AutoRun. |
| /une | Formate la sortie de la commande interne dans un canal ou un fichier en tant qu'American National Standards Institute (ANSI). |
| /u | Formate la sortie de la commande interne dans un tube ou un fichier au format Unicode. |
| /t :{<B><F>|<F>} | Définit les couleurs d'arrière-plan (B) et de premier plan (F). |
| /e:sur | Active les extensions de commande. |
| /e:off | Désactive les extensions de commandes. |
| /f:sur | Active la complétion des noms de fichiers et de répertoires. |
| /f:off | Désactive la complétion des noms de fichiers et de répertoires. |
| /v:sur | Active l'expansion différée des variables d'environnement. |
| /v:off | Désactive l'expansion différée des variables d'environnement. |
| <Chaîne> | Spécifie la commande que vous souhaitez exécuter. |
| /? | Affiche l'aide à l'invite de commande. |
Le tableau suivant répertorie les chiffres hexadécimaux valides que vous pouvez utiliser comme valeurs pour <B> et <F>
| Valeur | Couleur |
| 0 | Noir |
| 1 | Bleu |
| 2 | Vert |
| 3 | Aqua |
| 4 | rouge |
| 5 | Mauve |
| 6 | Jaune |
| sept | blanc |
| 8 | Gris |
| 9 | Bleu clair |
| une | Vert clair |
| b | Aqua clair |
| c | Rouge clair |
| ré | Violet clair |
| e | Jaune clair |
| F | Blanc brillant |
Voici une liste complète des commandes d'invite de commande. Vous pouvez également télécharger toutes les commandes avec leur syntaxe à partir du lien au bas de cet article.
| Commander | La description |
| Ajouter | La commande append peut être utilisée par des programmes pour ouvrir des fichiers dans un autre répertoire comme s'ils se trouvaient dans le répertoire courant. La commande append est disponible dans MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande append n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Arp | La commande arp est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier des entrées dans le cache ARP. La commande arp est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. |
| Assoc | La commande assoc est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier le type de fichier associé à une extension de fichier particulière. La commande assoc est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| À | La commande at est utilisée pour planifier l'exécution de commandes et d'autres programmes à une date et une heure spécifiques. La commande at est disponible dans Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. À partir de Windows 8, la planification des tâches en ligne de commande doit plutôt être complétée avec la commande schtasks. |
| Administrateur | La commande atmadm est utilisée pour afficher les informations relatives aux connexions en mode de transfert asynchrone (ATM) sur le système. La commande atmadm est disponible dans Windows XP. La prise en charge d'ATM a été supprimée à partir de Windows Vista, rendant la commande atmadm inutile. |
| Attribut | La commande attrib est utilisée pour modifier les attributs d'un seul fichier ou d'un répertoire. La commande attrib est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Auditpol | La commande auditpol est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier les stratégies d'audit. La commande auditpol est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Bcdboot | La commande bcdboot est utilisée pour copier les fichiers de démarrage sur la partition système et pour créer un nouveau magasin BCD système. La commande bcdboot est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| Bcdedit | La commande bcdedit est utilisée pour afficher ou apporter des modifications aux données de configuration de démarrage. La commande bcdedit est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. La commande bcdedit a remplacé la commande bootcfg à partir de Windows Vista. |
| Bdehdcfg | La commande bdehdcfg est utilisée pour préparer un disque dur pour le chiffrement de lecteur BitLocker. La commande bdehdcfg est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| Bitsadmin | La commande bitsadmin est utilisée pour créer, gérer et surveiller les tâches de téléchargement et de chargement. La commande bitsadmin est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. Bien que la commande bitsadmin soit disponible dans Windows 8 et Windows 7, elle est progressivement supprimée. Les applets de commande BITS PowerShell doivent être utilisées à la place. |
| Bootcfg | La commande bootcfg est utilisée pour créer, modifier ou afficher le contenu du fichier boot.ini, un fichier caché utilisé pour identifier dans quel dossier, sur quelle partition et sur quel disque dur se trouve Windows. La commande bootcfg est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande bootcfg a été remplacée par la commande bcdedit à partir de Windows Vista. Bootcfg est toujours disponible dans Windows 8, 7 et Vista, mais il n'a aucune valeur réelle puisque boot.ini n'est pas utilisé dans ces systèmes d'exploitation. |
| Bootsect | La commande bootsect est utilisée pour configurer le code de démarrage principal sur un code compatible avec BOOTMGR (Vista et versions ultérieures) ou NTLDR (XP et versions antérieures). La commande bootsect est disponible dans Windows 8. La commande bootsect est également disponible dans Windows 7 et Windows Vista, mais uniquement à partir de l'invite de commande disponible dans les options de récupération système. |
| Casser | La commande break définit ou efface la vérification CTRL + C étendue sur les systèmes DOS. La commande break est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. La commande break est disponible dans Windows XP et les versions ultérieures de Windows pour assurer la compatibilité avec les fichiers MS-DOS, mais elle n'a aucun effet dans Windows lui-même. |
| Cacls | La commande cacls est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier les listes de contrôle d'accès des fichiers. La commande cacls est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande cacls est progressivement supprimée au profit de la commande icacls, qui devrait être utilisée à la place dans toutes les versions de Windows après Windows XP. |
| Appeler | La commande call est utilisée pour exécuter un script ou un programme batch à partir d'un autre script ou programme batch. La commande d'appel est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. La commande d'appel n'a aucun effet en dehors d'un script ou d'un fichier batch. En d'autres termes, l'exécution de la commande call à l'invite de commande ou à l'invite MS-DOS ne fera rien. |
| CD | La commande cd est la version abrégée de la commande chdir. La commande cd est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Certreq | La commande certreq est utilisée pour exécuter diverses fonctions de certificat d'autorité de certification (CA). La commande certreq est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Certutil | La commande certutil est utilisée pour vider et afficher les informations de configuration de l'autorité de certification (CA) en plus d'autres fonctions CA. La commande certutil est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Changer | La commande change modifie divers paramètres du serveur Terminal Server, tels que les modes d'installation, les mappages de ports COM et les connexions. La commande de modification est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| CHCP | La commande chcp affiche ou configure le numéro de page de code actif. La commande chcp est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Chdir | La commande chdir est utilisée pour afficher la lettre de lecteur et le dossier dans lesquels vous vous trouvez actuellement. Chdir peut également être utilisé pour modifier le lecteur et/ou le répertoire dans lequel vous souhaitez travailler. La commande chdir est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, comme ainsi que sous MS-DOS. |
| Vérifier l'isolation du réseau | La commande checknetisolation est utilisée pour tester les applications qui nécessitent des capacités réseau. La commande checknetisolation est disponible dans Windows 8. |
| Chglogon | La commande chglogon active, désactive ou vide les connexions de session Terminal Server. La commande chglogon est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. L'exécution de la commande chglogon est identique à l'exécution de la connexion change. |
| Chgport | La commande chgport peut être utilisée pour afficher ou modifier les mappages de port COM pour la compatibilité DOS. La commande chgport est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. L'exécution de la commande chgport est identique à l'exécution de change port. |
| Chgusr | La commande chgusr est utilisée pour modifier le mode d'installation du serveur Terminal Server. La commande chgusr est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. L'exécution de la commande chgusr est identique à l'exécution du changement d'utilisateur. |
| Chkdsk | La commande chkdsk, souvent appelée vérification du disque, est utilisée pour identifier et corriger certaines erreurs de disque dur. La commande chkdsk est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Chkntfs | La commande chkntfs est utilisée pour configurer ou afficher la vérification du lecteur de disque pendant le processus de démarrage de Windows. La commande chkntfs est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Choix | La commande choice est utilisée dans un script ou un programme batch pour fournir une liste de choix et renvoyer la valeur de ce choix au programme. La commande choice est disponible sous MS-DOS et toutes les versions de Windows à l'exception de Windows XP. Utilisez la commande set avec le commutateur /p à la place de la commande choice dans les fichiers de commandes et les scripts que vous prévoyez d'utiliser dans Windows XP. |
| Chiffrer | La commande cipher affiche ou modifie l'état de chiffrement des fichiers et des dossiers sur les partitions NTFS. La commande de chiffrement est disponible dans Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Agrafe | La commande clip est utilisée pour rediriger la sortie de n'importe quelle commande vers le presse-papiers de Windows. La commande clip est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Cls | La commande cls efface l'écran de toutes les commandes et autres textes saisis précédemment. La commande cls est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Commande | La commande cmd démarre une nouvelle instance de l'interpréteur de commandes cmd.exe. La commande cmd est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Cmdkey | La commande cmdkey est utilisée pour afficher, créer et supprimer les noms d'utilisateur et les mots de passe stockés. La commande cmdkey est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| cmstp | La commande cmstp installe ou désinstalle un profil de service Connection Manager. La commande cmstp est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Couleur | La commande de couleur est utilisée pour modifier les couleurs du texte et de l'arrière-plan dans la fenêtre d'invite de commande. La commande de couleur est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Commander | La commande 'command' démarre une nouvelle instance de l'interpréteur de commandes command.com. La commande 'command' est disponible sous MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande 'command' n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Comp | La commande comp est utilisée pour comparer le contenu de deux fichiers ou ensembles de fichiers. La commande comp est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Compact | La commande compact est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier l'état de compression des fichiers et des répertoires sur les partitions NTFS. La commande compacte est disponible dans Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Convertir | La commande convert est utilisée pour convertir les volumes formatés FAT ou FAT32 au format NTFS. La commande de conversion est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Copie | La commande de copie fait simplement cela - elle copie un ou plusieurs fichiers d'un emplacement à un autre. La commande de copie est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. La commande xcopy est considérée comme une version plus « puissante » de la commande copy. |
| Cscript | La commande cscript est utilisée pour exécuter des scripts via Microsoft Script Host. La commande cscript est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. La commande cscript est généralement utilisée pour gérer les imprimantes à partir de la ligne de commande à l'aide de scripts tels que prncnfg.vbs, prndrvr.vbs, prnmngr.vbs, etc. |
| Cté | La commande ctty est utilisée pour modifier les périphériques d'entrée et de sortie par défaut du système. La commande ctty est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95 ainsi que sous MS-DOS. Les fonctions fournies par la commande ctty n'étaient plus nécessaires à partir de Windows XP car l'interpréteur command.com (MS-DOS) n'est plus l'interpréteur de ligne de commande par défaut. |
| Date | La commande date est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier la date actuelle. La commande date est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Dblspace | La commande dblspace est utilisée pour créer ou configurer des lecteurs compressés DoubleSpace. La commande dblspace est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. DriveSpace, exécuté à l'aide de la commande drvspace, est une version mise à jour de DoubleSpace. Windows gère nativement la compression à partir de Windows XP. |
| Déboguer | La commande debug démarre Debug, une application en ligne de commande utilisée pour tester et modifier des programmes. La commande de débogage est disponible dans MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande de débogage n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Défragmenter | La commande defrag est utilisée pour défragmenter un lecteur que vous spécifiez. La commande defrag est la version en ligne de commande du défragmenteur de disque de Microsoft. La commande defrag est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Suppr | La commande del est utilisée pour supprimer un ou plusieurs fichiers. La commande del est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. La commande del est la même que la commande erase. |
| Deltree | La commande deltree est utilisée pour supprimer un répertoire et tous les fichiers et sous-répertoires qu'il contient. La commande deltree est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. À partir de Windows XP, un dossier et ses fichiers et sous-dossiers peuvent être supprimés à l'aide de la fonction /s de la commande rmdir. Deltree n'était plus nécessaire avec cette nouvelle capacité rmdir, la commande a donc été supprimée. |
| Diantz | La commande diantz est utilisée pour compresser sans perte un ou plusieurs fichiers. La commande diantz est parfois appelée Cabinet Maker. La commande diantz est disponible sous Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande diantz est identique à la commande makecab. |
| Réal | La commande dir est utilisée pour afficher une liste des fichiers et dossiers contenus dans le dossier dans lequel vous travaillez actuellement. La commande dir affiche également d'autres informations importantes telles que le numéro de série du disque dur, le nombre total de fichiers répertoriés, leur taille combinée, la quantité totale d'espace libre restant sur le disque, et plus encore. La commande dir est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Disquecomp | La commande diskcomp est utilisée pour comparer le contenu de deux disquettes. La commande diskcomp est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Copie de disque | La commande diskcopy est utilisée pour copier tout le contenu d'une disquette sur une autre. La commande diskcopy est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Part de disque | La commande diskpart est utilisée pour créer, gérer et supprimer des partitions de disque dur. La commande diskpart est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande diskpart a remplacé la commande fdisk à partir de Windows XP. |
| Diskperf | La commande diskperf est utilisée pour gérer à distance les compteurs de performances des disques. La commande diskperf est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Disque dur | La commande diskraid démarre l'outil DiskRAID qui est utilisé pour gérer et configurer les matrices RAID. La commande diskraid est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Disme | La commande dism démarre l'outil de maintenance et de gestion des images de déploiement (DISM). L'outil DISM est utilisé pour gérer les fonctionnalités des images Windows. La commande dism est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| Dispdiag | La commande dispdiag est utilisée pour générer un journal d'informations sur le système d'affichage. La commande dispdiag est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Déjoindre | La commande djoin est utilisée pour créer un nouveau compte d'ordinateur dans un domaine. La commande djoin est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Doskey | La commande doskey est utilisée pour modifier les lignes de commande, créer des macros et rappeler les commandes saisies précédemment. La commande doskey est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Dosshell | La commande dosshell démarre DOS Shell, un outil graphique de gestion de fichiers pour MS-DOS. La commande dosshell est disponible dans Windows 95 (en mode MS-DOS) ainsi que dans MS-DOS version 6.0 et les versions MS-DOS ultérieures qui ont été mises à niveau à partir de versions précédentes contenant la commande dosshell. Un gestionnaire de fichiers graphique, Windows Explorer, est devenu une partie intégrante du système d'exploitation à partir de Windows 95. |
| Dox | La commande dosx est utilisée pour démarrer l'interface en mode protégé DOS (DPMI), un mode spécial conçu pour permettre aux applications MS-DOS d'accéder à plus que les 640 Ko normalement autorisés. La commande dosx est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande dosx n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. La commande dosx et DPMI ne sont disponibles que sous Windows pour prendre en charge les anciens programmes MS-DOS. |
| Requête de pilote | La commande driverquery est utilisée pour afficher une liste de tous les pilotes installés. La commande driverquery est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Espace Drv | La commande drvspace est utilisée pour créer ou configurer des lecteurs compressés DriveSpace. La commande drvspace est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. DriveSpace est une version mise à jour de DoubleSpace, exécutée à l'aide de la commande dblspace. Windows gère nativement la compression à partir de Windows XP. |
| Écho | La commande echo est utilisée pour afficher des messages, le plus souvent à partir de fichiers de script ou de commandes. La commande echo peut également être utilisée pour activer ou désactiver la fonction d'écho. La commande echo est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Éditer | La commande d'édition démarre l'outil Éditeur MS-DOS qui est utilisé pour créer et modifier des fichiers texte. La commande d'édition est disponible sous MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande d'édition n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Edlin | La commande edlin lance l'outil Edlin qui est utilisé pour créer et modifier des fichiers texte à partir de la ligne de commande. La commande edlin est disponible dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows mais n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. Dans MS-DOS, la commande edlin n'est disponible que jusqu'à MS-DOS 5.0, donc à moins que votre dernière version de MS-DOS ait été mise à niveau à partir de 5.0 ou d'une version antérieure, vous ne verrez pas la commande edlin. |
| Emm386 | La commande emm386 est utilisée pour permettre à MS-DOS d'accéder à plus de 640 Ko de mémoire. La commande emm386 est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. Windows lui-même a accès à la mémoire étendue et paginée à partir de Windows 95. |
| Endlocal | La commande endlocal est utilisée pour terminer la localisation des changements d'environnement dans un fichier batch ou script. La commande endlocal est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Effacer | La commande erase est utilisée pour supprimer un ou plusieurs fichiers. La commande d'effacement est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. La commande erase est la même que la commande del. |
| Esentutl | La commande esentutl est utilisée pour gérer les bases de données Extensible Storage Engine. La commande esentutl est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Créer un événement | La commande eventcreate est utilisée pour créer un événement personnalisé dans un journal des événements. La commande eventcreate est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Déclencheurs d'événements | La commande eventtriggers est utilisée pour configurer et afficher les déclencheurs d'événements. La commande eventtriggers est disponible dans Windows XP. À partir de Windows Vista, les déclencheurs d'événements sont créés à l'aide de la fonctionnalité Attacher une tâche à cet événement dans l'Observateur d'événements, ce qui rend inutile la commande eventtriggers. |
| Exe2bin | La commande exe2bin est utilisée pour convertir un fichier du type de fichier EXE (fichier exécutable) en un fichier binaire. La commande exe2bin est disponible dans les versions 32 bits de Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande exe2bin n'est disponible dans aucune version 64 bits de Windows. |
| Sortir | La commande exit est utilisée pour mettre fin à la session cmd.exe (Windows) ou command.com (MS-DOS) dans laquelle vous travaillez actuellement. La commande exit est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS . |
| Étendre | La commande expand est utilisée pour extraire les fichiers et dossiers contenus dans les fichiers Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). La commande expand est disponible sous MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions de Windows. La commande d'expansion n'est pas disponible dans la version 64 bits de Windows XP. |
| Extrac32 | La commande extrac32 est utilisée pour extraire les fichiers et dossiers contenus dans les fichiers Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). La commande extrac32 est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. La commande extrac32 est en fait un programme d'extraction CAB à utiliser par Internet Explorer, mais peut être utilisée pour extraire n'importe quel fichier Microsoft Cabinet. Utilisez la commande expand au lieu de la commande extrac32 si possible. |
| Extrait | La commande d'extraction est utilisée pour extraire les fichiers et dossiers contenus dans les fichiers Microsoft Cabinet (CAB). La commande extract est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95. La commande extract a été remplacée par la commande expand à partir de Windows XP. |
| Aide rapide | La commande fasthelp fournit des informations plus détaillées sur toutes les autres commandes MS-DOS. La commande fasthelp n'est disponible que sous MS-DOS. La commande help a remplacé la commande fasthelp à partir de Windows 95. |
| Fastopen | La commande fastopen est utilisée pour ajouter l'emplacement du disque dur d'un programme à une liste spéciale stockée en mémoire, améliorant potentiellement le temps de lancement du programme en supprimant la nécessité pour MS-DOS de localiser l'application sur le lecteur. La commande fastopen est disponible sous MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande fastopen n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. Fastopen n'est disponible que sous Windows 8, 7, Vista et XP pour prendre en charge les anciens fichiers MS-DOS. |
| FC | La commande fc est utilisée pour comparer deux fichiers individuels ou ensembles de fichiers, puis afficher les différences entre eux. La commande fc est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Fdisque | La commande fdisk est utilisée pour créer, gérer et supprimer des partitions de disque dur. La commande fdisk est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. La commande fdisk a été remplacée par la commande diskpart à partir de Windows XP. La gestion des partitions est également disponible à partir de la gestion des disques sous Windows 8, 7, Vista et XP. |
| Trouver | La commande find est utilisée pour rechercher une chaîne de texte spécifiée dans un ou plusieurs fichiers. La commande find est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Findstr | La commande findstr est utilisée pour rechercher des modèles de chaîne de texte dans un ou plusieurs fichiers. La commande findstr est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Doigt | La commande finger est utilisée pour renvoyer des informations sur un ou plusieurs utilisateurs sur un ordinateur distant qui exécute le service Finger. La commande finger est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Fltmc | La commande fltmc est utilisée pour charger, décharger, répertorier et autrement gérer les pilotes de filtre. La commande fltmc est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Fondue | La commande fondue, abréviation de Features on Demand User Experience Tool, est utilisée pour installer l'une des nombreuses fonctionnalités facultatives de Windows à partir de la ligne de commande. La commande fondue est disponible dans Windows 8. Les fonctionnalités facultatives de Windows peuvent également être installées à partir de l'applet Programmes et fonctionnalités du Panneau de configuration. |
| Pour | La commande for est utilisée pour exécuter une commande spécifiée pour chaque fichier d'un ensemble de fichiers. La commande for est le plus souvent utilisée dans un fichier de commandes ou de script. La commande for est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Forcés | La commande forcedos est utilisée pour démarrer le programme spécifié dans le sous-système MS-DOS. La commande forcedos n'est disponible que dans les versions 32 bits de Windows XP. La commande forcedos n'est utilisée que pour les programmes MS-DOS qui ne sont pas reconnus comme tels par Windows XP. |
| Pourfichiers | La commande forfiles sélectionne un ou plusieurs fichiers sur lesquels exécuter une commande spécifiée. La commande forfiles est le plus souvent utilisée dans un fichier batch ou script. La commande forfiles est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Format | La commande format est utilisée pour formater un lecteur dans le système de fichiers que vous spécifiez. La commande format est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. Le formatage du disque est également disponible à partir de la gestion des disques sous Windows 8, 7, Vista et XP. |
| FsutilName | La commande fsutil est utilisée pour effectuer diverses tâches de système de fichiers FAT et NTFS, telles que la gestion des points d'analyse et des fichiers fragmentés, le démontage d'un volume et l'extension d'un volume. La commande fsutil est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| FTP | La commande ftp peut être utilisée pour transférer des fichiers vers et depuis un autre ordinateur. L'ordinateur distant doit fonctionner comme un serveur FTP. La commande ftp est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. |
| Ftype | La commande ftype est utilisée pour définir un programme par défaut pour ouvrir un type de fichier spécifié. La commande ftype est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Getmac | La commande getmac est utilisée pour afficher l'adresse MAC (Media Access Control) de tous les contrôleurs réseau d'un système. La commande getmac est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Aller à | La commande goto est utilisée dans un fichier de commandes ou de script pour diriger le processus de commande vers une ligne étiquetée dans le script. La commande goto est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Grésultat | La commande gpresult est utilisée pour afficher les paramètres de stratégie de groupe. La commande gpresult est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Gpupdate | La commande gpupdate est utilisée pour mettre à jour les paramètres de stratégie de groupe. La commande gpupdate est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Greffable | La commandegraftabl est utilisée pour permettre à Windows d'afficher un jeu de caractères étendu en mode graphique. La commandegraftabl est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows et dans MS-DOS jusqu'à la version 5.0. La commandegraftabl n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Graphique | La commande graphics est utilisée pour charger un programme capable d'imprimer des graphiques. La commande graphique est disponible sous MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande graphique n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Aider | La commande help fournit des informations plus détaillées sur toutes les autres commandes d'invite de commande ou MS-DOS. La commande help est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Nom d'hôte | La commande hostname affiche le nom de l'hôte actuel. La commande hostname est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Hwrcomp | La commande hwrcomp est utilisée pour compiler des dictionnaires personnalisés pour la reconnaissance de l'écriture manuscrite. La commande hwrcomp est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| Hwrreg | La commande hwrreg est utilisée pour installer un dictionnaire personnalisé préalablement compilé pour la reconnaissance de l'écriture manuscrite. La commande hwrreg est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| Icacls | La commande icacls est utilisée pour afficher ou modifier les listes de contrôle d'accès des fichiers. La commande icacls est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. La commande icacls est une version mise à jour de la commande cacls. |
| Si | La commande if est utilisée pour exécuter des fonctions conditionnelles dans un fichier batch. La commande if est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Lien | La commande interlnk est utilisée pour connecter deux ordinateurs via une connexion série ou parallèle pour partager des fichiers et des imprimantes. La commande interlnk n'est disponible que sous MS-DOS. La possibilité de connecter directement deux ordinateurs est gérée par les fonctions de mise en réseau dans toutes les versions de Windows. |
| Intersvr | La commande intersvr est utilisée pour démarrer le serveur Interlnk et pour copier les fichiers Interlnk d'un ordinateur à un autre. La commande intersvr n'est disponible que sous MS-DOS. La possibilité de connecter directement deux ordinateurs est gérée par les fonctions de mise en réseau dans toutes les versions de Windows. |
| ipconfig | La commande ipconfig est utilisée pour afficher des informations IP détaillées pour chaque carte réseau utilisant TCP/IP. La commande ipconfig peut également être utilisée pour libérer et renouveler des adresses IP sur des systèmes configurés pour les recevoir via un serveur DHCP. La commande ipconfig est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. |
| Ipxroute | La commande ipxroute est utilisée pour afficher et modifier les informations sur les tables de routage IPX. La commande ipxroute est disponible dans Windows XP. Microsoft a supprimé son client NetWare natif à partir de Windows Vista, supprimant également la commande ipxroute associée. |
| Irftp | La commande irftp est utilisée pour transmettre des fichiers sur une liaison infrarouge. La commande irftp est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Iscsicli | La commande iscsicli démarre l'initiateur Microsoft iSCSI, utilisé pour gérer iSCSI. La commande iscsicli est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Ko16 | La commande kb16 est utilisée pour prendre en charge les fichiers MS-DOS qui doivent configurer un clavier pour une langue spécifique. La commande kb16 est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande kb16 n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. La commande kb16 a remplacé la commande keyb à partir de Windows XP, mais n'existe que pour prendre en charge les anciens fichiers MS-DOS. |
| Cléb | La commande keyb est utilisée pour configurer un clavier pour une langue spécifique. La commande keyb est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. Voir la commande kb16 pour une commande équivalente dans les versions ultérieures de Windows. Les paramètres de langue du clavier sont gérés par les applets Région et langue ou Options régionales et linguistiques (selon la version de Windows) du Panneau de configuration dans Windows à partir de Windows XP. |
| Klist | La commande klist est utilisée pour répertorier les tickets de service Kerberos. La commande klist peut également être utilisée pour purger les tickets Kerberos. La commande klist est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| KsetupGenericName | La commande ksetup est utilisée pour configurer les connexions à un serveur Kerberos. La commande ksetup est disponible sous Windows 8 et Windows 7. |
| KtmutilName | La commande ktmutil démarre l'utilitaire Kernel Transaction Manager. La commande ktmutil est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7 et Windows Vista. |
| Étiqueter | La commande label est utilisée pour gérer le nom de volume d'un disque. La commande label est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Lh | La commande lh est la version abrégée de la commande loadhigh. La commande lh est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. |
| Licensingdiag | La commande licensingdiag est un outil utilisé pour générer un journal textuel et d'autres fichiers de données contenant l'activation du produit et d'autres informations de licence Windows. La commande licensingdiag est disponible dans Windows 8. |
| Loadfix | La commande loadfix est utilisée pour charger le programme spécifié dans les 64 premiers Ko de mémoire, puis exécute le programme. La commande loadfix est disponible sous MS-DOS ainsi que dans toutes les versions 32 bits de Windows. La commande loadfix n'est pas disponible dans les versions 64 bits de Windows. |
| Charge élevée | La commande loadhigh est utilisée pour charger un programme en mémoire haute et est généralement utilisée à partir du fichier autoexec.bat. La commande loadhigh est disponible sous Windows 98 et 95, ainsi que sous MS-DOS. L'utilisation de la mémoire est gérée automatiquement à partir de Windows XP. |
| Verrouiller | La commande de verrouillage est utilisée pour verrouiller un lecteur, permettant un accès direct au disque pour un programme. La commande de verrouillage n'est disponible que sous Windows 98 et 95. Le verrouillage du lecteur n'est plus disponible à partir de Windows XP. |
| Lodctr | La commande lodctr est utilisée pour mettre à jour les valeurs de registre liées aux compteurs de performance. La commande lodctr est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. |
| Logman | La commande logman est utilisée pour créer et gérer les journaux de session et de performances d'Event Trace. La commande logman prend également en charge de nombreuses fonctions de l'Analyseur de performances. La commande logman est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Se déconnecter | La commande logoff est utilisée pour terminer une session. La commande de déconnexion est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. |
| Lpq | La commande lpq affiche l'état d'une file d'attente d'impression sur un ordinateur exécutant Line Printer Daemon (LPD). La commande lpq est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. La commande lpq n'est pas disponible par défaut dans Windows 8, 7 ou Vista, mais peut être activée en activant les fonctionnalités du service d'impression LPD et du moniteur de port LPR dans Programmes et fonctionnalités du Panneau de configuration. |
| Lpr | La commande lpr est utilisée pour envoyer un fichier à un ordinateur exécutant Line Printer Daemon (LPD). La commande lpr est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows. La commande lpr n'est pas disponible par défaut dans Windows 8, 7 ou Vista, mais peut être activée en activant les fonctionnalités du service d'impression LPD et du moniteur de port LPR dans Programmes et fonctionnalités du Panneau de configuration. |
| Makecab | La commande makecab est utilisée pour compresser sans perte un ou plusieurs fichiers. La commande makecab est parfois appelée Cabinet Maker. La commande makecab est disponible sous Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista et Windows XP. La commande makecab est identique à la commande diantz, une commande qui a été supprimée après Windows 7. |
| Gérer-bde | La commande manage-bde est utilisée pour configurer le chiffrement de lecteur BitLocker à partir de la ligne de commande. La commande manage-bde est disponible dans Windows 8 et Windows 7. Un script du nom de manage-bde.wsf existe dans Windows Vista et peut être utilisé avec la commande cscript pour effectuer des tâches BitLocker à partir de la ligne de commande dans ce système d'exploitation. |
| Maryland | La commande md est la version abrégée de la commande mkdir. La commande md est disponible dans toutes les versions de Windows, ainsi que dans MS-DOS. |
| Mémoire | The mem command shows information about used and free memory areas and programs that are currently loaded into memory in the MS-DOS subsystem. The mem command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The mem command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Memmaker | The memmaker command is used to start MemMaker, a memory optimization tool. The memaker command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Memory usage is automatically optimized beginning in Windows XP. |
| Mkdir | The mkdir command is used to create a new folder. The mkdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mklink | The mklink command is used to create a symbolic link. The mklink command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Mode | The mode command is used to configure system devices, most often COM and LPT ports. The mode command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mofcomp | The mofcomp command properly displays the data within a Managed Object Format (MOF) file. The mofcomp command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Suite | The more command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The more command can also be used to paginate the results of any other Command Prompt or MS-DOS command. The more command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Monter | The mount command is used to mount Network File System (NFS) network shares. The mount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The mount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The mount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Mountvol | The mountvol command is used to display, create, or remove volume mount points. The mountvol command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Se déplacer | The move command is used to move one or files from one folder to another. The move command is also used to rename directories. The move command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Mrinfo | The mrinfo command is used to provide information about a router's interfaces and neighbors. The mrinfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msav | The msav command starts Microsoft Antivirus. The msav command is only available in MS-DOS. Microsoft Antivirus was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Msbackup | The msbackup command starts Microsoft Backup, a tool used to back up and restore one or more files. The msbackup command is only available in MS-DOS. The msbackup command was replaced with Microsoft Backup beginning in Windows 95 and then Backup and Restore in later versions of Windows. |
| Mscdex | The mscdex command is used to provide CD-ROM access to MS-DOS. The mscdex command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Windows provides access to CD-ROM drives for the MS-DOS subsystem beginning in Windows XP, so the mscdex command is unnecessary in this and later operating systems. |
| Msd | The msd command starts Microsoft Diagnostics, a tool used to display information about your computer. The msd command is only available in MS-DOS. The msd command was replaced with System Information beginning in Windows 95. |
| Msg | The msg command is used to send a message to a user. The msg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Msiexec | The msiexec command is used to start Windows Installer, a tool used to install and configure software. The msiexec command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Muiunattend | The muiunattend command starts the Multilanguage User Interface unattended setup process. The muiunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Nbtstat | The nbtstat command is used to show TCP/IP information and other statistical information about a remote computer. The nbtstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net | The net command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Net1 | The net1 command is used to display, configure, and correct a wide variety of network settings. The net1 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The net command should be used instead of the net1 command. The net1 command was made available in Windows NT and Windows 2000 as a temporary fix for a Y2K issue that the net command had, which was corrected before the release of Windows XP. The net1 command remains in later versions of Windows only for compatibility with older programs and scripts that utilized the command. |
| Netcfg | The netcfg command is used to install the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE), a lightweight version of Windows used to deploy workstations. The netcfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Netsh | The netsh command is used to start Network Shell, a command-line utility used to manage the network configuration of the local, or a remote, computer. The netsh command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Netstat | The netstat command is most commonly used to display all open network connections and listening ports. The netstat command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Nfsadmin | The nfsadmin command is used to manage Server for NFS or Client for NFS from the command line. The nfsadmin command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The nfsadmin command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The nfsadmin command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Nlsfunc | The nlsfunc command is used to load information specific to a particular country or region. The nlsfunc command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The nlsfunc command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Nlsfunc is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Nltest | The nltest command is used to test secure channels between Windows computers in a domain and between domain controllers that are trusting other domains. The nltest command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Nslookup | The nslookup is most commonly used to display the hostname of an entered IP address. The nslookup command queries your configured DNS server to discover the IP address. The nslookup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ntbackup | The ntbackup command is used to perform various backup functions from the Command Prompt or from within a batch or script file. The ntbackup command is available in Windows XP. The ntbackup command was replaced with the wbadmin beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Ntsd | The ntsd command is used to perform certain command line debugging tasks. The ntsd command is available in Windows XP. The ntsd command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the addition of dump file support in Task Manager. |
| Ocsetup | The ocsetup command starts the Windows Optional Component Setup tool, used to install additional Windows features. The ocsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Beginning in Windows 8, Microsoft is depreciating the ocsetup command in favor of the dism command. |
| Openfiles | The openfiles command is used to display and disconnect open files and folders on a system. The openfiles command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Chemin | The path command is used to display or set a specific path available to executable files. The path command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pathping | The pathping command functions much like the tracert command but will also report information about network latency and loss at each hop. The pathping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pause | The pause command is used within a batch or script file to pause the processing of the file. When the pause command is used, a “Press any key to continue…” message displays in the command window. The pause command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pentnt | The pentnt command is used to detect floating point division errors in the Intel Pentium chip. The pentnt command is also used to enable floating point emulation and disable floating point hardware. The pentnt command is available in Windows XP. The pentnt command was removed beginning in Windows Vista due to the lack of Intel Pentium CPU use at the time of this operating system release. |
| Ping | The ping command sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request message to a specified remote computer to verify IP-level connectivity. The ping command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Pkgmgr | The pkgmgr command is used to start the Windows Package Manager from the Command Prompt. Package Manager installs, uninstalls, configures, and updates features and packages for Windows. The pkgmgr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnpunattend | The pnpunattend command is used to automate the installation of hardware device drivers. The pnpunattend command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Pnputil | The pnputil command is used to start the Microsoft PnP Utility, a tool used to install a Plug and Play device from the command line. The pnputil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Popd | The popd command is used to change the current directory to the one most recently stored by the pushd command. The popd command is most often utilized from within a batch or script file. The popd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pouvoir | The power command is used to reduce the power consumed by a computer by monitoring software and hardware devices. The power command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The power command was replaced by operating system integrated power management functions beginning in Windows XP. |
| Powercfg | The powercfg command is used to manage the Windows power management settings from the command line. The powercfg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Imprimer | The print command is used to print a specified text file to a specified printing device. The print command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Prompt | The prompt command is used to customize the appearance of the prompt text in Command Prompt or MS-DOS. The prompt command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Pushd | The pushd command is used to store a directory for use, most commonly from within a batch or script program. The pushd command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Pwlauncher | The pwlauncher command is used to enable, disable, or show the status of your Windows To Go startup options. The pwlauncher command is available in Windows 8. |
| Qappsrv | The qappsrv command is used to display all Remote Desktop Session Host servers available on the network. The qappsrv command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Qbasic | The qbasic command starts QBasic, the MS-DOS based programming environment for the BASIC programming language. The qbasic command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The qbasic command is not installed by default with Windows 98 or 95 but is available from the installation disc or disks. |
| Qprocess | The qprocess command is used to display information about running processes. The qprocess command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Query | The query command is used to display the status of a specified service. The query command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Quser | The quser command is used to display information about users currently logged on to the system. The quser command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Qwinsta | The qwinsta command is used to display information about open Remote Desktop Sessions. The qwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasautou | The rasautou command is used to manage Remote Access Dialer AutoDial addresses. The rasautou command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rasdial | The rasdial command is used to start or end a network connection for a Microsoft client. The rasdial command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rcp | The rcp command is used to copy files between a Windows computer and a system running the rshd daemon. The rcp command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rcp command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rcp command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rd | The rd command is the shorthand version of the rmdir command. The rd command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Rdpsign | The rdpsign command is used to sign a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) file. The rdpsign command is available in Windows 7. |
| Reagentc | The reagentc command is used to configure the Windows Recovery Environment (RE). The reagentc command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Recimg | The recimg command is used to create a custom refresh image. The recimg command is available in Windows 8. |
| Récupérer | The recover command is used to recover readable data from a bad or defective disk. The recover command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Reg | The reg command is used to manage the Windows Registry from the command line. The reg command can perform common registry functions like adding registry keys, exporting the registry, etc. The reg command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Regini | The regini command is used to set or change registry permissions and registry values from the command line. The regini command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Register-cimprovider | The register-cimprovider command is used to register a Common Information Model (CIM) Provider in Windows. The register-cimprovider command is available in Windows 8. |
| Regsvr32 | The regsvr32 command is used to register a DLL file as a command component in the Windows Registry. The regsvr32 command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Relog | The relog command is used to create new performance logs from data in existing performance logs. The relog command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rem | The rem command is used to record comments or remarks in a batch or script file. The rem command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Ren | The ren command is the shorthand version of the rename command. The ren command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Renommer | The rename command is used to change the name of the individual file that you specify. The rename command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Repair-bde | The repair-bde command is used to repair or decrypt a damaged drive that's been encrypted using BitLocker. The repair-bde command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Replace | The replace command is used to replace one or more files with one or more other files. The replace command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Réinitialiser | The reset command, executed as reset session, is used to reset the session subsystem software and hardware to known initial values. The reset command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Restaurer | The restore command is used to restore files that were backed up using the backup command. The restore command is only available in MS-DOS. The backup command was only available up to MS-DOS 5.00 but the restore command was included by default with later versions of MS-DOS to provide a way to restore files that were backed up in previous versions of MS-DOS. |
| Rexec | The rexec command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rexec daemon. The rexec command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here. The rexec command is not available in Windows 7 but can be executed in Windows XP via Windows XP Mode if need be. |
| Rmdir | The rmdir command is used to delete an existing or completely empty folder. The rmdir command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Robocopy | The robocopy command is used to copy files and directories from one location to another. This command is also called Robust File Copy. The robocopy command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The robocopy command is superior to both the copy command and the xcopy command because robocopy supports many more options. |
| Route | The route command is used to manipulate network routing tables. The route command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Rpcinfo | The rpcinfo command makes a remote procedure call (RPC) to an RPC server and reports what it finds. The rpcinfo command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The rpcinfo command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The rpcinfo command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rpcping | The rpcping command is used to ping a server using RPC. The rpcping command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Rsh | The rsh command is used to run commands on remote computers running the rsh daemon. The rsh command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The rsh command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel and then installing the Utilities and SDK for UNIX-based Applications available here for Windows Vista and here for Windows 7. The rsh command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Rsm | The rsm command is used to manage media resources using Removable Storage. The rsm command is available in Windows Vista and Windows XP. The rsm command was optional in Windows Vista and then removed in Windows 7 due to Removable Storage Manager being removed from the operating system. Search for the rsm command in the C:\Windows\winsxs folder in Windows Vista if you're having trouble executing the command. |
| Runas | The runas command is used to execute a program using another user's credentials. The runas command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Rwinsta | The rwinsta command is the shorthand version of the reset session command. The rwinsta command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Sc | The sc command is used to configure information about services. The sc command communicates with the Service Control Manager. The sc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Scandisk | The scandisk command is used to start Microsoft ScanDisk, a disk repair program. The scandisk command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The scandisk command was replaced by the chkdsk command beginning in Windows XP. |
| Scanreg | The scanreg command starts Windows Registry Checker, a basic registry repair program and backup utility. The scanreg command is available in Windows 98 and Windows 95. The functions provided by the scanreg command were no longer necessary beginning in Windows XP due to changes in how the Windows Registry functions. |
| Schtasks | The schtasks command is used to schedule specified programs or commands to run at certain times. The schtasks command can be used to create, delete, query, change, run, and end scheduled tasks. The schtasks command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.? |
| Sdbinst | The sdbinst command is used to deploy customized SDB database files. The sdbinst command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Secedit | The secedit command is used to configure and analyze system security by comparing the current security configuration to a template. The secedit command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ensemble | The set command is used to display, enable, or disable environment variables in MS-DOS or from the Command Prompt. The set command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Setlocal | The setlocal command is used to start the localization of environment changes inside a batch or script file. The setlocal command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Setspn | The setspn command is used to manage the Service Principal Names (SPN) for an Active Directory (AD) service account. The setspn command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Setver | The setver command is used to set the MS-DOS version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. The setver command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The setver command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. |
| Setx | The setx command is used to create or change environment variables in the user environment or the system environment. The setx command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sfc | The sfc command is used to verify and replace important Windows system files. The sfc command is also referred to as System File Checker or Windows Resource Checker, depending on the operating system. The sfc command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Ombre | The shadow command is used to monitor another Remote Desktop Services session. The shadow command is available in Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Partager | The share command is used to install file locking and file sharing functions in MS-DOS. The share command is available in MS-DOS as well as in all 32-bit versions of Windows. The share command is not available in 64-bit versions of Windows. Share is only available in Windows 8, 7, Vista, and XP to support older MS-DOS files. |
| Shift | The shift command is used to change the position of replaceable parameters in a batch or script file. The shift command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Showmount | The showmount command is used to display information about NFS mounted file systems. The showmount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The showmount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The showmount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Shutdown | The shutdown command can be used to shut down, restart, or log off the current system or a remote computer. The shutdown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Smartdrv | The smartdrv command installs and configures SMARTDrive, a disk caching utility for MS-DOS. The smartdrv command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. Caching is automatic beginning in Windows XP, making the smartdrv command unnecessary. |
| Sorte | The sort command is used to read data from a specified input, sort that data, and return the results of that sort to the Command Prompt screen, a file, or another output device. The sort command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Démarrer | The start command is used to open a new command line window to run a specified program or command. The start command can also be used to start an application without creating a new window. The start command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Subst | The subst command is used to associate a local path with a drive letter. The subst command is a lot like the net use command except a local path is used instead of a shared network path. The subst command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. The subst command replaced the assign command beginning with MS-DOS 6.0. |
| Sxstrace | The sxstrace command is used to start the WinSxs Tracing Utility, a programming diagnostic tool. The sxstrace command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Sys | The sys command is used to copy the MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk. The sys command is available in Windows 98 and 95, as well as in MS-DOS. The sys command is used most often to create a simple bootable disk or hard drive. The necessary system files for Windows are too large to fit on a disk, so the sys command was removed beginning in Windows XP. |
| Systeminfo | The systeminfo command is used to display basic Windows configuration information for the local or a remote computer. The systeminfo command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Takeown | The takedown command is used to regain access to a file that that an administrator was denied access to when reassigning ownership of the file. The takeown command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Taskkill | The taskkill command is used to terminate a running task. The taskkill command is the command line equivalent of ending a process in Task Manager in Windows. The taskkill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tasklist | Displays a list of applications, services, and the Process ID (PID) currently running on either a local or a remote computer. The tasklist command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tcmsetup | The tcmsetup command is used to set up or disable the Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) client. The tcmsetup command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Telnet | The telnet command is used to communicate with remote computers that use the Telnet protocol. The telnet command is available in all versions of Windows. The telnet command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tftp | The tftp command is used to transfer files to and from a remote computer that's running the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) service or daemon. The tftp command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tftp command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the TFTP Client Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Temps | The time command is used to show or change the current time. The time command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Temps libre | The timeout command is typically used in a batch or script file to provide a specified timeout value during a procedure. The timeout command can also be used to ignore keypresses. The timeout command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Titre | The title command is used to set the Command Prompt window title. The title command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tlntadmn | The tlntadmn command is used to administer a local or remote computer running Telnet Server. The tlntadmn command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. The tlntadmn command is not available by default in Windows 8, 7, or Vista, but can be enabled by turning on the Telnet Server Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. |
| Tpmvscmgr | The tpmvscmgr command is used to create and destroy TPM virtual smart cards. The tpmvscmgr command is available in Windows 8. |
| Tracerpt | The tracerpt command is used to process event trace logs or real-time data from instrumented event trace providers. The tracerpt command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tracert | The tracert command sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to a specified remote computer with increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values and displays the IP address and hostname, if available, of the router interfaces between the source and destination. The tracert command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Arbre | The tree command is used to graphically display the folder structure of a specified drive or path. The tree command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Tscon | The tscon command is used to attach a user session to a Remote Desktop session. The tscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsdiscon | The tsdiscon command is used to disconnect a Remote Desktop session. The tsdiscon command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tskill | The tskill command is used to end the specified process. The tskill command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tsshutdn | The tsshutdn command is used to remotely shut down or restart a terminal server. The tsshutdn command is available in Windows XP. The ability to shut down a computer remotely is also available in the more powerful shutdown command, so tsshutdn was removed beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Taper | The type command is used to display the information contained in a text file. The type command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Typeperf | The typerperf command displays performance data in the Command Prompt window or writes the data to specified log file. The typeperf command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Tzutil | The tzutil command is used to display or configure the current system's time zone. The tzutil command can also be used to enable or disable Daylight Saving Time adjustments. The tzutil command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Umount | The umount command is used to remove Network File System (NFS) mounted network shares. The umount command is available in Windows 7 and Windows Vista. The umount command is not available by default in Windows Vista or Windows 7 but can be enabled by turning on the Services for NFS Windows feature from Programs and Features in Control Panel. The umount command is not available in Windows 8 because Service for UNIX (SFU) was discontinued. |
| Undelete | The undelete command is used to undo a deletion performed with the MS-DOS delete command. The undelete command is only available in MS-DOS. The undelete command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to the availability of the Recycle Bin in Windows. Additionally, free file recovery programs are available from third-party software makers. |
| Unformat | The unformat command is used to undo the formatting on a drive performed by the MS-DOS format command. The unformat command is only available in MS-DOS. The unformat command was removed beginning in Windows 95 due to file system changes. |
| Unlock | The unlock command is used to unlock a drive, disabling direct disk access for a program. The unlock command is only available in Windows 98 and 95. Drive locking is no longer available as of Windows XP. |
| Unlodctr | The unlodctr command removes Explain text and Performance counter names for a service or device driver from the Windows Registry. The unlodctr command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Vaultcmd | The vaultcmd command is used to create, remove, and show stored credentials. The vaultcmd command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
| Ver | The ver command is used to display the current Windows or MS-DOS version number. The ver command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vérifier | The verify command is used to enable or disable the ability of Command Prompt, or MS-DOS, to verify that files are written correctly to a disk. The verify command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vol | The vol command shows the volume label and serial number of a specified disk, assuming this information exists. The vol command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. |
| Vsafe | The vsafe command is used to start VSafe, a basic virus protection system for MS-DOS. The vsafe command is only available in MS-DOS. VSafe was designed for MS-DOS and Windows 3.x only. Microsoft provides an optional virus protection suite called Microsoft Security Essentials for Windows XP and later operating systems, and third-party antivirus tools are available for all versions of Windows. |
| Vssadmin | The vssadmin command starts the Volume Shadow Copy Service administrative command line tool which displays current volume shadow copy backups and all installed shadow copy writers and providers. The vssadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| W32tm | The w32tm command is used to diagnose issues with Windows Time. The w32tm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Waitfor | The waitfor command is used to send or wait for a signal on a system. The waitfor command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wbadmin | The wbadmin command is used to start and stop backup jobs, display details about a previous backup, list the items within a backup, and report on the status of a currently running backup. The wbadmin command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. The wbadmin command replaced the ntbackup command beginning in Windows Vista. |
| Wecutil | The wecutil command is used to manage subscriptions to events that are forwarded from WS-Management supported computers. The wecutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wevtutil | The wevtutil command starts the Windows Events Command Line Utility which is used to manage event logs and publishers. The wevtutil command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Where | The where command is used to search for files that match a specified pattern. The where command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Whoami | The whoami command is used to retrieve user name and group information on a network. The whoami command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winmgmt | The winmgmt command starts the command line version of WMI, a scripting tool in Windows. The winmgmt command is available in all versions of Windows. |
| Winrm | The winrm command is used to start the command line version of Windows Remote Management, used to manage secure communications with local and remote computers using web services. The winrm command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winrs | The winrs command is used to open a secure command window with a remote host. The winrs command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Winsat | The winsat command starts the Windows System Assessment Tool, a program that assesses various features, attributes, and capabilities of a computer running Windows. The winsat command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Wmic | The wmic command starts the Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC), a scripting interface that simplifies the use of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and systems managed via WMI. The wmic command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP. |
| Wsmanhttpconfig | The wsmanhttpconfig command is used to manage aspects of the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service. The wsmanhttpconfig command is available in Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. |
| Xcopy | The xcopy command can copy one or more files or directory trees from one location to another. The xcopy command is generally considered a more “powerful” version of the copy command through the robocopy command trumps even xcopy. The xcopy command is available in all versions of Windows, as well as in MS-DOS. A command by the name of xcopy32 existed in Windows 95 and Windows 98. To avoid a long and confusing explanation here, just know that no matter if you executed the xcopy command or the xcopy32 command, you were always executing the most updated version of the command. |
| Xwizard | The xwizard command, short for Extensible Wizard, is used to register data in Windows, often from a preconfigured XML file. The xwizard command is available in Windows 8 and Windows 7. |
The above list is a set of most essential commands of command prompt. To view or download a PDF version of complete set of windows commands, please click on the below button.

Télécharger au format PDF
Pour plus de conseils, d'astuces et de mises à jour liées à la technologie, abonnez-vous à Tweak Library et si vous préférez les vidéos liées à la technologie, regardez et abonnez-vous à notre chaîne YouTube . Vous pouvez également nous joindre sur Facebook et Pinterest .
